Las traducciones son generadas a través de traducción automática. En caso de conflicto entre la traducción y la version original de inglés, prevalecerá la version en inglés.
Cree su primera aplicación con Infrastructure Composer
En este tutorial, se utiliza AWS Infrastructure Composer para crear, leer, actualizar y eliminar (CRUD) una aplicación sin servidor que gestione los usuarios de una base de datos.
Para este tutorial, utilizamos Infrastructure Composer en. AWS Management Console Le recomendamos que utilice Google Chrome o Microsoft Edge, y una ventana de navegador a pantalla completa.
¿Es la primera vez que utiliza la tecnología sin servidor?
Se recomienda tener conocimientos básicos de los siguientes temas:
Para obtener más información, consulte Conceptos sin servidor para AWS Infrastructure Composer.
Temas
- Referencia de propiedades del recurso
- Paso 1: Crea tu proyecto
- Paso 2: Añade cartas al lienzo
- Paso 3: Configure su API puerta de enlace REST API
- Paso 4: Configure las funciones de Lambda
- Paso 5: Conecta tus tarjetas
- Paso 6: Organice el lienzo
- Paso 7: Agregar y conectar una tabla de DynamoDB
- Paso 8: Revise la plantilla AWS CloudFormation
- Paso 9: Intégrelo en sus flujos de trabajo de desarrollo
- Pasos a seguir a continuación
Referencia de propiedades del recurso
Al crear la aplicación, utilice esta tabla como referencia para configurar las propiedades de Amazon API Gateway y sus AWS Lambda recursos.
| Método | Ruta | Nombre de la función |
|---|---|---|
|
GET |
/artículos |
getItems |
|
GET |
/elementos/ {id} |
getItem |
|
PUT |
/items/ {id} |
updateItem |
|
POST |
/artículo |
addItem |
|
DELETE |
/items/ {id} |
deleteItem |
Paso 1: Crea tu proyecto
Para empezar a utilizar su aplicación CRUD sin servidor, cree un proyecto nuevo en Infrastructure Composer y active la sincronización local.
Para crear un nuevo proyecto en blanco
-
Inicie sesión en la consola de Infrastructure Composer
. -
En la página de inicio, elija Crear proyecto.
Como se muestra en la imagen siguiente, Infrastructure Composer abre el lienzo visual y carga una plantilla de aplicación inicial (en blanco).
Para activar la sincronización local
-
En el menú de Infrastructure Composer, seleccione Guardar > Activar la sincronización local.
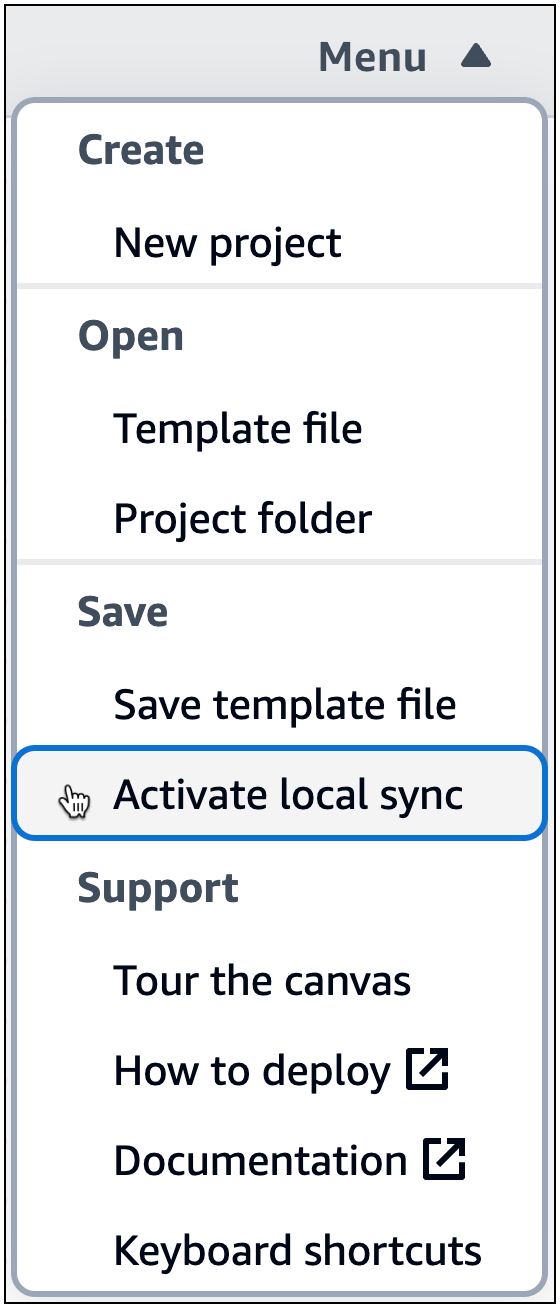
-
Para la ubicación del proyecto, pulse Seleccionar carpeta y elija un directorio. Aquí es donde Infrastructure Composer guardará y sincronizará los archivos y carpetas de la plantilla a medida que vaya diseñando.
La ubicación del proyecto no debe contener una plantilla de aplicación existente.
nota
La sincronización local requiere un navegador compatible con el acceso al sistema de archivosAPI. Para obtener más información, consulte Data Infrastructure Composer obtiene acceso a.
-
Cuando se te pida que permitas el acceso, selecciona Ver archivos.
-
Presiona Activar para activar la sincronización local. Cuando se te pida que guardes los cambios, selecciona Guardar cambios.
Cuando esté activado, el indicador de guardado automático se mostrará en el área superior izquierda del lienzo.
Paso 2: Añade cartas al lienzo
Comience a diseñar la arquitectura de su aplicación con tarjetas de componentes mejoradas, empezando por una API puerta de enlace REST API y cinco funciones Lambda.
Para añadir tarjetas API Gateway y Lambda al lienzo
En la paleta Recursos, en la sección Componentes mejorados, haga lo siguiente:
-
Arrastra una carta APIGateway al lienzo.
-
Arrastre una tarjeta de Función Lambda al lienzo. Repita el proceso hasta que haya agregado cinco tarjetas de Función Lambda al lienzo.
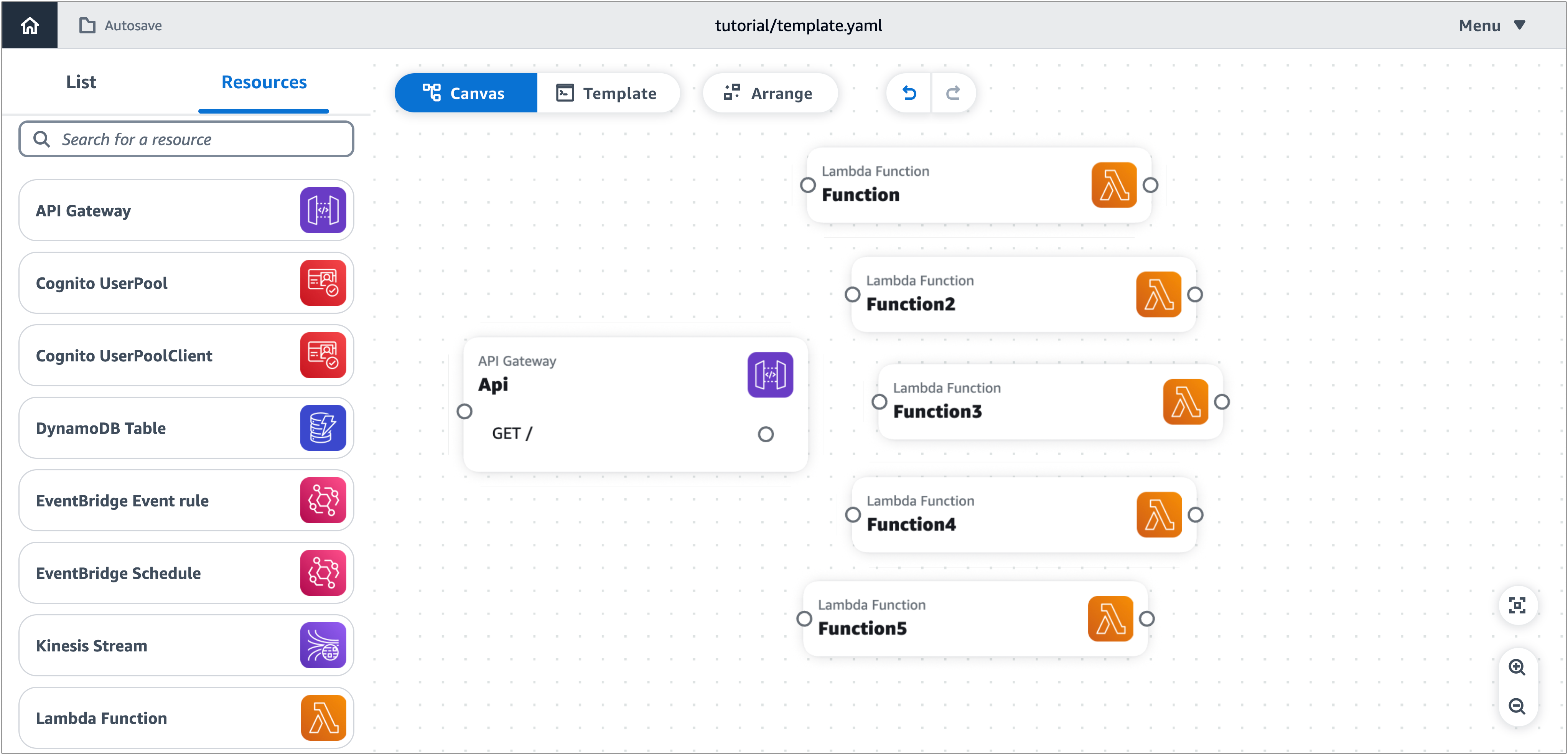
Paso 3: Configure su API puerta de enlace REST API
A continuación, añada cinco rutas en su tarjeta API Gateway.
Para añadir rutas a la tarjeta API Gateway
-
Abra el panel de propiedades del recurso de la tarjeta APIGateway. Para abrir el panel, haga doble clic en la tarjeta. O bien, selecciona la tarjeta y, a continuación, selecciona Detalles.
-
En el panel de propiedades del recurso, en Rutas, haga lo siguiente:
nota
Para cada una de las siguientes rutas, utilice los valores de HTTP método y ruta especificados en la tabla de referencia de propiedades del recurso.
-
En Método, elija el HTTP método especificado. Por ejemplo, GET.
-
En Ruta, introduzca la ruta especificada. Por ejemplo,
/items. -
Seleccione Añadir ruta.
-
Repita los pasos anteriores hasta que haya agregado las cinco rutas especificadas.
-
-
Seleccione Guardar.
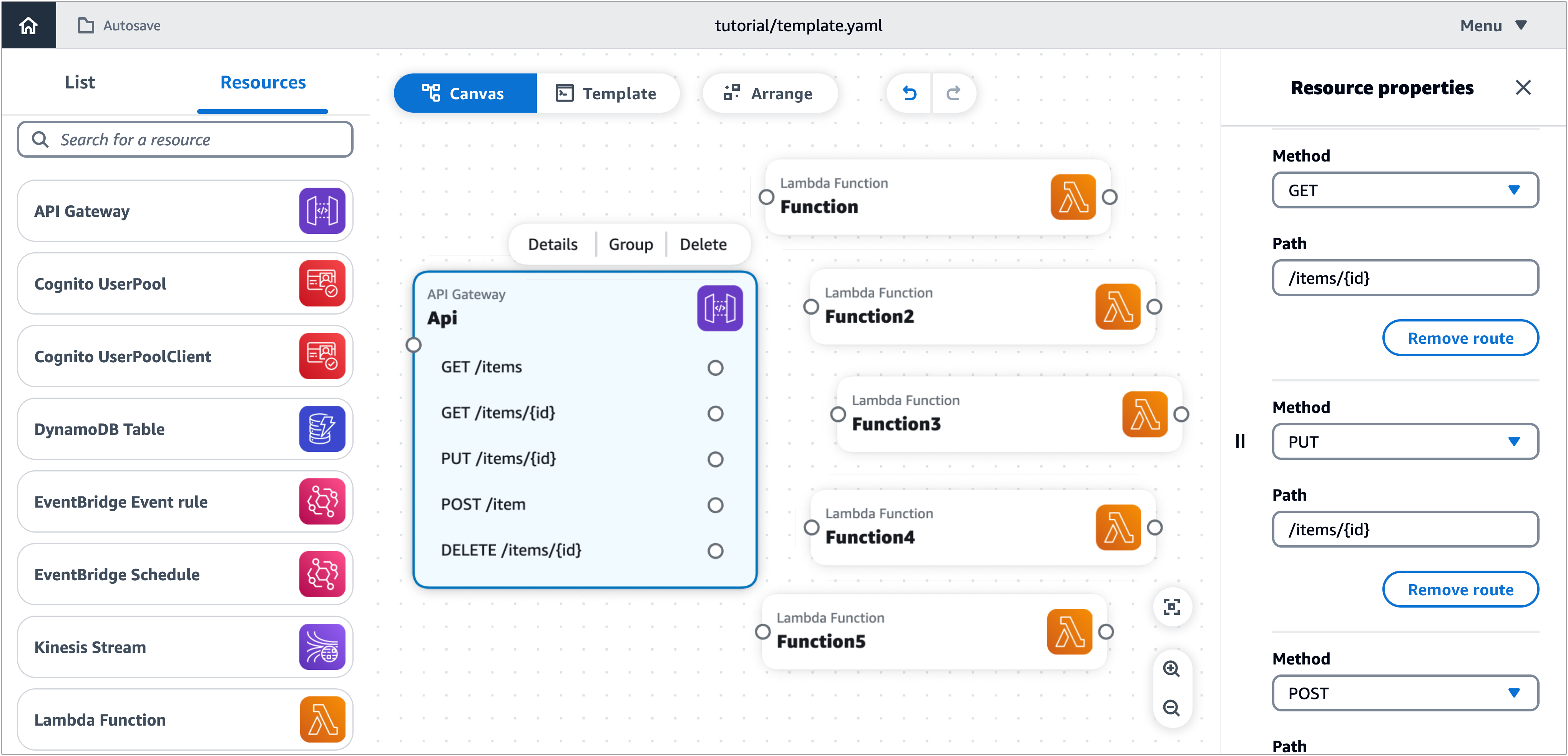
Paso 4: Configure las funciones de Lambda
Asigne un nombre a cada una de las cinco funciones Lambda tal y como se especifica en la tabla de referencia de propiedades del recurso.
Para asignar un nombre a las funciones Lambda
-
Abra el panel de propiedades del recurso de una tarjeta de función Lambda. Para abrir el panel, haga doble clic en la tarjeta. O bien, selecciona la tarjeta y, a continuación, selecciona Detalles.
-
En el panel de propiedades del recurso, en Logical ID, introduzca el nombre de una función específica. Por ejemplo,
getItems. -
Seleccione Guardar.
-
Repita los pasos anteriores hasta que haya asignado un nombre a las cinco funciones.
Paso 5: Conecta tus tarjetas
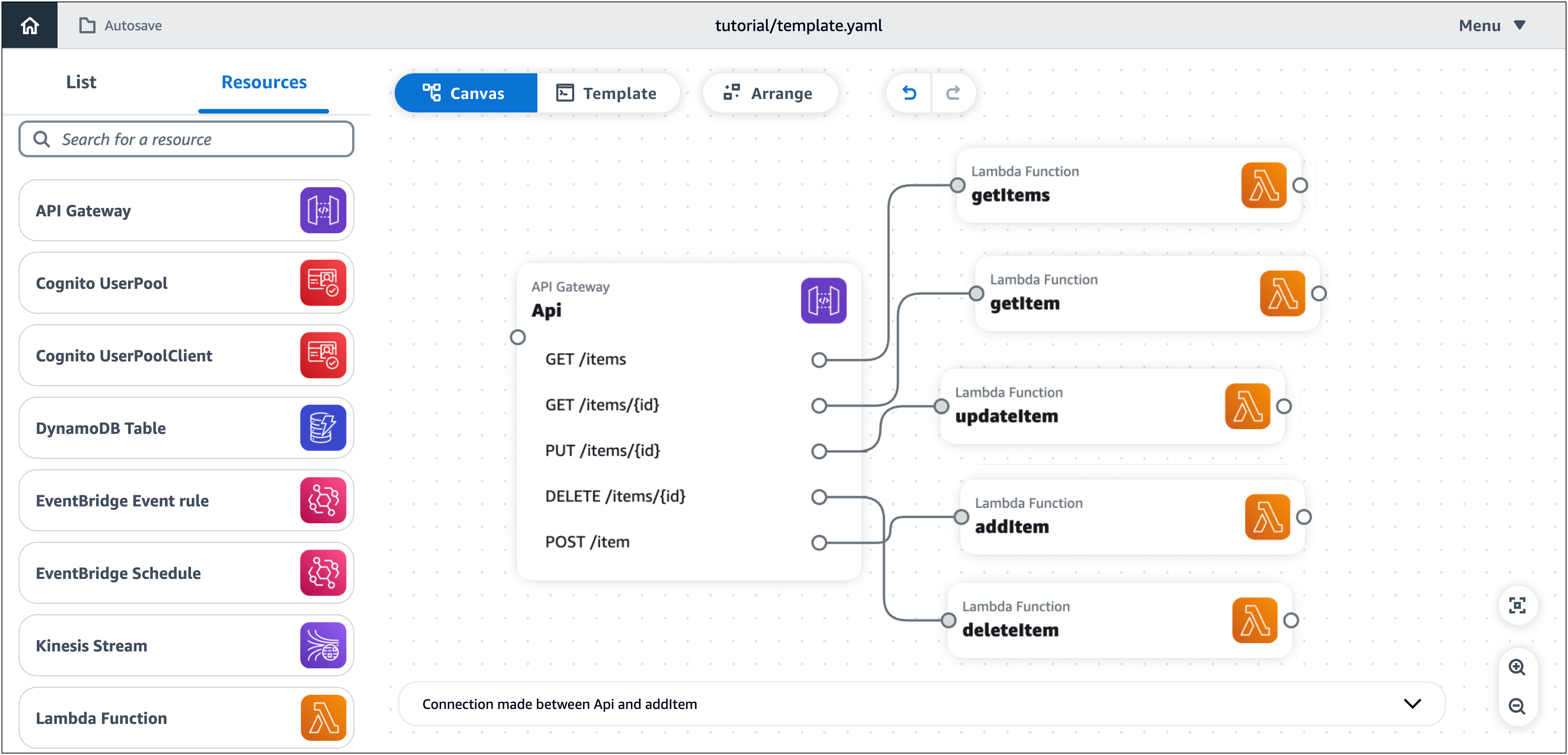
Conecte cada ruta de la tarjeta APIGateway a su tarjeta de función Lambda relacionada, tal y como se especifica en la tabla de referencia de propiedades del recurso.
Para conectar sus tarjetas
-
Haga clic en un puerto derecho de la tarjeta APIGateway y arrástrelo hasta el puerto izquierdo de la tarjeta de función Lambda especificada. Por ejemplo, haga clic en el puerto GET/items y arrástrelo hasta el puerto izquierdo de. getItems
-
Repita el paso anterior hasta conectar las cinco rutas de la tarjeta APIGateway a las tarjetas de función Lambda correspondientes.
Paso 6: Organice el lienzo
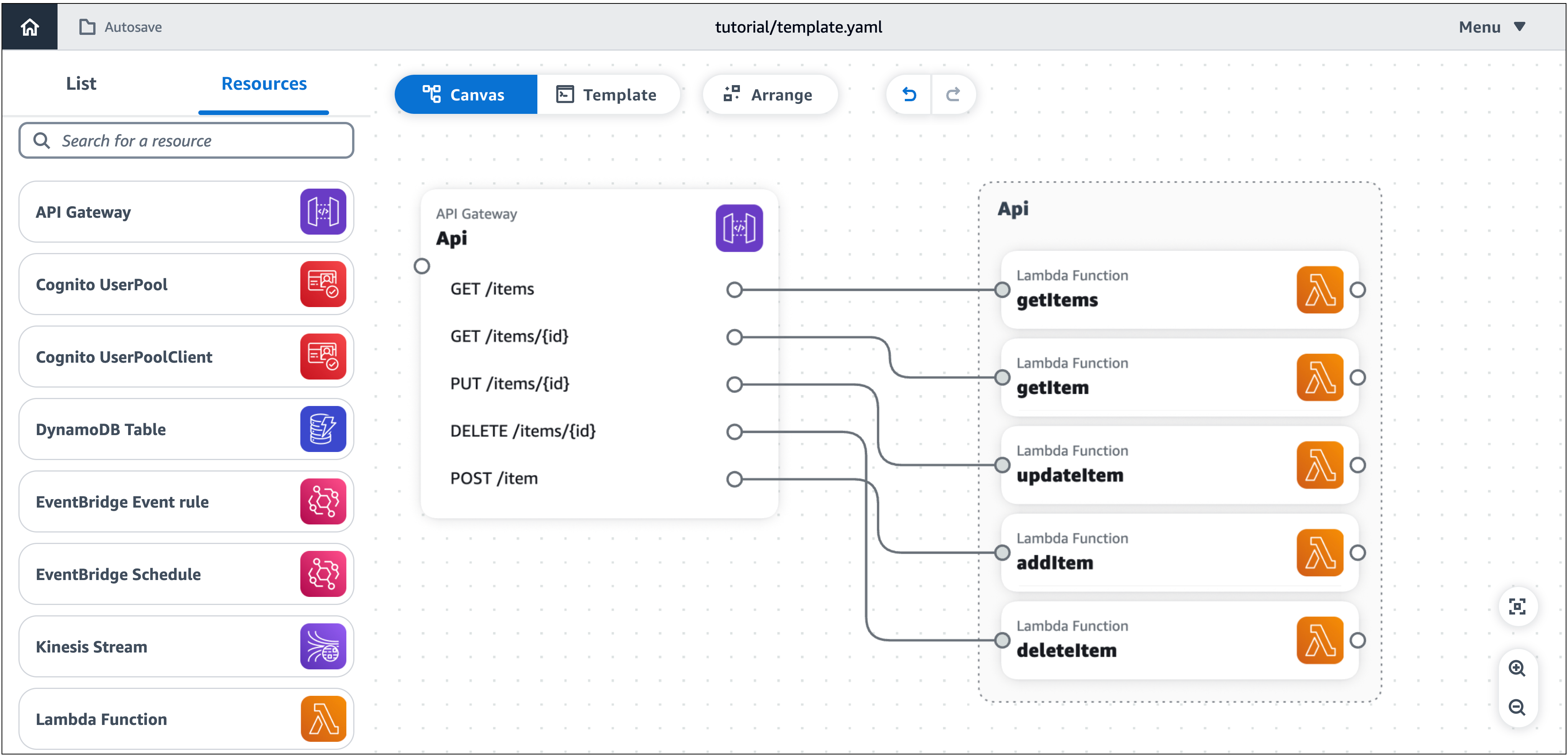
Organice el lienzo visual agrupando las funciones de Lambda y organizando todas las tarjetas.
Para agrupar sus funciones
-
Mantenga pulsada la tecla Mayús y, a continuación, seleccione cada tarjeta de Función Lambda del lienzo.
-
Seleccione Agrupar.
Para asignar un nombre a su grupo
-
Haga doble clic en la parte superior del grupo, cerca del nombre del grupo (Grupo).
Se abre el panel de propiedades del grupo.
-
En el panel de propiedades del grupo, introduzca el nombre del grupo
API. -
Seleccione Guardar.
Para organizar las tarjetas
En el lienzo, sobre el área de visualización principal, selecciona Organizar.
Infrastructure Composer organiza y alinea todas las cartas en el lienzo visual, incluido el nuevo grupo (API), como se muestra a continuación:
Paso 7: Agregar y conectar una tabla de DynamoDB
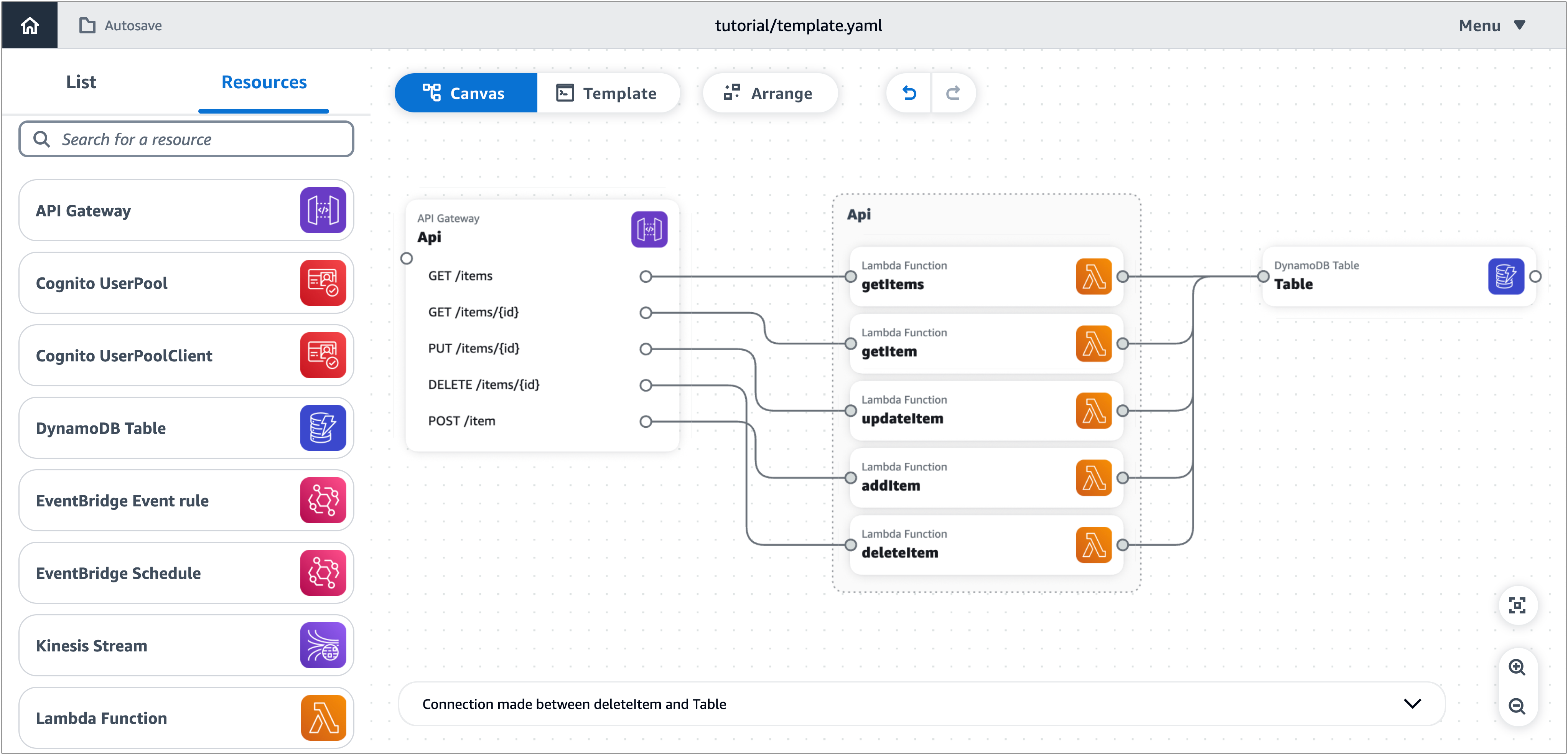
Ahora, añada una tabla de DynamoDB a la arquitectura de la aplicación y conéctela a las funciones de Lambda.
Para añadir y conectar una tabla de DynamoDB
-
Desde la paleta de recursos (Recursos), en la sección Componentes mejorados, arrastre una tarjeta de DynamoDB Table al lienzo.
-
Haga clic en el puerto derecho de una tarjeta de función Lambda y arrástrelo hasta el puerto izquierdo de la tarjeta de tabla de DynamoDB.
-
Repita el paso anterior hasta conectar las cinco tarjetas de función Lambda a la tarjeta de tabla de DynamoDB.
-
(Opcional) Para reorganizar y realinear las cartas en el lienzo, elija Organizar.
Paso 8: Revise la plantilla AWS CloudFormation
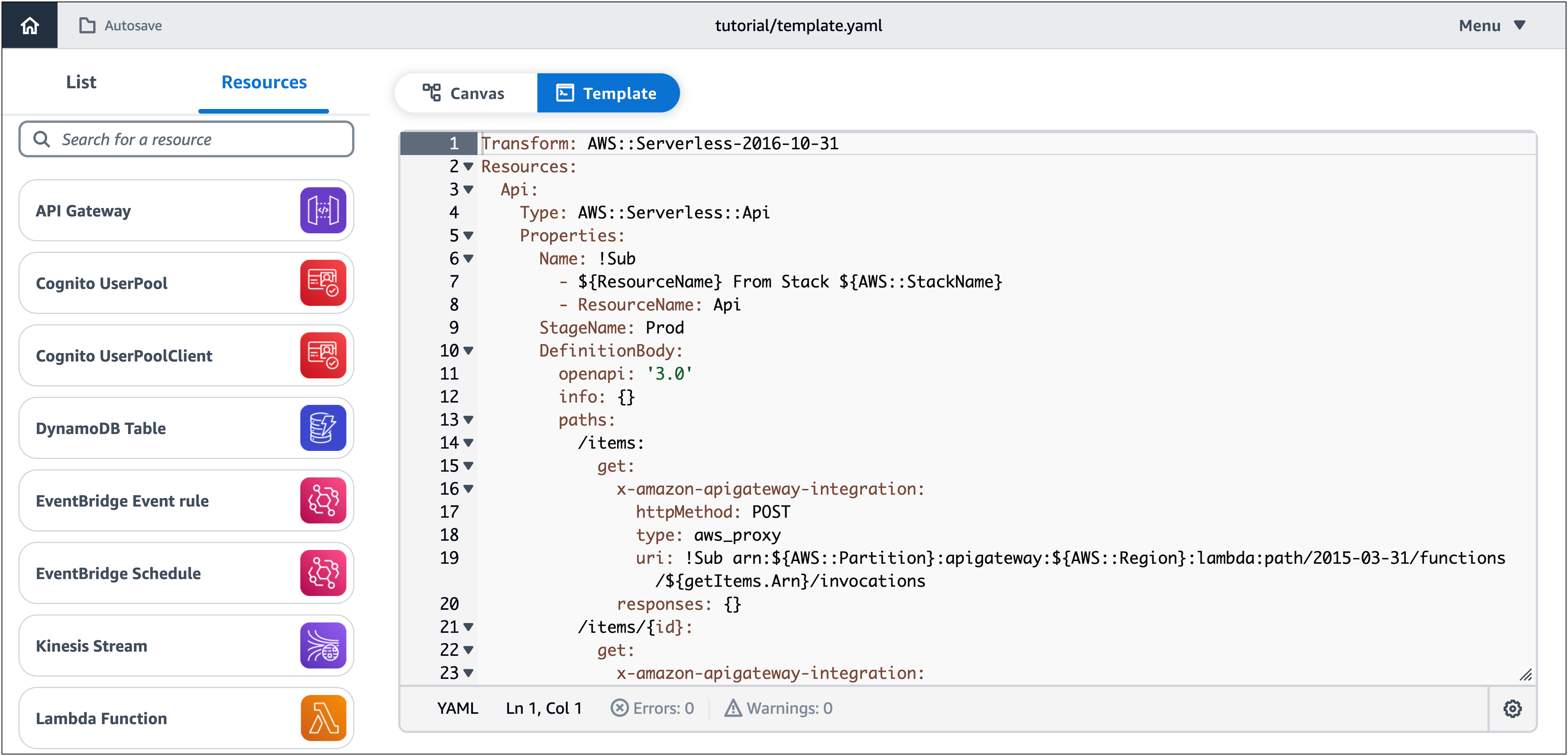
¡Enhorabuena! Diseñó correctamente una aplicación sin servidor que está lista para su implementación. Por último, elija Plantilla para revisar la AWS CloudFormation plantilla que Infrastructure Composer ha generado automáticamente para usted.
En la plantilla, Infrastructure Composer ha definido lo siguiente:
-
La
Transformdeclaración, que especifica la plantilla como una plantilla AWS Serverless Application Model (AWS SAM). Para obtener más información, consulta la anatomía AWS SAM de la plantilla en la Guía para AWS Serverless Application Model desarrolladores. -
Un
AWS::Serverless::Apirecurso que especifica su API puerta de enlace REST API con sus cinco rutas. -
Cinco
AWS::Serverless::Functionrecursos, que especifican las configuraciones de las funciones de Lambda, incluidas sus variables de entorno y políticas de permisos. -
Un
AWS::DynamoDB::Tablerecurso que especifica la tabla de DynamoDB y sus propiedades. -
La
Metadatasección, que contiene información sobre el grupo de recursos () API. Para obtener más información sobre esta sección, consulte Metadatos en la Guía del AWS CloudFormation usuario.
Paso 9: Intégrelo en sus flujos de trabajo de desarrollo
Utilice el archivo de plantilla y los directorios de proyectos que creó Infrastructure Composer para realizar más pruebas e implementar.
-
Con la sincronización local, puede conectar Infrastructure Composer IDE a su máquina local para acelerar el desarrollo. Para obtener más información, consulte Conecte la consola de Infrastructure Composer con su consola local IDE.
-
Con la sincronización local, puede utilizar la interfaz de línea de AWS Serverless Application Model comandos (AWS SAM CLI) de su máquina local para probar e implementar la aplicación. Para obtener más información, consulte Implemente su aplicación sin servidor Infrastructure Composer en la nube AWS.
Pasos a seguir a continuación
Ahora está listo para crear sus propias aplicaciones con Infrastructure Composer. Para obtener información detallada sobre el uso de Infrastructure Composer, consulteCómo componer en AWS Infrastructure Composer. Cuando esté listo para implementar la aplicación, consulteImplemente su aplicación sin servidor Infrastructure Composer en la nube AWS.