VPC-to-on-premises traffic inspection
The following diagram shows the traffic flow if an Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instance in
Workload spoke VPC1 wants to communicate with an on-premises server.
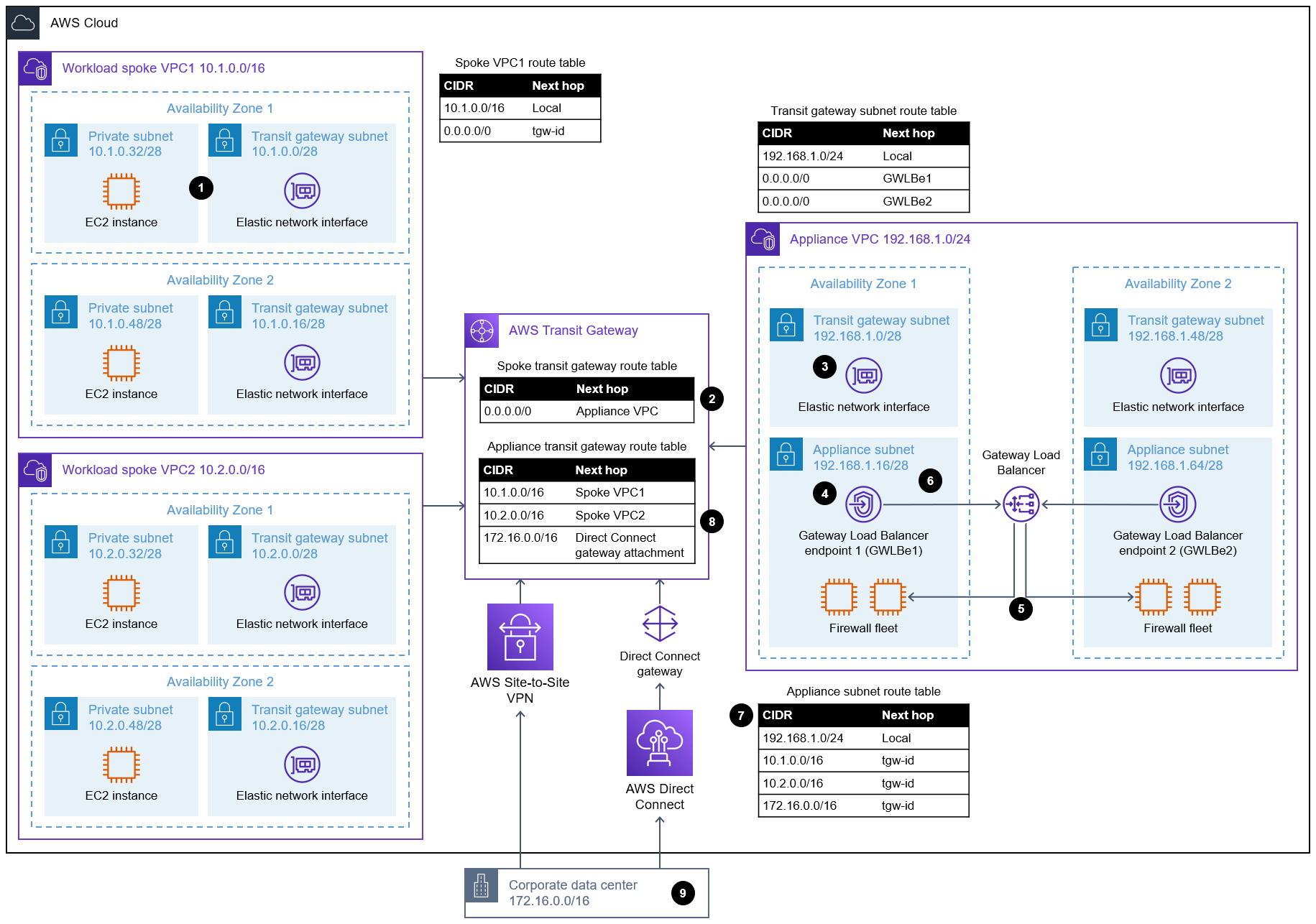
The diagram shows the following workflow:
-
A packet from an EC2 instance in
Workload spoke VPC 1in Availability Zone 1 arrives at the Transit Gateway elastic network interface in Availability Zone 1 in the transit gateway subnet forWorkload spoke VPC 1. Based on the VPC route table associated to the Transit Gateway elastic network interface subnet, the packet lands on the transit gateway. -
In the transit gateway, the
Spoke transit gateway route tableis associated with theWorkload spoke VPC 1attachment and this determines the next hop. -
The next hop is the appliance VPC. Based on 4-tuple hash for the life of a flow, the Transit Gateway determines which Transit Gateway elastic network interface to send the traffic to.
-
If Transit Gateway chooses the Transit Gateway elastic network interface in Availability Zone 1, it checks the VPC route table associated to the Transit Gateway elastic network interface subnet in Availability Zone 1 in the appliance VPC. Transit Gateway sends the traffic to the Gateway Load Balancer endpoint in Availability Zone 1.
-
The Gateway Load Balancer endpoint is logically connected to the Gateway Load Balancer through AWS PrivateLink that then forwards the traffic to the firewall appliance for traffic inspection. The Gateway Load Balancer creates a GENEVE tunnel between the Gateway Load Balancer and the firewall appliances.
-
If the traffic is allowed, the packet is sent back to the Gateway Load Balancer and the Gateway Load Balancer endpoint in Availability Zone 1.
-
At the Gateway Load Balancer endpoint, the packet checks the VPC route table and the next hop is the transit gateway.
-
The packet arrives at the transit gateway and performs a lookup on the appliance transit gateway route table that is associated to the appliance VPC attachment for the next hop to the
172.16.0.0/16network. -
The packet is then sent to the destination server on premises. The response traffic follows the same path but in reverse.