Les traductions sont fournies par des outils de traduction automatique. En cas de conflit entre le contenu d'une traduction et celui de la version originale en anglais, la version anglaise prévaudra.
Règles relatives aux ports de configuration réseau
Assurez-vous de respecter les configurations réseau suivantes :
-
Connectivité configurée entre l'Amazon sur VPC lequel vous souhaitez créer l'instance de base de données RDS personnalisée pour le SQL serveur et votre Active Directory autogéré ou AWS Managed Microsoft AD. Pour un Active Directory autogéré, configurez la connectivité à l'aide de AWS Direct Connect AWS VPN, de VPC peering ou de AWS Transit Gateway. Pour configurer AWS Managed Microsoft AD la connectivité à l'aide du VPC peering.
-
Assurez-vous que le groupe de sécurité et le VPC réseau du ou ACLs des sous-réseaux sur lesquels vous créez votre instance de base de données RDS Custom for SQL Server autorisent le trafic sur les ports et dans les directions indiquées dans le schéma suivant.
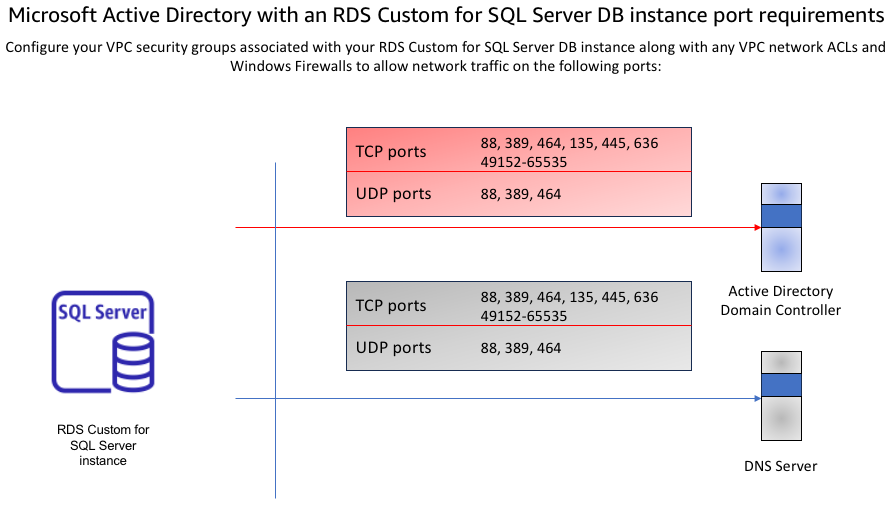
Le tableau suivant identifie le rôle de chaque port.
Protocole Ports Rôle TCP/UDP 53 Système de noms de domaine (DNS) TCP/UDP 88 Authentification Kerberos TCP/UDP 464 Changement/définition de mot de passe TCP/UDP 389 Protocole léger d'accès aux annuaires (LDAP) TCP 135 Environnement informatique distribué/Endpoint Mapper (DCE/EPMAP) TCP 445 Partage de SMB fichiers avec les services d'annuaire TCP 636 Protocole léger d'accès aux répertoires viaTLS/SSL(LDAPS) TCP 49152 - 65535 Ports éphémères pour RPC En général, les DNS serveurs de domaine sont situés dans les contrôleurs de domaine AD. Il n'est pas nécessaire de configurer le jeu d'VPCDHCPoptions pour utiliser cette fonctionnalité. Pour plus d'informations, consultez les ensembles d'DHCPoptions dans le guide de VPC l'utilisateur Amazon.
Important
Si vous utilisez le VPC réseauACLs, vous devez également autoriser le trafic sortant sur les ports dynamiques (49152-65535) depuis votre RDS instance de base de données Custom for Server. SQL Assurez-vous que ces règles de trafic sont également reflétées sur les pare-feux qui s'appliquent à chacun des contrôleurs de domaine AD, aux DNS serveurs et aux instances de base de données RDS Custom for SQL Server.
Alors que les groupes de VPC sécurité exigent que les ports soient ouverts uniquement dans le sens où le trafic réseau est initié, la plupart des pare-feux et VPC réseaux Windows ACLs exigent que les ports soient ouverts dans les deux sens.