Pass session tags in AWS STS
Session tags are key-value pair attributes that you pass when you assume an IAM role or
federate a user in AWS STS. You do this by making an AWS CLI or AWS API request through AWS STS or
through your identity provider (IdP). When you use AWS STS to request temporary security
credentials, you generate a session. Sessions expire and have credentials, such as an access key pair and a
session token. When you use the session credentials to make a subsequent request, the request context includes the aws:PrincipalTag context key. You can
use the aws:PrincipalTag key in the Condition element of your policies
to allow or deny access based on those tags.
When you use temporary credentials to make a request, your principal might include a set of tags. These tags come from the following sources:
-
Session tags – The tags passed when you assume the role or federate the user using the AWS CLI or AWS API. For more information about these operations, see Session tagging operations.
-
Incoming transitive session tags – The tags inherited from a previous session in a role chain. For more information, see Chaining roles with session tags later in this topic.
-
IAM tags – The tags attached to your IAM assumed role.
Topics
Session tagging operations
You can pass session tags using the following AWS CLI or AWS API operations in AWS STS. The AWS Management Console Switch Role feature does not allow you to pass session tags.
You can also set the session tags as transitive. Transitive tags persist during role chaining. For more information, see Chaining roles with session tags.
The following table compares methods for passing session tags.
| Operation | Who can assume the role | Method to pass tags | Method to set transitive tags |
|---|---|---|---|
assume-role
CLI or AssumeRole
API operation |
IAM user or a session | Tags API parameter or --tags CLI option |
TransitiveTagKeys API parameter or
--transitive-tag-keys CLI option |
assume-role-with-saml CLI or AssumeRoleWithSAML API operation |
Any user authenticated using a SAML identity provider | PrincipalTag SAML attribute |
TransitiveTagKeys SAML Attribute |
assume-role-with-web-identity CLI or AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity API operation |
Any user authenticated using an OIDC provider | PrincipalTag OIDC token |
TransitiveTagKeys OIDC token |
get-federation-token CLI or GetFederationToken API operation |
IAM user or root user | Tags API parameter or --tags CLI option |
Not supported |
Operations that support session tagging can fail under the following conditions:
-
You pass more than 50 session tags.
-
The plaintext of your session tag keys exceeds 128 characters.
-
The plaintext of your session tag values exceeds 256 characters.
-
The total size of the plaintext of session policies exceeds 2048 characters.
-
The total packed size of the combined session policies and tags is too large. If the operation fails, the error message shows how close the policies and tags combined come to the upper size limit, by percentage.
Things to know about session tags
Before you use session tags, review the following details about sessions and tags.
-
When using session tags, trust policies for all roles connected to the identity provider (IdP) passing tags must have the sts:TagSession permission. For roles without this permission in the trust policy, the
AssumeRoleoperation fails. -
When you request a session, you can specify principal tags as the session tags. The tags apply to requests that you make using the session's credentials.
-
Session tags use key-value pairs. For example, to add contact information to a session, you can add the session tag key
emailand the tag valuejohndoe@example.com. -
Session tags must follow the rules for naming tags in IAM and AWS STS. This topic includes information about case sensitivity and restricted prefixes that apply to your session tags.
-
New session tags override existing assumed role or federated user session tags with the same tag key, regardless of character case.
-
You cannot pass session tags using the AWS Management Console.
-
Session tags are valid only for the current session.
-
Session tags support role chaining. By default, AWS STS does not pass tags to subsequent role sessions. However, you can set session tags as transitive. Transitive tags persist during role chaining and replace matching
ResourceTagvalues after the evaluation of the role trust policy. For more information, see Chaining roles with session tags. -
You can use session tags to control access to resources or to control what tags can be passed into a subsequent session. For more information, see IAM tutorial: Use SAML session tags for ABAC.
-
You can view the principal tags for your session, including the session tags, in the AWS CloudTrail logs. For more information, see Viewing session tags in CloudTrail.
-
You must pass a single value for each session tag. AWS STS does not support multi-valued session tags.
-
You can pass a maximum of 50 session tags. The number and size of IAM resources in an AWS account are limited. For more information, see IAM and AWS STS quotas.
-
An AWS conversion compresses the passed session policies and session tags combined into a packed binary format with a separate limit. If you exceed this limit, the AWS CLI or AWS API error message shows how close the policies and tags combined come to the upper size limit, by percentage.
Permissions required to add session tags
In addition to the action that matches the API operation, you must have the following permissions-only action in your policy:
sts:TagSession
Important
When using session tags, the role trust policies for all roles connected to an identity
provider (IdP) must have the sts:TagSession permission. The
AssumeRole operation fails for any role connected to an IdP passing session
tags without this permission. If you don't want to update the role trust policy for each
role, you can use a separate IdP instance for passing session tags. Then, add the
sts:TagSession permission to only the roles connected to the separate
IdP.
You can use the sts:TagSession action with the following condition
keys.
-
aws:PrincipalTag– Compares the tag attached to the principal making the request with the tag you specified in the policy. For example, you can allow a principal to pass session tags only if the principal making the request has the specified tags. -
aws:RequestTag– Compares the tag key-value pair passed in the request with the tag pair you specified in the policy. For example, you can allow the principal to pass the specified session tags, but only with the specified values. -
aws:ResourceTag– Compares the tag key-value pair you specified in the policy with the key-value pair attached to the resource. For example, you can allow the principal to pass session tags only if the role they assume includes the specified tags. -
aws:TagKeys– Compares the tag keys in a request with the keys you specified in the policy. For example, you can allow the principal to pass only session tags with the specified tag keys. This condition key limits the maximum set of session tags that can be passed. -
sts:TransitiveTagKeys- Compares the transitive session tag keys in the request with those specified in the policy. For example, you can write a policy to allow a principal to set only specific tags as transitive. Transitive tags persist during role chaining. For more information, see Chaining roles with session tags.
For example, the following role trust policy
allows the test-session-tags user to assume the role with the attached policy.
When that user assumes the role, they must use the AWS CLI or AWS API to pass the three
required session tags and the required external ID. Additionally, the user can choose to set the Project and
Department tags as transitive.
Example role trust policy for session tags
What does this policy do?
-
The
AllowIamUserAssumeRolestatement allows thetest-session-tagsuser to assume the role with the attached policy. When that user assumes the role, they must pass the required session tags and external ID.-
The first condition block of this statement requires the user to pass the
Project,CostCenter, andDepartmentsession tags. The tag values do not matter in this statement, so you can use wildcards (*) for the tag values. This block ensures that user passes at least these three session tags. Otherwise, the operation fails. The user can pass additional tags. -
The second condition block requires the user to pass an external ID with the value
Example987.
-
-
The
AllowPassSessionTagsAndTransitivestatement allows thests:TagSessionpermissions-only action. This action must be allowed before the user can pass session tags. If your policy includes the first statement without the second statement, the user can't assume the role.-
The first condition block of this statement allows the user to pass any value for the
CostCenterandProjectsession tags. You do this by using wildcards (*) for the tag value in the policy, which requires that you use the StringLike condition operator. -
The second condition block allows the user to pass only the
EngineeringorMarketingvalue for theDepartmentsession tag. -
The third condition block lists the maximum set of tags you can set as transitive. The user can choose to set a subset or no tags as transitive. They cannot set additional tags as transitive. You can require that they set at least one of the tags as transitive by adding another condition block that includes
"Null":{"sts:TransitiveTagKeys":"false"}.
-
Passing session tags using AssumeRole
The AssumeRole operation returns a set of temporary credentials you can use
to access AWS resources. You can use IAM user or role credentials to call
AssumeRole. To pass session tags while assuming a role, use the
--tags AWS CLI option or the Tags AWS API parameter.
To set tags as transitive, use the --transitive-tag-keys AWS CLI option or the
TransitiveTagKeys AWS API parameter. Transitive tags persist during role
chaining. For more information, see Chaining roles with session tags.
The following example shows a sample request that uses AssumeRole. In this
example, when you assume the my-role-example role, you create a session named
my-session. You add the session tag key-value pairs Project =
Automation, CostCenter = 12345, and
Department = Engineering. You also set the Project
and Department tags as transitive by specifying their keys. You must pass a
single value for each session tag. AWS STS does not support multi-valued session tags.
Example AssumeRole CLI request
aws sts assume-role \ --role-arn arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/my-role-example \ --role-session-name my-session \ --tags Key=Project,Value=Automation Key=CostCenter,Value=12345 Key=Department,Value=Engineering \ --transitive-tag-keys Project Department \ --external-id Example987
Passing session tags using AssumeRoleWithSAML
The AssumeRoleWithSAML operation authenticates with SAML-based federation.
This operation returns a set of temporary credentials you can use to access AWS resources.
For more information about using SAML-based federation for AWS Management Console access, see Enabling SAML 2.0 federated principals
to access the AWS Management Console. For details about AWS CLI or AWS
API access, see SAML 2.0 federation. For a tutorial on configuring SAML federation for
your Active Directory users, see AWS Federated Authentication with Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS)
As an administrator, you can allow members of your company directory to federate into
AWS using the AWS STS AssumeRoleWithSAML operation. To do this, you must complete
the following tasks:
AWS includes identity providers with certified end-to-end experience for session tags with their identity solutions. To learn how to use these identity providers to configure session tags, see Integrate third-party SAML solution providers with AWS.
To pass SAML attributes as session tags, include the Attribute element with
the Name attribute set to
https://aws.amazon.com/SAML/Attributes/PrincipalTag:.
Use the {TagKey}AttributeValue element to specify the value of the tag. Include a
separate Attribute element for each session tag.
For example, assume that you want to pass the following identity attributes as session tags:
-
Project:Automation -
CostCenter:12345 -
Department:Engineering
To pass these attributes, include the following elements in your SAML assertion.
Example snippet of a SAML assertion
<Attribute Name="https://aws.amazon.com/SAML/Attributes/PrincipalTag:Project"> <AttributeValue>Automation</AttributeValue> </Attribute> <Attribute Name="https://aws.amazon.com/SAML/Attributes/PrincipalTag:CostCenter"> <AttributeValue>12345</AttributeValue> </Attribute> <Attribute Name="https://aws.amazon.com/SAML/Attributes/PrincipalTag:Department"> <AttributeValue>Engineering</AttributeValue> </Attribute>
To set the preceding tags as transitive, include another Attribute element
with the Name attribute set to
https://aws.amazon.com/SAML/Attributes/TransitiveTagKeys. Transitive tags persist
during role chaining. For more information, see Chaining roles with session tags.
To set the Project and Department tags as transitive, use the
following multi-valued attribute:
Example snippet of a SAML assertion
<Attribute Name="https://aws.amazon.com/SAML/Attributes/TransitiveTagKeys"> <AttributeValue>Project</AttributeValue> <AttributeValue>Department</AttributeValue> </Attribute>
Passing session tags using AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity
Use OpenID Connect (OIDC)-compliant federation to authenticate the
AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity operation. This operation returns a set of temporary
credentials you can use to access AWS resources. For more information about using web
identity federation for AWS Management Console access, see OIDC federation.
To pass session tags from OpenID Connect (OIDC), you must include the session tags in the
JSON Web Token (JWT) when you submit the AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity request. To
learn more about OIDC tokens and claims, see Using
Tokens with User Pools in the Amazon Cognito Developer
Guide.
AWS supports two claim formats for including session tags in the JWT:
-
Nested claim format
-
Flattened claim format
Nested claim format
The nested claim format uses a structure within the
https://aws.amazon.com/tags namespace in the JWT. In this format:
-
Principal tags are represented as a nested object under the
principal_tagskey. -
Each principal tag is a single string value.
-
Transitive tag keys are represented in an array under the
transitive_tag_keyskey. -
Both
principal_tagsandtransitive_tag_keysare nested under thehttps://aws.amazon.com/tagsnamespace.
The following example demonstrates a decoded JWT using the nested object format:
Example decoded JSON Web Token using the nested claim format
{ "sub": "johndoe", "aud": "ac_oic_client", "jti": "ZYUCeRMQVtqHypVPWAN3VB", "iss": "https://xyz.com", "iat": 1566583294, "exp": 1566583354, "auth_time": 1566583292, "https://aws.amazon.com/tags": { "principal_tags": { "Project": ["Automation"], "CostCenter": ["987654"], "Department": ["Engineering"] }, "transitive_tag_keys": [ "Project", "CostCenter" ] } }
Flattened claim format
The flattened claim format is compatible with identity providers that don't support nested objects in JWT claims, such as Microsoft Entra ID. In this format:
-
Principal tags are represented as separate claims with the prefix
https://aws.amazon.com/tags/principal_tags/. -
Each principal tag is a single string value.
-
Transitive tag keys are represented in a single claim as an array of strings with the prefix
https://aws.amazon.com/tags/transitive_tag_keys.
Now, let's look at how the same information is represented using the flattened claim format:
Example decoded JSON Web Token using the flattened claim format
{ "sub": "johndoe", "aud": "ac_oic_client", "jti": "ZYUCeRMQVtqHypVPWAN3VB", "iss": "https://xyz.com", "iat": 1566583294, "exp": 1566583354, "auth_time": 1566583292, "https://aws.amazon.com/tags/principal_tags/Project": "Automation", "https://aws.amazon.com/tags/principal_tags/CostCenter": "987654", "https://aws.amazon.com/tags/principal_tags/Department": "Engineering", "https://aws.amazon.com/tags/transitive_tag_keys": [ "Project", "CostCenter" ] }
Both decoded JWT examples show a call to AssumeRoleWithWebIdentity with the
Project, CostCenter, and Department session tags.
Both tokens set the Project and CostCenter tags as transitive.
Transitive tags persist during role chaining. For more information, see Chaining roles with session tags.
The flattened claim format achieves the same result as the nested claim format but uses a flattened structure for tags. It allows you to include session tags in environments where nested JSON objects are not supported in JWT claims. When using either format, ensure that your identity provider is configured to issue tokens with the appropriate claim structures. AWS supports both claim formats, so you can choose the one that best fits your identity provider's specific requirements.
Passing session tags using GetFederationToken
The GetFederationToken allows you to federate your user. This operation
returns a set of temporary credentials you can use to access AWS resources. To add tags to
your federated user session, use the --tags AWS CLI option or the Tags
AWS API parameter. You can't set session tags as transitive when you use
GetFederationToken, because you can't use the temporary credentials to assume a
role. You cannot use role chaining in this case.
The following example shows a sample request using GetFederationToken. In
this example, when you request the token, you create a session named my-fed-user.
You add the session tag key-value pairs Project = Automation and
Department = Engineering.
Example GetFederationToken CLI request
aws sts get-federation-token \ --name my-fed-user \ --tags key=Project,value=Automation key=Department,value=Engineering
When you use the temporary credentials returned by the GetFederationToken
operation, the session principal tags include the user tags and the passed session
tags.
Chaining roles with session tags
You can assume one role and then use the temporary credentials to assume another role. You can continue from session to session. This is called role chaining. When you pass session tags while assuming a role, you can set the keys as transitive. This ensures that those session tags pass to subsequent sessions in a role chain. You cannot set role tags as transitive. To pass these tags to subsequent sessions, specify them as session tags.
Note
Transitive tags persist during role chaining and replace matching
ResourceTag values after the evaluation of the role trust policy.
The following example shows how AWS STS passes session tags, transitive tags, and role tags into subsequent sessions in a role chain.
In this example role chaining scenario, you use an IAM user access key in the AWS CLI to
assume a role named Role1. You then use the resulting session credentials to
assume a second role named Role2. You can then use the second session credentials
to assume a third role named Role3. These requests occur as three separate
operations. Each role is already tagged in IAM. And during each request, you pass additional
session tags.

When you chain roles, you can ensure that tags from an earlier session persist to the
later sessions. To do this using the assume-role CLI command, you must pass the
tag as a session tag and set the tag as transitive. You pass the tag Star =
1 as a session tag. The command also attaches the tag Heart =
1 to the role and applies as a principal tag when you use the session. However,
you also want the Heart = 1 tag to automatically pass to the second
or third session. To do that, you manually include it as a session tag. The resulting session
principal tags include both of these tags, and sets them as transitive.

You perform this request using the following AWS CLI command:
Example AssumeRole CLI request
aws sts assume-role \ --role-arn arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/Role1 \ --role-session-name Session1 \ --tags Key=Star,Value=1 Key=Heart,Value=1 \ --transitive-tag-keys Star Heart
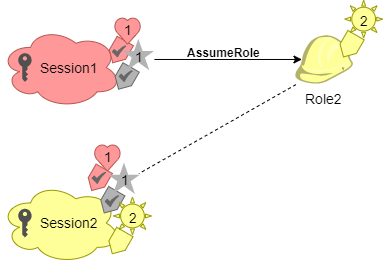
You then use the credentials for that session to assume Role2. The command
attaches the tag Sun = 2 to the second role and applies as a
principal tag when you use the second session. The Heart and Star
tags inherits the transitive session tags in the first session. The second session resulting
principal tags are Heart = 1, Star = 1,
and Sun = 2. Heart and Star continue to be
transitive. The Sun tag attached to Role2 is not marked as
transitive because it is not a session tag. Future sessions do not inherit this tag.
You perform this second request using the following AWS CLI command:
Example AssumeRole CLI request
aws sts assume-role \ --role-arn arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/Role2 \ --role-session-name Session2
You then use the second session credentials to assume Role3. The principal
tags for the third session come from any new session tags, the inherited transitive session
tags, and the role tags. The Heart = 1 and Star =
1 tags on the second session are inherited from the transitive session tag in
the first session. If you try to pass the Sun = 2 session tag, the
operation fails. The inherited Star = 1 session tag overrides the role
Star = 3 tag. In role chaining, the value of a transitive tag
overrides the role matching the ResourceTag value after the evaluation of the
role trust policy. In this example, if Role3 uses Star as a
ResourceTag in the role trust policy, and sets ResourceTag value
to the transitive tag value from the calling role session. The role Lightning tag
also applies to the third session, and not set as transitive.

You perform the third request using the following AWS CLI command:
Example AssumeRole CLI request
aws sts assume-role \ --role-arn arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/Role3 \ --role-session-name Session3
Using session tags for ABAC
Attribute-based access control (ABAC) uses an authorization strategy that defines permissions based on tag attributes.
If your company uses an OIDC or SAML-based identity provider (IdP) to manage user identities, you can configure your assertion to pass session tags to AWS. For example, with corporate user identities, when your employees federate into AWS, AWS applies their attributes to their resulting principal. You can then use ABAC to allow or deny permissions based on those attributes. For details, see IAM tutorial: Use SAML session tags for ABAC.
For more information about using IAM Identity Center with ABAC, see Attributes for access control in the AWS IAM Identity Center User Guide.
Viewing session tags in CloudTrail
You can use AWS CloudTrail to view the requests used to assume roles or federate users. The CloudTrail log file includes information about the principal tags for the assumed-role or federated user session. For more information, see Logging IAM and AWS STS API calls with AWS CloudTrail.
For example, assume that you make an AWS STS AssumeRoleWithSAML request, pass
session tags, and set those tags as transitive. You can find the following information in your
CloudTrail log.
Example AssumeRoleWithSAML CloudTrail log
"requestParameters": { "sAMLAssertionID": "_c0046cEXAMPLEb9d4b8eEXAMPLE2619aEXAMPLE", "roleSessionName": "MyRoleSessionName", "principalTags": { "CostCenter": "987654", "Project": "Unicorn" }, "transitiveTagKeys": [ "CostCenter", "Project" ], "durationSeconds": 3600, "roleArn": "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:role/SAMLTestRoleShibboleth", "principalArn": "arn:aws:iam::123456789012:saml-provider/Shibboleth" },
You can view the following example CloudTrail logs to view events that use session tags.