How Amazon Q network troubleshooting works
Amazon Q network troubleshooting is a feature of Amazon Q that works with Amazon VPC Reachability Analyzer. With Amazon Q network troubleshooting, you can query reachability between resources in your AWS account by asking questions in plain English. Amazon Q network troubleshooting uses generative AI and large language models (LLMs) to interpret your question to provide guidance. Amazon Q can be used to help troubleshoot a problem or to walk you through completing a tasks. It does this by calling specific resource APIs on a customer's behalf.
To use Amazon Q network troubleshooting, you must first sign in to the console and then open Amazon Q . You can
ask Amazon Q for help with network connectivity issues by choosing the Amazon Q icon (
![]() ) on the top right corner of the AWS Management Console.
) on the top right corner of the AWS Management Console.
Topics
Amazon Q Developer permissions
To use Amazon Q on the console, the following AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) permissions are required:
-
q:PassRequest -
q:SendMessage -
q:StartConversation -
q:GetConversation -
q:ListConversations
To set or manage these permissions, see Amazon Q Developer permissions reference in the Amazon Q Developer Guide.
Supported resource types
Amazon Q network troubleshooting can analyze the path between the following resources.
-
Amazon EC2 instance
-
Amazon RDS DB instance
-
Auto Scaling group
-
Elastic network interface
-
Internet gateway
-
NAT gateway
-
Transit gateway
-
Virtual private gateway
-
VPC
-
VPC endpoint
-
VPC peering connection
-
VPC subnet
Examples of types of questions supported by Amazon Q network troubleshooting
When asking network connectivity questions in Amazon Q, we recommend phrasing them similarly to the following question types.
-
Why am I unable to SSH into my EC2 Linux instance?
-
Why am I getting timeout errors when accessing my EC2 Windows instance via RDP
-
Why can't I access the internet from EC2 instance?
-
Why are my EC2 instances unable to reach the internet?
-
Why can I not reach the internet from my EC2 instances in private subnets?
-
How can I verify connectivity between my corporate network and my VPC?
-
How do I check if my VPC peering connection is working properly??
-
Are my routes set up correctly to allow internet access?
-
Can I connect to my RDS database instance from my on-premises network?
-
Can you verify whether my EC2 Instances in us-east-1 and us-west-2 are accessible from the internet?
Example: Use Amazon Q to troubleshoot a problem
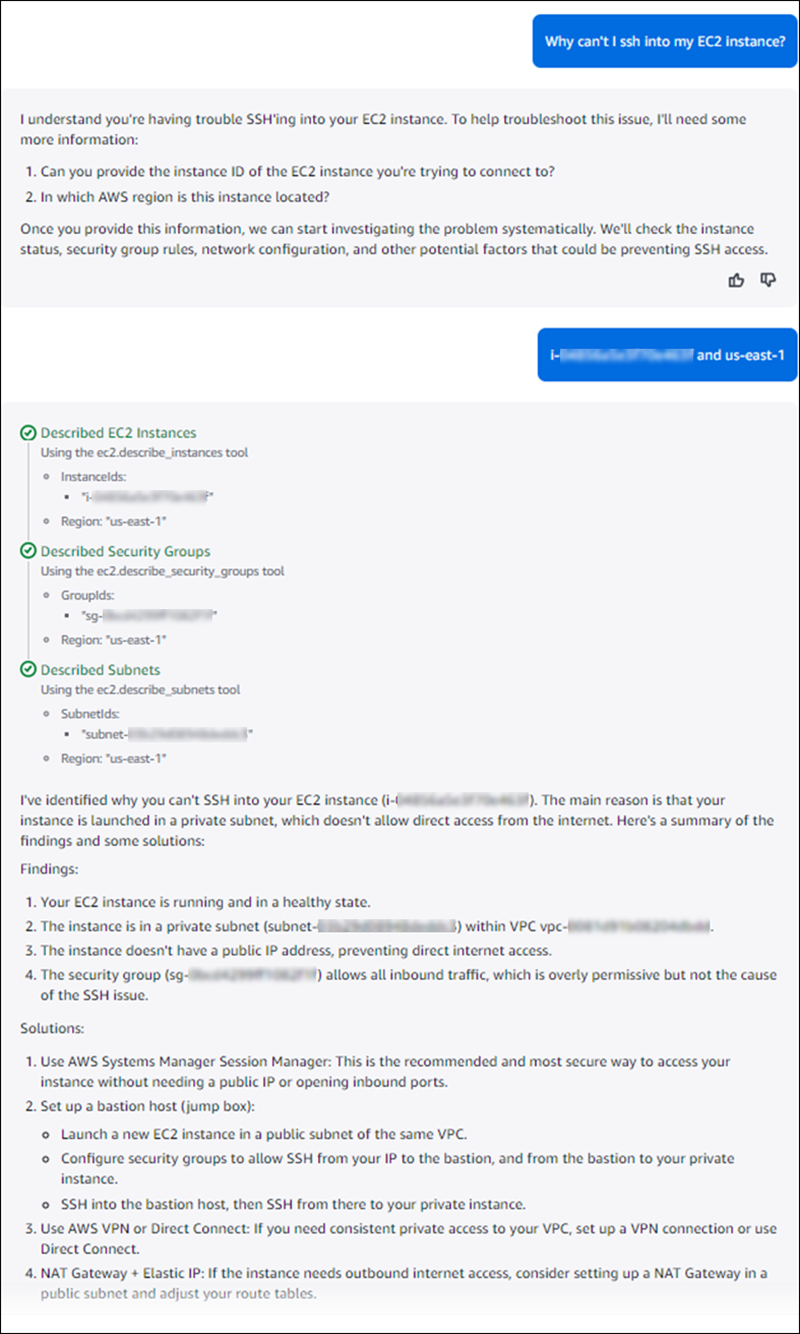
Use Amazon Q to help you troubleshoot a problem. In this example, a user wants to know
why they can't reach their EC2 instances and asks Amazon Q: Why can't
I ssh into my EC2 instance?. Amazon Q network troubleshooting might return a response
similar to the example below, suggesting troubleshooting steps as well as providing links to
other resources. Since there are multiple instance IDs and Regions, Amazon Q asks for the
specific instance ID and Region where the instance is located. Once the required information
is provided, Amazon Q investigates the problem and returns a list of possible problems, along
with solutions and recommendations to try and fix the problem.

Example: Use Amazon Q for the steps to perform a task
In this example, a user asks Amazon Q how to perform a task with the question
How do I verify my Application Load Balancer is routing traffic
to my EC2 instances?. Amazon Q then checks the status of EC2
instances and configuration.

Once the checks are completed, Amazon Q provides the specific steps for the user to carry out, as shown in the following diagram:

Example: Use Amazon Q to verify information
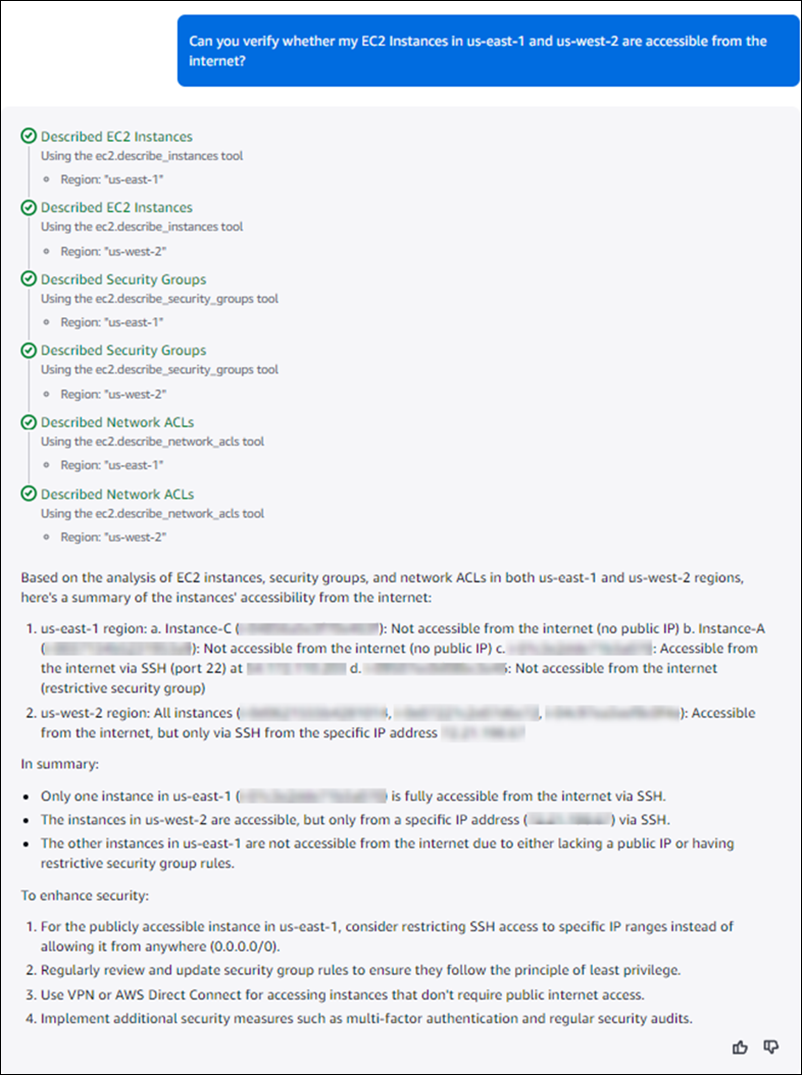
Use Amazon Q to verify information about a connection, enabling you to make more
well-informed decisions about how you might want to modify connections. In this example, a
user wants to know whether instances in two Regions are accessible from the internet. They
ask Amazon Q: Can you verify whether my EC2 instances in us-east-1 and
us-west-2 are accessible from the internet?. Amazon Q network troubleshooting might
return a response similar to the example below. In t his example, Amazon Q analyzes the
instances and then lets the user know that instances in
us-east-1 are not accessible from the internet, while
instances in us-west-2 are. Based on this information the user
can then decide to modify access to either Region, along with suggested recommendations and
steps.
If the Amazon Q can't immediately answer the question, it'll prompt you for more
information. In this example, a user asks Is my server farm in Region A
accessible from my office network?. Because Amazon Q can't
immediately help based on the question itself, it prompts the user for more
information:
