Observability in Amazon OpenSearch Service
The default installation of OpenSearch Dashboards for Amazon OpenSearch Service includes the Observability plugin, which you can use to visualize data-driven events using Piped Processing Language (PPL) in order to explore, discover, and query data stored in OpenSearch. The plugin requires OpenSearch 1.2 or later.
The Observability plugin provides a unified experience for collecting and monitoring metrics, logs, and traces from common data sources. Data collection and monitoring in one place enables full-stack, end-to-end observability of your entire infrastructure.
Note
This documentation provides a brief overview of Observability in OpenSearch Service. For
comprehensive documentation of the Observability plugin, including permissions, see
Observability
Everyone's process for exploring data is different. If you’re new to exploring data and creating visualizations, we recommend trying a workflow like the following.
Explore your data with event analytics
To start, let's say that you're collecting flight data in your OpenSearch Service domain and you want to find out which airline had the most flights arriving in Pittsburgh International Airport last month. You write the following PPL query:
source=opensearch_dashboards_sample_data_flights | stats count() by Dest, Carrier | where Dest = "Pittsburgh International Airport"
This query pulls data from the index named
opensearch_dashboards_sample_data_flights. It then uses the
stats command to get a total count of flights and groups it according
to destination airport and carrier. Finally, it uses the where clause to
filter the results to flights arriving in Pittsburgh International Airport.
Here's what the data looks like when displayed over the last month:

You can choose the PPL button in the query editor to get usage information and examples for each PPL command:
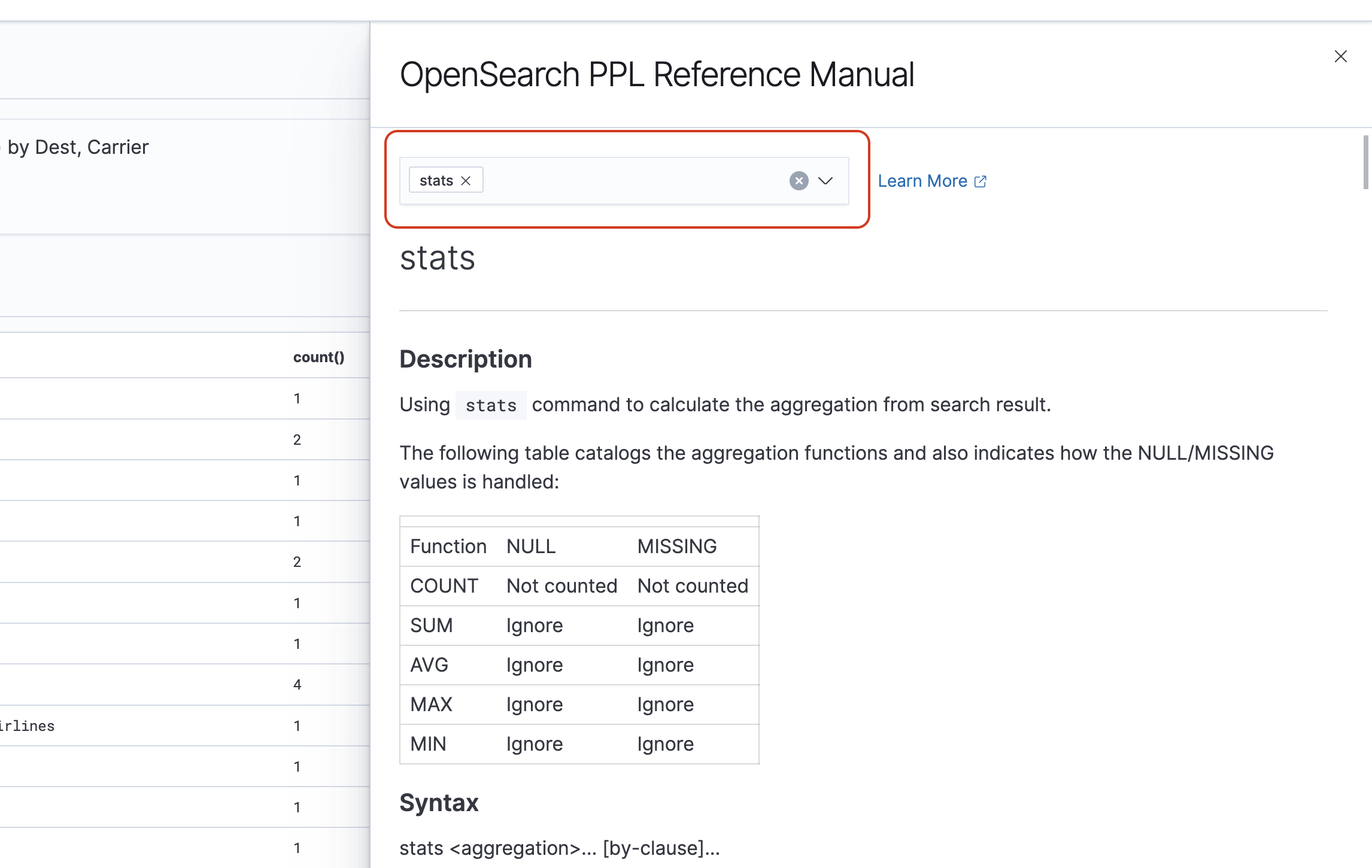
Let's look at a more complex example, which queries for information about flight delays:
source=opensearch_dashboards_sample_data_flights | where FlightDelayMin > 0 | stats sum(FlightDelayMin) as minimum_delay, count() as total_delayed by Carrier, Dest | eval avg_delay=minimum_delay / total_delayed | sort - avg_delay
Each command in the query impacts the final output:
-
source=opensearch_dashboards_sample_data_flights- pulls data from the same index as the previous example -
where FlightDelayMin > 0- filters the data to flights that were delayed -
stats sum(FlightDelayMin) as minimum_delay, count() as total_delayed by Carrier- for each carrier, gets the total minimum delay time and the total count of delayed flights -
eval avg_delay=minimum_delay / total_delayed- calculates the average delay time for each carrier by dividing the minimum delay time by the total number of delayed flights -
sort - avg_delay- sorts the results by average delay in descending order
With this query, you can determine that OpenSearch Dashboards Airlines has, on average, fewer delays.

You can find more sample PPL queries under Queries and Visualizations on the Event analytics page.
Create visualizations
Once you correctly query the data that you're interested in, you can save those queries as visualizations:

Then add those visualizations to operational panels
Dive deeper with Trace Analytics
Trace Analytics provides a way to visualize the flow of events in your OpenSearch data to identify and fix performance problems in distributed applications.
