aws-constructs-factories

| Language | Package |
|---|---|
 Python
Python
|
aws_solutions_constructs.aws_constructs_factories
|
 Typescript
Typescript
|
@aws-solutions-constructs/aws-constructs-factories
|
 Java
Java
|
software.amazon.awsconstructs.services.constructsfactories
|
Overview
This AWS Solutions Construct exposes the same code used to create our underlying resources as factories, so clients can create individual resources that are well-architected. There are factories to create:
Amazon S3 buckets - Create a well architected S3 bucket (e.g. - includes an access logging bucket) AWS Step Functions state machines - Create a well architected Step Functions state machine and log group (e.g. log group has /aws/vendedlogs/ name prefix to avoid resource policy issues)
S3 Buckets
Create fully well-architected S3 buckets with as little as one function call. Here is a minimal deployable pattern definition:
S3BucketFactory Function Signature
s3BucketFactory(id: string, props: S3BucketFactoryProps): S3BucketFactoryResponse
S3BucketFactoryProps
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| bucketProps? |
s3.BucketProps
|
Optional user provided props to override the default props for the S3 Bucket. |
| logS3AccessLogs? |
boolean
|
Whether to turn on Access Logging for the S3 bucket. Creates an S3 bucket with associated storage costs for the logs. Enabling Access Logging is a best practice. default - true |
| loggingBucketProps? |
s3.BucketProps
|
Optional user provided props to override the default props for the S3 Logging Bucket. |
S3BucketFactoryResponse
Default settings
Out of the box implementation of the Construct without any override will set the following defaults:
-
An S3 Content Bucket
-
AWS managed Server Side Encryption (AES256)
-
Lifecycle rule to transition objects to Glacier storage class in 90 days
-
Access Logging enabled
-
All Public access blocked
-
Versioning enabled
-
UpdateReplacePolicy is delete
-
Deletion policy is delete
-
Bucket policy requiring SecureTransport
-
-
An S3 Bucket for Access Logs
-
AWS managed Server Side Encryption (AES256)
-
All public access blocked
-
Versioning enabled
-
UpdateReplacePolicy is delete
-
Deletion policy is delete
-
Bucket policy requiring SecureTransport
-
Bucket policy granting PutObject privileges to the S3 logging service, from the content bucket in the content bucket account.
-
cfn_nag suppression of access logging finding (not logging access to the access log bucket)
-
Architecture

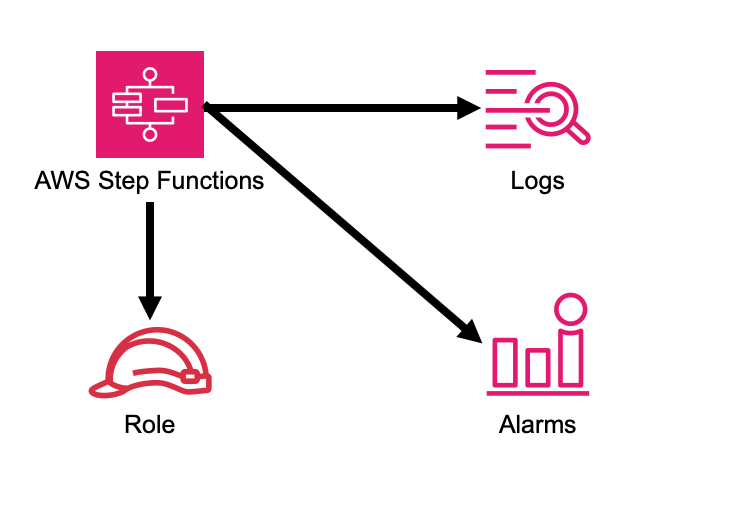
Step Functions State Machines
Create fully well-architected Step Functions state machine with log group. The log group name includes the vendedlogs prefix. Here but is unique to the stack, avoiding naming collions between instances. is a minimal deployable pattern definition:
stateMachineFactory Function Signature
stateMachineFactory(id: string, props: StateMachineFactoryProps): StateMachineFactoryResponse
StateMachineFactoryProps
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| stateMachineProps |
sfn.StateMachineProps
|
The CDK properties that define the state machine. This property is required and must include a definitionBody or definition (definition is deprecated) |
| logGroup? |
[]logs.LogGroup](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cdk/api/v2/docs/aws-cdk-lib.aws_logs.LogGroup.html)
|
An existing LogGroup to which the new state machine will write log entries. Default: none, the construct will create a new log group. |
| createCloudWatchAlarms? | boolean | Whether to create recommended CloudWatch alarms for the State Machine. Default: the alarms are created |
| cloudWatchAlarmsPrefix? | string | Creating multiple State Machines with one Factories construct will result in name collisions as the cloudwatch alarms originally had fixed resource ids. This value was added to avoid collisions while not making changes that would be destructive for existing stacks. Unless you are creating multiple State Machines using factories you can ignore it |
StateMachineFactoryResponse
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| stateMachineProps |
sfn.StateMachineProps
|
|
| logGroup |
[]logs.LogGroupProps](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cdk/api/v2/docs/aws-cdk-lib.aws_logs.LogGroupProps.html)
|
|
| cloudwatchAlarms? |
cloudwatch.Alarm[]
|
The alarms created by the factory (ExecutionFailed, ExecutionThrottled, ExecutionAborted) |
Default settings
Out of the box implementation of the Construct without any override will set the following defaults:
-
An AWS Step Functions State Machine
-
Configured to log to the new log group at LogLevel.ERROR
-
-
Amazon CloudWatch Logs Log Group
-
Log name is prefaced with /aws/vendedlogs/ to avoid resource policy issues. The Log Group name is still created to be unique to the stack to avoid name collisions.
-
-
CloudWatch alarms for:
-
1 or more failed executions
-
1 or more executions being throttled
-
1 or more executions being aborted
-
Architecture
SQS Queues
Create SQS queues complete with DLQs and KMS CMKs with one function call. Here is a minimal deployable pattern definition:
SqsQueueFactory Function Signature
SqsQueueFactory(id: string, props: SqsQueueFactoryProps): SqsQueueFactoryResponse
SqsQueueFactoryProps
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| queueProps? | sqs.QueueProps | Optional user provided props to override the default props for the primary queue. |
| enableEncryptionWithCustomerManagedKey? | boolean | If no key is provided, this flag determines whether the queue is encrypted with a new CMK or an AWS managed key. This flag is ignored if any of the following are defined: queueProps.encryptionMasterKey, encryptionKey or encryptionKeyProps. default - False if queueProps.encryptionMasterKey, encryptionKey, and encryptionKeyProps are all undefined. |
| encryptionKey? | kms.Key | An optional, imported encryption key to encrypt the SQS Queue with. Default - none |
| encryptionKeyProps? | kms.KeyProps | Optional user provided properties to override the default properties for the KMS encryption key used to encrypt the SQS Queue with. @default - None |
| deployDeadLetterQueue? | boolean | Whether to deploy a secondary queue to be used as a dead letter queue. |
| deadLetterQueueProps? | sqs.QueueProps | Optional user provided properties for the dead letter queue |
| maxReceiveCount? | number |
The number of times a message can be unsuccessfully
dequeued before being moved to the dead letter queue.
default -
code |
SqsQueueFactoryResponse
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| queue | sqs.Queue | The queue created by the factory. |
| key | kms.IKey | The key used to encrypt the queue, if the queue was configured to use a CMK |
| deadLetterQueue? | sqs.DeadLetterQueue | The dead letter queue associated with the queue created by the factory |
Default settings
Out of the box implementation of the Construct without any override will set the following defaults:
-
An SQS queue
-
Encrypted by default with KMS managed key by default, can be KMS CMK if flag is set
-
Only queue owner can perform operations by default (your IAM policies can override)
-
Enforced encryption for data in transit
-
DLQ configured
-
-
An SQS dead letter queue
-
Receives messages not processable in maxReceiveCount attempts
-
Encrypted with KMS managed key
-
Enforced encryption for data in transit
-
Architecture

GitHub
| To view the code for this pattern, create/view issues and pull requests, and more: | |
|---|---|

|
@aws-solutions-constructs/aws-constructs-factories |