Set up and customize your Drupal website on Lightsail
Here are a few steps you should take to get started after your Drupal instance is up and running on Amazon Lightsail:
Contents
-
Step 2: Get the default application password to access the Drupal administration dashboard
-
Step 4: Sign in to the administration dashboard of your Drupal website
-
Step 5: Route traffic for your registered domain name to your Drupal website
-
Step 7: Read the Drupal documentation and continue configuring your website
Step 1: Read the Bitnami documentation
Read the Bitnami documentation to learn how to configure your Drupal application. For
more information, see the Drupal
Packaged By Bitnami For AWS Cloud
Step 2: Get the default application password to access the Drupal administration dashboard
Complete the following procedure to get the default application password required to access the administration dashboard for your Drupal website. For more information, see Getting the application user name and password for your Bitnami instance in Amazon Lightsail.
-
On your instance management page, under the Connect tab, choose Connect using SSH.

-
After you're connected, enter the following command to get the application password:
cat $HOME/bitnami_application_passwordYou should see a response similar to the following example, which contains the default application password:

Step 3: Attach a static IP address to your instance
The public IP address assigned to your instance when you first create it will change
every time you stop and start your instance. You should create and attach a static IP
address to your instance to ensure its public IP address doesn't change. Later, when you
use a registered domain name, such as example.com, with your instance, you
don’t have to update your domain’s DNS records every time you stop and start your
instance. You can attach one static IP to an instance.
On the instance management page, under the Networking tab, choose Create a static IP or Attach static IP (if you previously created a static IP that you can attach to your instance), then follow the instructions on the page. For more information, see Create a static IP and attach it to an instance.

Step 4: Sign in to the administration dashboard of your Drupal website
Now that you have the default user password, navigate to your Drupal website's home page, and sign in to the administration dashboard. After you’re signed in, you can start customizing your website and making administrative changes. For more information about what you can do in Drupal, see the Step 7: Read the Drupal documentation and continue configuring your website section later in this guide.
-
On your instance management page, under the Connect tab, make note of the public IP address of your instance. The public IP address is also displayed in the header section of your instance management page.

-
Browse to the public IP address of your instance, for example by going to
http://203.0.113.0.The home page of your Drupal website should appear.
-
Choose Manage in the bottom right corner of your Drupal website home page.
If the Manage banner is not shown, you can reach the sign in page by browsing to
http://. Replace<PublicIP>/user/login<PublicIP> -
Sign in using the default user name (
user) and the default password retrieved earlier in this guide.The Drupal administration dashboard appears.

Step 5: Route traffic for your registered domain name to your Drupal website
To route traffic for your registered domain name, such as example.com, to
your Drupal website, you add a record to the domain name system (DNS) of your domain.
DNS records are typically managed and hosted at the registrar where you registered your
domain. However, we recommend that you transfer management of your domain's DNS records
to Lightsail so that you can administer it using the Lightsail console.
On the Lightsail console home page, under the Domains & DNS tab, choose Create DNS zone, then follow the instructions on the page. For more information, see Creating a DNS zone to manage your domain’s DNS records in Lightsail.
If you browse to the domain name that you configured for your instance, you should be redirected to the home page of your Drupal website. Next, you should generate and configure an SSL/TLS certificate to enable HTTPS connections for your Drupal website. For more information, continue to the next Step 6: Configure HTTPS for your Drupal website section of this guide.
Step 6: Configure HTTPS for your Drupal website
Complete the following procedure to configure HTTPS on your Drupal website. These
steps show you how to use the Bitnami HTTPS Configuration Tool
(bncert-tool), which is a command line tool for requesting Let's Encrypt
SSL/TLS certificates. For more information see Learn About The Bitnami
HTTPS Configuration Tool
Important
Before starting with this procedure, make sure that you configured your domain to route traffic to your Drupal instance. Otherwise, the SSL/TLS certificate validation process will fail.
-
On your instance management page, under the Connect tab, choose Connect using SSH.

-
After you're connected, enter the following command to confirm the bncert tool is installed on your instance.
sudo /opt/bitnami/bncert-toolYou should see one of the following responses:
-
If you see command not found in the response, then the bncert tool is not installed on your instance. Continue to the next step in this procedure to install the bncert tool on your instance.
-
If you see Welcome to the Bitnami HTTPS configuration tool in the response, then the bncert tool is installed on your instance. Continue to the step 8 of this procedure.
-
If the bncert tool has been installed on your instance for a while, then you might see a message indicating that an updated version of the tool is available. Choose to download it, and then enter the
sudo /opt/bitnami/bncert-toolcommand to run the bncert tool again. Continue to the step 8 of this procedure.
-
-
Enter the following command to download the bncert run file to your instance.
wget -O bncert-linux-x64.run https://downloads.bitnami.com/files/bncert/latest/bncert-linux-x64.run -
Enter the following command to create a directory for the bncert tool run file on your instance.
sudo mkdir /opt/bitnami/bncert -
Enter the following command to make the bncert run a file that can be executed as a program.
sudo chmod +x /opt/bitnami/bncert/bncert-linux-x64.run -
Enter the following command to create a symbolic link that runs the bncert tool when you enter the sudo /opt/bitnami/bncert-tool command.
sudo ln -s /opt/bitnami/bncert/bncert-linux-x64.run /opt/bitnami/bncert-toolYou are now done installing the bncert tool on your instance.
-
Enter the following command to run the bncert tool.
sudo /opt/bitnami/bncert-tool -
Enter your primary domain name and alternate domain names separated by a space as shown in the following example.
If your domain is not configured to route traffic to the public IP address of your instance, the
bncerttool will ask you to make that configuration before continuing. Your domain must be routing traffic to the public IP address of the instance from which you are using thebncerttool to enable HTTPS on the instance. This confirms that you own the domain, and serves as the validation for your certificate.
-
The
bncerttool will ask you how you want your website's redirection to be configured. These are the options available:-
Enable HTTP to HTTPS redirection - Specifies whether users who browse to the HTTP version of your website (i.e.,
http:/example.com) are automatically redirected to the HTTPS version (i.e.,https://example.com). We recommend enabling this option because it forces all visitors to use the encrypted connection. TypeYand press Enter to enable it. -
Enable non-www to www redirection - Specifies whether users who browse to the apex of your domain (i.e.,
https://example.com) are automatically redirected to your domain'swwwsubdomain (i.e.,https://www.example.com). We recommend enabling this option. However, you may want to disable it and enable the alternate option (enablewwwto non-wwwredirection) if you have specified the apex of your domain as your preferred website address in search engine tools like Google's webmaster tools, or if your apex points directly to your IP and yourwwwsubdomain references your apex via a CNAME record. TypeYand press Enter to enable it. -
Enable www to non-www redirection - Specifies whether users who browse to your domain's
wwwsubdomain (i.e.,https://www.example.com) are automatically redirected to the apex of your domain (i.e.,https://example.com). We recommend disabling this, if you enabled non-wwwredirection towww. TypeNand press Enter to disable it.
Your selections should look like the following example.

-
-
The changes that are going to be made are listed. Type
Yand press Enter to confirm and continue.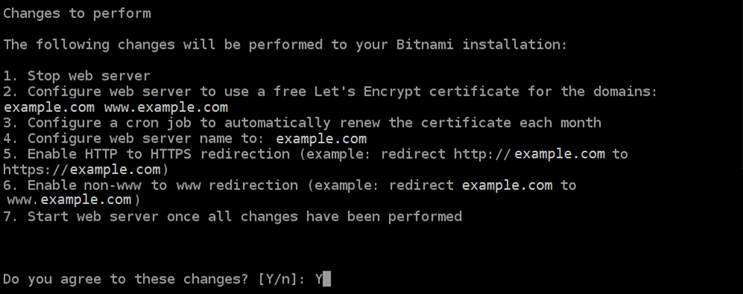
-
Enter your email address to associate with your Let's Encrypt certificate and press Enter.

-
Review the Let's Encrypt Subscriber Agreement. Type
Yand press Enter to accept the agreement and continue.
The actions are performed to enable HTTPS on your instance, including requesting the certificate and configuring the redirections you specified.

Your certificate is successfully issued and validated, and the redirections are successfully configured on your instance if you see a message similar to the following example.

The
bncerttool will perform an automatic renewal of your certificate every 80 days before it expires. Repeat the above steps if you wish to use additional domains and subdomains with your instance, and you want to enable HTTPS for those domains.You are now done enabling HTTPS on your Drupal instance. Next time you browse to your Drupal website using the domain you configured, you should see that it redirects to the HTTPS connection.
Step 7: Read the Drupal documentation and continue configuring your website
Read the Drupal documentation to learn how to administer and customize your website.
For more information, see the Drupal
Documentation
Step 8: Create a snapshot of your instance
After you configure your Drupal website the way you want it, create periodic snapshots of your instance to back it up. You can create snapshots manually, or enable automatic snapshots to have Lightsail create daily snapshots for you. If something goes wrong with your instance, you can create a new replacement instance using the snapshot. For more information, see Snapshots.
On the instance management page, under the Snapshot tab, choose Create a snapshot or choose to enable automatic snapshots.

For more information, see Creating a snapshot of your Linux or Unix instance in Amazon Lightsail or Enabling or disabling automatic snapshots for instances or disks in Amazon Lightsail.