Amazon RDS creates a storage volume snapshot of your DB instance, backing up the entire DB instance and not just individual databases. Creating this DB snapshot on a Single-AZ DB instance results in a brief I/O suspension that can last from a few seconds to a few minutes, depending on the size and class of your DB instance. For MariaDB, MySQL, Oracle, and PostgreSQL, I/O activity is not suspended on your primary during backup for Multi-AZ deployments, because the backup is taken from the standby. For SQL Server, I/O activity is suspended briefly during backup for Multi-AZ deployments.
When you create a DB snapshot, you need to identify which DB instance you are going to back up, and then give your DB snapshot a name so you can restore from it later. The amount of time it takes to create a snapshot varies with the size of your databases. Since the snapshot includes the entire storage volume, the size of files, such as temporary files, also affects the amount of time it takes to create the snapshot.
Note
Your DB instance must be in the available state to take a DB snapshot.
For PostgreSQL DB instances, data in unlogged tables might not be restored from snapshots. For more information, see Best practices for working with PostgreSQL.
Unlike automated backups, manual snapshots aren't subject to the backup retention period. Snapshots don't expire.
For very long-term backups of MariaDB, MySQL, and PostgreSQL data, we recommend exporting snapshot data to Amazon S3. If the major version of your DB engine is no longer supported, you can't restore to that version from a snapshot. For more information, see Exporting DB snapshot data to Amazon S3 for Amazon RDS.
You can create a DB snapshot using the AWS Management Console, the AWS CLI, or the RDS API.
To create a DB snapshot
-
Sign in to the AWS Management Console and open the Amazon RDS console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/rds/
. -
In the navigation pane, choose Snapshots.
The Manual snapshots list appears.
-
Choose Take snapshot.
The Take DB snapshot window appears.
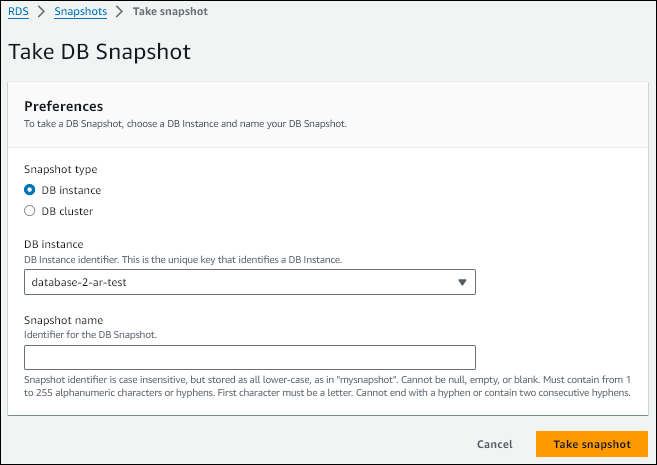
-
Choose the DB instance for which you want to take a snapshot.
-
Enter the Snapshot name.
-
Choose Take snapshot.
The Manual snapshots list appears, with the new DB snapshot's status shown as Creating.
After its status is Available, you can see its creation time.
When you create a DB snapshot using the AWS CLI, you need to identify which DB instance you
are going to back up, and then give your DB snapshot a name so you can restore from it
later. You can do this by using the AWS CLI create-db-snapshot command with the following
parameters:
-
--db-instance-identifier -
--db-snapshot-identifier
In this example, you create a DB snapshot called mydbsnapshot for
a DB instance called mydbinstance.
For Linux, macOS, or Unix:
aws rds create-db-snapshot \ --db-instance-identifiermydbinstance\ --db-snapshot-identifiermydbsnapshot
For Windows:
aws rds create-db-snapshot ^ --db-instance-identifiermydbinstance^ --db-snapshot-identifiermydbsnapshot
When you create a DB snapshot using the Amazon RDS API, you need to identify which DB instance
you are going to back up, and then give your DB snapshot a name so you can restore from
it later. You can do this by using the Amazon RDS API CreateDBSnapshot command with the following
parameters:
-
DBInstanceIdentifier -
DBSnapshotIdentifier