Maintaining a DB instance
Periodically, Amazon RDS performs maintenance on Amazon RDS resources. The following topics describe these maintenance actions and how to apply them.
Contents
Overview of DB instance maintenance updates
Maintenance most often involves updates to the following resources in your DB instance:
-
Underlying hardware
-
Underlying operating system (OS)
-
Database engine version
Updates to the operating system most often occur for security issues. We recommend that you do them as soon as possible. For more information about operating system updates, see Applying updates to a DB instance.
Topics
Offline resources during maintenance updates
Some maintenance items require that Amazon RDS take your DB instance offline for a short time. Maintenance items that require a resource to be offline include required operating system or database patching. Required patching is automatically scheduled only for patches that are related to security and instance reliability. Such patching occurs infrequently, typically once every few months. It seldom requires more than a fraction of your maintenance window.
Deferred DB instance modifications
Deferred DB instance modifications that you have chosen not to apply immediately are applied during the maintenance window. For example, you might choose to change the DB instance class or parameter group during the maintenance window. Such modifications that you specify using the pending reboot setting don't show up in the Pending maintenance list. For information about modifying a DB instance, see Modifying an Amazon RDS DB instance.
To see the modifications that are pending for the next
maintenance window, use the describe-db-instancesPendingModifiedValues field.
Eventual consistency for the DescribePendingMaintenanceActions API
The Amazon RDS DescribePendingMaintenanceActions API follows an eventual
consistency model. This means that the result of the
DescribePendingMaintenanceActions command might not be immediately
visible to all subsequent RDS commands. Keep this in mind when you use
DescribePendingMaintenanceActions immediately after using a previous
API command.
Eventual consistency can affect the way you managed your maintenance updates. For
example, if you run the ApplyPendingMaintenanceActions command to update
the database engine version for a DB instance, it will eventually be visible to
DescribePendingMaintenanceActions. In this scenario,
DescribePendingMaintenanceActions might show that the maintenance
action wasn't applied even though it was.
To manage eventual consistency, you can do the following:
-
Confirm the state of your DB instance before you run a command to modify it. Run the appropriate
DescribePendingMaintenanceActionscommand using an exponential backoff algorithm to ensure that you allow enough time for the previous command to propagate through the system. To do this, run theDescribePendingMaintenanceActionscommand repeatedly, starting with a couple of seconds of wait time, and increasing gradually up to five minutes of wait time. -
Add wait time between subsequent commands, even if a
DescribePendingMaintenanceActionscommand returns an accurate response. Apply an exponential backoff algorithm starting with a couple of seconds of wait time, and increase gradually up to about five minutes of wait time.
Viewing pending maintenance updates
View whether a maintenance update is available for your DB instance by using the RDS console, the AWS CLI, or the RDS API. If an update is available, it is indicated in the Maintenance column for the DB instance on the Amazon RDS console, as shown in this figure.
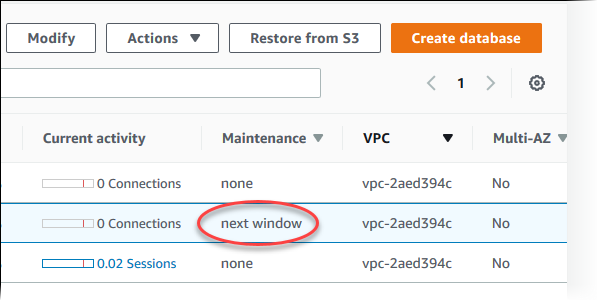
If no maintenance update is available for a DB instance, the column value is none for it.
If a maintenance update is available for a DB instance, the following column values are possible:
-
required – The maintenance action will be applied to the resource and can't be deferred indefinitely.
-
available – The maintenance action is available, but it will not be applied to the resource automatically. You can apply it manually.
-
next window – The maintenance action will be applied to the resource during the next maintenance window.
-
In progress – The maintenance action is being applied to the resource.
If an update is available, you can do one of the following:
-
If the maintenance value is next window, defer the maintenance actions by choosing Defer upgrade from Actions. You can't defer a maintenance action that has already started.
-
Apply the maintenance actions immediately.
-
Apply the maintenance actions during your next maintenance window.
-
Take no action.
To take an action by using the AWS Management Console
-
Choose the DB instance to show its details.
-
Choose Maintenance & backups. The pending maintenance actions appear.
-
Choose the action to take, then choose when to apply it.

The maintenance window determines when pending operations start, but doesn't limit the total run time of these operations. Maintenance operations aren't guaranteed to finish before the maintenance window ends, and can continue beyond the specified end time. For more information, see Amazon RDS maintenance window.
You can also view whether a maintenance update is available for your DB instance by running the describe-pending-maintenance-actions AWS CLI command.
For information about applying maintenance updates, see Applying updates to a DB instance.
Maintenance actions for Amazon RDS
The following maintenance actions apply to RDS DB instances:
-
ca-certificate-rotation– Update the Amazon RDS Certificate Authority certificate for the DB instance. -
db-upgrade– Upgrade the DB engine version for the DB instance. -
hardware-maintenance– Perform maintenance on the underlying hardware for the DB instance. -
system-update– Update the operating system for the DB instance.
Maintenance for Multi-AZ deployments
Running a DB instance as a Multi-AZ deployment can further reduce the impact of a maintenance event. This result is because Amazon RDS applies operating system updates by following these steps:
-
Perform maintenance on the standby.
-
Promote the standby to primary.
-
Perform maintenance on the old primary, which becomes the new standby.
If you upgrade the database engine for your DB instance in a Multi-AZ deployment, Amazon RDS modifies both primary and secondary DB instances at the same time. In this case, both the primary and secondary DB instances in the Multi-AZ deployment are unavailable during the upgrade. This operation causes downtime until the upgrade is complete. The duration of the downtime varies based on the size of your DB instance.
If there are underlying operating system patches that need to be applied, a short Multi-AZ failover is required to apply the patches to the primary DB instance. This failover typically lasts less than a minute.
If your DB instance runs RDS for MySQL, RDS for PostgreSQL, or RDS for MariaDB, you can minimize the downtime required for an upgrade by using a blue/green deployment. For more information, see Using Amazon RDS Blue/Green Deployments for database updates. If you upgrade an RDS for SQL Server or RDS Custom for SQL Server DB instance in a Multi-AZ deployment, then Amazon RDS performs rolling upgrades, so you have an outage only for the duration of a failover. For more information, see Multi-AZ and in-memory optimization considerations.
If your DB instance runs RDS for SQL Server in a Multi-AZ deployment, you can apply an update to the underlying operating system by using one of the following methods:
-
Modify the DB instance class to a different size and then modify it back to the original size.
-
Scale up the DB instance size and the scale back down to the original size.
-
Modify the DB instance from Multi-AZ to Single-AZ, stop and start the DB instance, and then change the instance back to Multi-AZ.
For more information about Multi-AZ deployments, see Configuring and managing a Multi-AZ deployment for Amazon RDS.