Die vorliegende Übersetzung wurde maschinell erstellt. Im Falle eines Konflikts oder eines Widerspruchs zwischen dieser übersetzten Fassung und der englischen Fassung (einschließlich infolge von Verzögerungen bei der Übersetzung) ist die englische Fassung maßgeblich.
Test-Setup mit Amazon EC2
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (AmazonEC2) bietet skalierbare Rechenkapazität in der Amazon Web Services Services-Cloud. Sie können Amazon verwendenEC2, um so viele oder so wenige virtuelle Server zu starten, wie Sie benötigen, Sicherheit und Netzwerke zu konfigurieren und Speicher zu verwalten. In diesem Setup verwenden wir Fleet Manager, eine Funktion von AWS Systems Manager, um mithilfe des Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) eine Verbindung zu einer Amazon EC2 Windows-Instance herzustellen.
Dieses Handbuch zeigt eine Testumgebung, um eine AWS Management Console Private Access-Verbindung zu Amazon Simple Storage Service von einer EC2 Amazon-Instance aus einzurichten und zu nutzen. In diesem Tutorial wird AWS CloudFormation das Netzwerk-Setup erstellt und konfiguriert, das von Amazon EC2 zur Visualisierung dieser Funktion verwendet werden soll.
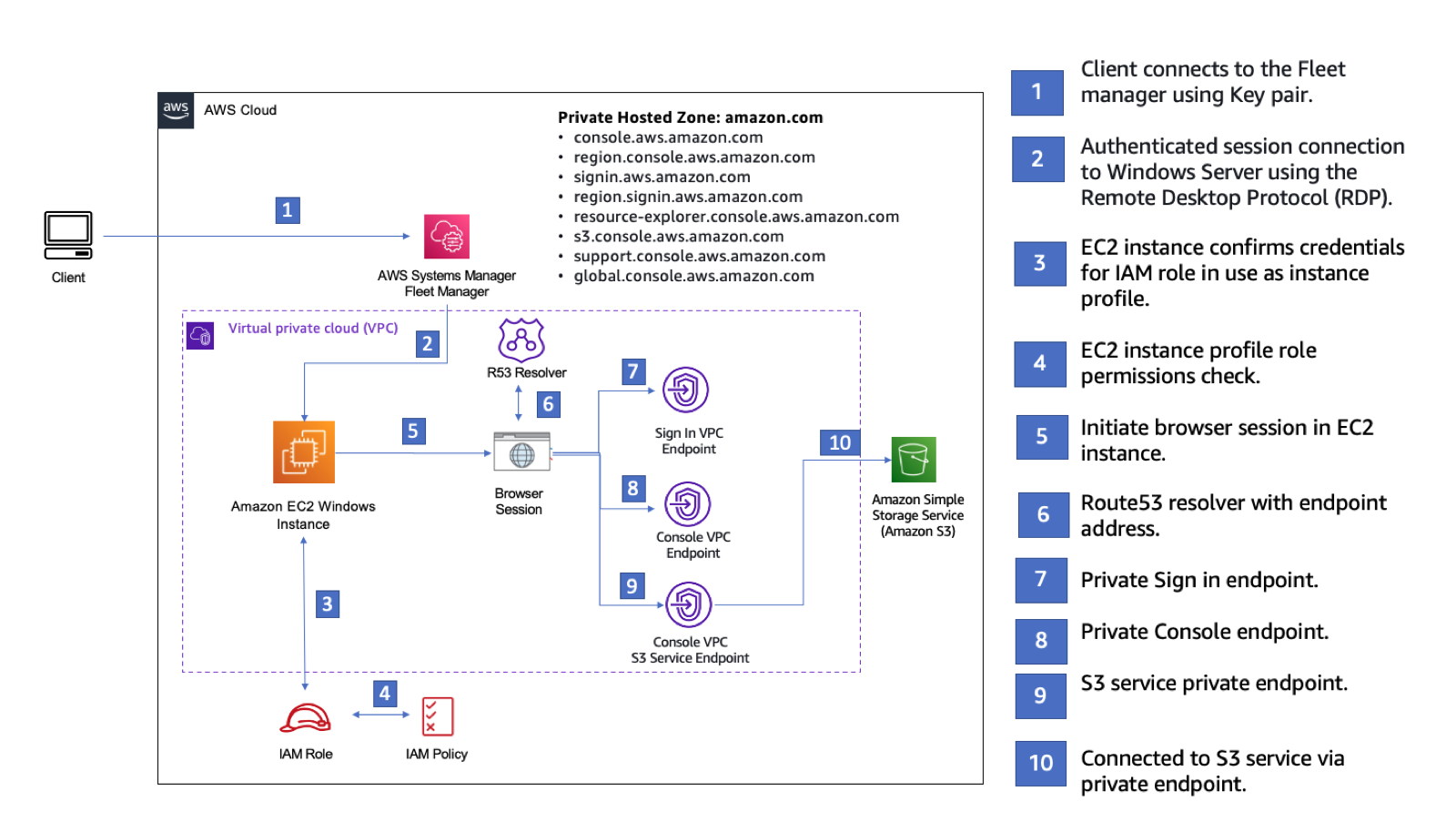
Das folgende Diagramm beschreibt den Arbeitsablauf für die Verwendung von Amazon für EC2 den Zugriff auf ein AWS Management Console Private Access-Setup. Es zeigt, wie ein Benutzer über einen privaten Endpunkt mit Amazon S3 verbunden wird.
Kopieren Sie die folgende AWS CloudFormation Vorlage und speichern Sie sie in einer Datei, die Sie in Schritt drei des Verfahrens So richten Sie ein Netzwerk ein.
Anmerkung
Diese AWS CloudFormation Vorlage verwendet Konfigurationen, die derzeit in der Region Israel (Tel Aviv) nicht unterstützt werden.
Description: | AWS Management Console Private Access. Parameters: VpcCIDR: Type: String Default: 172.16.0.0/16 Description: CIDR range for VPC Ec2KeyPair: Type: AWS::EC2::KeyPair::KeyName Description: The EC2 KeyPair to use to connect to the Windows instance PublicSubnet1CIDR: Type: String Default: 172.16.1.0/24 Description: CIDR range for Public Subnet A PublicSubnet2CIDR: Type: String Default: 172.16.0.0/24 Description: CIDR range for Public Subnet B PublicSubnet3CIDR: Type: String Default: 172.16.2.0/24 Description: CIDR range for Public Subnet C PrivateSubnet1CIDR: Type: String Default: 172.16.4.0/24 Description: CIDR range for Private Subnet A PrivateSubnet2CIDR: Type: String Default: 172.16.5.0/24 Description: CIDR range for Private Subnet B PrivateSubnet3CIDR: Type: String Default: 172.16.3.0/24 Description: CIDR range for Private Subnet C LatestWindowsAmiId: Type: 'AWS::SSM::Parameter::Value<AWS::EC2::Image::Id>' Default: '/aws/service/ami-windows-latest/Windows_Server-2022-English-Full-Base' InstanceTypeParameter: Type: String Default: 't2.medium' Resources: ######################### # VPC AND SUBNETS ######################### AppVPC: Type: 'AWS::EC2::VPC' Properties: CidrBlock: !Ref VpcCIDR InstanceTenancy: default EnableDnsSupport: true EnableDnsHostnames: true PublicSubnetA: Type: 'AWS::EC2::Subnet' Properties: VpcId: !Ref AppVPC CidrBlock: !Ref PublicSubnet1CIDR MapPublicIpOnLaunch: true AvailabilityZone: Fn::Select: - 0 - Fn::GetAZs: "" PublicSubnetB: Type: 'AWS::EC2::Subnet' Properties: VpcId: !Ref AppVPC CidrBlock: !Ref PublicSubnet2CIDR MapPublicIpOnLaunch: true AvailabilityZone: Fn::Select: - 1 - Fn::GetAZs: "" PublicSubnetC: Type: 'AWS::EC2::Subnet' Properties: VpcId: !Ref AppVPC CidrBlock: !Ref PublicSubnet3CIDR MapPublicIpOnLaunch: true AvailabilityZone: Fn::Select: - 2 - Fn::GetAZs: "" PrivateSubnetA: Type: 'AWS::EC2::Subnet' Properties: VpcId: !Ref AppVPC CidrBlock: !Ref PrivateSubnet1CIDR AvailabilityZone: Fn::Select: - 0 - Fn::GetAZs: "" PrivateSubnetB: Type: 'AWS::EC2::Subnet' Properties: VpcId: !Ref AppVPC CidrBlock: !Ref PrivateSubnet2CIDR AvailabilityZone: Fn::Select: - 1 - Fn::GetAZs: "" PrivateSubnetC: Type: 'AWS::EC2::Subnet' Properties: VpcId: !Ref AppVPC CidrBlock: !Ref PrivateSubnet3CIDR AvailabilityZone: Fn::Select: - 2 - Fn::GetAZs: "" InternetGateway: Type: AWS::EC2::InternetGateway InternetGatewayAttachment: Type: AWS::EC2::VPCGatewayAttachment Properties: InternetGatewayId: !Ref InternetGateway VpcId: !Ref AppVPC NatGatewayEIP: Type: AWS::EC2::EIP DependsOn: InternetGatewayAttachment NatGateway: Type: AWS::EC2::NatGateway Properties: AllocationId: !GetAtt NatGatewayEIP.AllocationId SubnetId: !Ref PublicSubnetA ######################### # Route Tables ######################### PrivateRouteTable: Type: 'AWS::EC2::RouteTable' Properties: VpcId: !Ref AppVPC DefaultPrivateRoute: Type: AWS::EC2::Route Properties: RouteTableId: !Ref PrivateRouteTable DestinationCidrBlock: 0.0.0.0/0 NatGatewayId: !Ref NatGateway PrivateSubnetRouteTableAssociation1: Type: 'AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation' Properties: RouteTableId: !Ref PrivateRouteTable SubnetId: !Ref PrivateSubnetA PrivateSubnetRouteTableAssociation2: Type: 'AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation' Properties: RouteTableId: !Ref PrivateRouteTable SubnetId: !Ref PrivateSubnetB PrivateSubnetRouteTableAssociation3: Type: 'AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation' Properties: RouteTableId: !Ref PrivateRouteTable SubnetId: !Ref PrivateSubnetC PublicRouteTable: Type: AWS::EC2::RouteTable Properties: VpcId: !Ref AppVPC DefaultPublicRoute: Type: AWS::EC2::Route DependsOn: InternetGatewayAttachment Properties: RouteTableId: !Ref PublicRouteTable DestinationCidrBlock: 0.0.0.0/0 GatewayId: !Ref InternetGateway PublicSubnetARouteTableAssociation1: Type: AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation Properties: RouteTableId: !Ref PublicRouteTable SubnetId: !Ref PublicSubnetA PublicSubnetBRouteTableAssociation2: Type: AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation Properties: RouteTableId: !Ref PublicRouteTable SubnetId: !Ref PublicSubnetB PublicSubnetBRouteTableAssociation3: Type: AWS::EC2::SubnetRouteTableAssociation Properties: RouteTableId: !Ref PublicRouteTable SubnetId: !Ref PublicSubnetC ######################### # SECURITY GROUPS ######################### VPCEndpointSecurityGroup: Type: 'AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup' Properties: GroupDescription: Allow TLS for VPC Endpoint VpcId: !Ref AppVPC SecurityGroupIngress: - IpProtocol: tcp FromPort: 443 ToPort: 443 CidrIp: !GetAtt AppVPC.CidrBlock EC2SecurityGroup: Type: 'AWS::EC2::SecurityGroup' Properties: GroupDescription: Default EC2 Instance SG VpcId: !Ref AppVPC ######################### # VPC ENDPOINTS ######################### VPCEndpointGatewayS3: Type: 'AWS::EC2::VPCEndpoint' Properties: ServiceName: !Sub 'com.amazonaws.${AWS::Region}.s3' VpcEndpointType: Gateway VpcId: !Ref AppVPC RouteTableIds: - !Ref PrivateRouteTable VPCEndpointInterfaceSSM: Type: 'AWS::EC2::VPCEndpoint' Properties: VpcEndpointType: Interface PrivateDnsEnabled: false SubnetIds: - !Ref PrivateSubnetA - !Ref PrivateSubnetB SecurityGroupIds: - !Ref VPCEndpointSecurityGroup ServiceName: !Sub 'com.amazonaws.${AWS::Region}.ssm' VpcId: !Ref AppVPC VPCEndpointInterfaceEc2messages: Type: 'AWS::EC2::VPCEndpoint' Properties: VpcEndpointType: Interface PrivateDnsEnabled: false SubnetIds: - !Ref PrivateSubnetA - !Ref PrivateSubnetB - !Ref PrivateSubnetC SecurityGroupIds: - !Ref VPCEndpointSecurityGroup ServiceName: !Sub 'com.amazonaws.${AWS::Region}.ec2messages' VpcId: !Ref AppVPC VPCEndpointInterfaceSsmmessages: Type: 'AWS::EC2::VPCEndpoint' Properties: VpcEndpointType: Interface PrivateDnsEnabled: false SubnetIds: - !Ref PrivateSubnetA - !Ref PrivateSubnetB - !Ref PrivateSubnetC SecurityGroupIds: - !Ref VPCEndpointSecurityGroup ServiceName: !Sub 'com.amazonaws.${AWS::Region}.ssmmessages' VpcId: !Ref AppVPC VPCEndpointInterfaceSignin: Type: 'AWS::EC2::VPCEndpoint' Properties: VpcEndpointType: Interface PrivateDnsEnabled: false SubnetIds: - !Ref PrivateSubnetA - !Ref PrivateSubnetB - !Ref PrivateSubnetC SecurityGroupIds: - !Ref VPCEndpointSecurityGroup ServiceName: !Sub 'com.amazonaws.${AWS::Region}.signin' VpcId: !Ref AppVPC VPCEndpointInterfaceConsole: Type: 'AWS::EC2::VPCEndpoint' Properties: VpcEndpointType: Interface PrivateDnsEnabled: false SubnetIds: - !Ref PrivateSubnetA - !Ref PrivateSubnetB - !Ref PrivateSubnetC SecurityGroupIds: - !Ref VPCEndpointSecurityGroup ServiceName: !Sub 'com.amazonaws.${AWS::Region}.console' VpcId: !Ref AppVPC ######################### # ROUTE53 RESOURCES ######################### ConsoleHostedZone: Type: "AWS::Route53::HostedZone" Properties: HostedZoneConfig: Comment: 'Console VPC Endpoint Hosted Zone' Name: 'console.aws.amazon.com' VPCs: - VPCId: !Ref AppVPC VPCRegion: !Ref "AWS::Region" ConsoleRecordGlobal: Type: AWS::Route53::RecordSet Properties: HostedZoneId: !Ref 'ConsoleHostedZone' Name: 'console.aws.amazon.com' AliasTarget: DNSName: !Select ['1', !Split [':', !Select ['0', !GetAtt VPCEndpointInterfaceConsole.DnsEntries]]] HostedZoneId: !Select ['0', !Split [':', !Select ['0', !GetAtt VPCEndpointInterfaceConsole.DnsEntries]]] Type: A GlobalConsoleRecord: Type: AWS::Route53::RecordSet Properties: HostedZoneId: !Ref 'ConsoleHostedZone' Name: 'global.console.aws.amazon.com' AliasTarget: DNSName: !Select ['1', !Split [':', !Select ['0', !GetAtt VPCEndpointInterfaceConsole.DnsEntries]]] HostedZoneId: !Select ['0', !Split [':', !Select ['0', !GetAtt VPCEndpointInterfaceConsole.DnsEntries]]] Type: A ConsoleS3ProxyRecordGlobal: Type: AWS::Route53::RecordSet Properties: HostedZoneId: !Ref 'ConsoleHostedZone' Name: 's3.console.aws.amazon.com' AliasTarget: DNSName: !Select ['1', !Split [':', !Select ['0', !GetAtt VPCEndpointInterfaceConsole.DnsEntries]]] HostedZoneId: !Select ['0', !Split [':', !Select ['0', !GetAtt VPCEndpointInterfaceConsole.DnsEntries]]] Type: A ConsoleSupportProxyRecordGlobal: Type: AWS::Route53::RecordSet Properties: HostedZoneId: !Ref 'ConsoleHostedZone' Name: "support.console.aws.amazon.com" AliasTarget: DNSName: !Select ['1', !Split [':', !Select ['0', !GetAtt VPCEndpointInterfaceConsole.DnsEntries]]] HostedZoneId: !Select ['0', !Split [':', !Select ['0', !GetAtt VPCEndpointInterfaceConsole.DnsEntries]]] Type: A ExplorerProxyRecordGlobal: Type: AWS::Route53::RecordSet Properties: HostedZoneId: !Ref 'ConsoleHostedZone' Name: "resource-explorer.console.aws.amazon.com" AliasTarget: DNSName: !Select ['1', !Split [':', !Select ['0', !GetAtt VPCEndpointInterfaceConsole.DnsEntries]]] HostedZoneId: !Select ['0', !Split [':', !Select ['0', !GetAtt VPCEndpointInterfaceConsole.DnsEntries]]] Type: A ConsoleRecordRegional: Type: AWS::Route53::RecordSet Properties: HostedZoneId: !Ref 'ConsoleHostedZone' Name: !Sub "${AWS::Region}.console.aws.amazon.com" AliasTarget: DNSName: !Select ['1', !Split [':', !Select ['0', !GetAtt VPCEndpointInterfaceConsole.DnsEntries]]] HostedZoneId: !Select ['0', !Split [':', !Select ['0', !GetAtt VPCEndpointInterfaceConsole.DnsEntries]]] Type: A SigninHostedZone: Type: "AWS::Route53::HostedZone" Properties: HostedZoneConfig: Comment: 'Signin VPC Endpoint Hosted Zone' Name: 'signin.aws.amazon.com' VPCs: - VPCId: !Ref AppVPC VPCRegion: !Ref "AWS::Region" SigninRecordGlobal: Type: AWS::Route53::RecordSet Properties: HostedZoneId: !Ref 'SigninHostedZone' Name: 'signin.aws.amazon.com' AliasTarget: DNSName: !Select ['1', !Split [':', !Select ['0', !GetAtt VPCEndpointInterfaceSignin.DnsEntries]]] HostedZoneId: !Select ['0', !Split [':', !Select ['0', !GetAtt VPCEndpointInterfaceSignin.DnsEntries]]] Type: A SigninRecordRegional: Type: AWS::Route53::RecordSet Properties: HostedZoneId: !Ref 'SigninHostedZone' Name: !Sub "${AWS::Region}.signin.aws.amazon.com" AliasTarget: DNSName: !Select ['1', !Split [':', !Select ['0', !GetAtt VPCEndpointInterfaceSignin.DnsEntries]]] HostedZoneId: !Select ['0', !Split [':', !Select ['0', !GetAtt VPCEndpointInterfaceSignin.DnsEntries]]] Type: A ######################### # EC2 INSTANCE ######################### Ec2InstanceRole: Type: AWS::IAM::Role Properties: AssumeRolePolicyDocument: Version: 2012-10-17 Statement: - Effect: Allow Principal: Service: - ec2.amazonaws.com Action: - sts:AssumeRole Path: / ManagedPolicyArns: - arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore Ec2InstanceProfile: Type: AWS::IAM::InstanceProfile Properties: Path: / Roles: - !Ref Ec2InstanceRole EC2WinInstance: Type: 'AWS::EC2::Instance' Properties: ImageId: !Ref LatestWindowsAmiId IamInstanceProfile: !Ref Ec2InstanceProfile KeyName: !Ref Ec2KeyPair InstanceType: Ref: InstanceTypeParameter SubnetId: !Ref PrivateSubnetA SecurityGroupIds: - Ref: EC2SecurityGroup BlockDeviceMappings: - DeviceName: /dev/sda1 Ebs: VolumeSize: 50 Tags: - Key: "Name" Value: "Console VPCE test instance"
So richten Sie ein Netzwerk ein:
-
Melden Sie sich bei dem Verwaltungskonto Ihrer Organisation an, und öffnen Sie die AWS CloudFormation -Konsole
. -
Wählen Sie Stack erstellen aus.
-
Wählen Sie Mit neuen Ressourcen (Standard). Laden Sie die AWS CloudFormation Vorlagendatei hoch, die Sie zuvor erstellt haben, und wählen Sie Weiter.
-
Geben Sie einen Namen für den Stack ein, z. B.
PrivateConsoleNetworkForS3, und wählen Sie Weiter aus. -
Geben Sie für VPCund Subnetze Ihre bevorzugten CIDR IP-Bereiche ein, oder verwenden Sie die bereitgestellten Standardwerte. Wenn Sie die Standardwerte verwenden, stellen Sie sicher, dass sie sich nicht mit den vorhandenen VPC Ressourcen in Ihrem AWS-Konto System überschneiden.
-
Wählen Sie für den KeyPairEc2-Parameter eines der vorhandenen EC2 Amazon-Schlüsselpaare in Ihrem Konto aus. Wenn Sie noch kein EC2 Amazon-Schlüsselpaar haben, müssen Sie eines erstellen, bevor Sie mit dem nächsten Schritt fortfahren. Weitere Informationen finden Sie unter Erstellen eines key pair mithilfe von Amazon EC2 im EC2Amazon-Benutzerhandbuch.
-
Wählen Sie Stack erstellen aus.
-
Nachdem der Stack erstellt wurde, wählen Sie die Registerkarte Ressourcen, um die erstellten Ressourcen anzuzeigen.
Um eine Verbindung mit der EC2 Amazon-Instance herzustellen
-
Melden Sie sich beim Verwaltungskonto Ihrer Organisation an und öffnen Sie die EC2Amazon-Konsole
. -
Wählen Sie im Navigationsbereich Instances aus.
-
Wählen Sie auf der Seite Instances die VPCEConsole-Testinstanz aus, die mit der AWS CloudFormation Vorlage erstellt wurde. Wählen Sie dann Verbinden aus.
Anmerkung
In diesem Beispiel wird Fleet Manager, eine Funktion von AWS Systems Manager Explorer, verwendet, um eine Verbindung zu Ihrem Windows Server herzustellen. Es kann einige Minuten dauern, bis die Verbindung hergestellt werden kann.
-
Wählen Sie auf der Seite Mit Instance verbinden die Option RDPClient und anschließend Connect using Fleet Manager aus.
-
Wählen Sie Fleet Manager Remote Destop aus.
-
Um das Administratorkennwort für die EC2 Amazon-Instance abzurufen und über die Weboberfläche auf den Windows-Desktop zuzugreifen, verwenden Sie den privaten Schlüssel, der dem EC2 Amazon-Schlüsselpaar zugeordnet ist, das Sie bei der Erstellung der AWS CloudFormation Vorlage verwendet haben.
-
Öffnen Sie von der Amazon EC2 Windows-Instance aus die AWS Management Console im Browser.
-
Nachdem Sie sich mit Ihren AWS Anmeldeinformationen angemeldet haben, öffnen Sie die Amazon S3 S3-Konsole
und stellen Sie sicher, dass Sie über AWS Management Console Private Access verbunden sind.
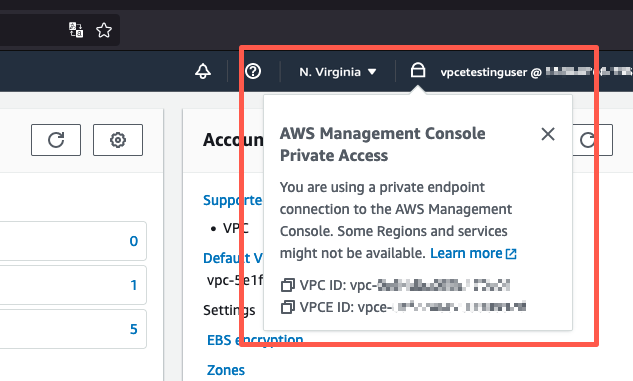
Um die Einrichtung von AWS Management Console Private Access zu testen
-
Melden Sie sich beim Verwaltungskonto Ihrer Organisation an, und öffnen Sie die Amazon S3-Konsole
. -
Wählen Sie das Schloss-Private-Symbol in der Navigationsleiste, um den verwendeten VPC Endpunkt anzuzeigen. Der folgende Screenshot zeigt die Position des Lock-Private-Symbols und die entsprechenden Informationen. VPC