Migrate SAP HANA to AWS using SAP HSR with the same hostname
Created by Pradeep Puliyampatta (AWS)
Summary
SAP HANA migrations to Amazon Web Services (AWS) can be performed using multiple options, including backup and restore, export and import, and SAP HANA System Replication (HSR). The selection of a particular option depends on the network connectivity between source and target SAP HANA databases, the size of the source database, downtime considerations, and other factors.
The SAP HSR option for migrating SAP HANA workloads to AWS works well when there is a stable network between the source and target systems and the entire database (SAP HANA DB replication snapshot) can be completely replicated within 1 day, as stipulated by SAP for network throughput requirements for SAP HSR. The downtime requirements with this approach are limited to performing the takeover on the target AWS environment, SAP HANA DB backup, and post-migration tasks.
SAP HSR supports the use of different hostnames (hostnames mapped to different IP addresses) for replication traffic between the primary, or source, and secondary, or target, systems. You can do this by defining those specific sets of hostnames under the [system_replication_hostname_resolution] section in global.ini. In this section, all hosts of the primary and the secondary sites must be defined on each host. For detailed configuration steps, see the SAP documentation
One key takeaway from this setup is that the hostnames in the primary system must be different from the hostnames in the secondary system. Otherwise, the following errors can be observed.
"each site must have a unique set of logical hostnames""remoteHost does not match with any host of the source site. All hosts of source and target site must be able to resolve all hostnames of both sites correctly"
However, the number of post-migration steps can be reduced by using the same SAP HANA DB hostname on the target AWS environment.
This pattern provides a workaround for using the same hostname on source and target environments when using the SAP HSR option. With this pattern, you can use the SAP HANA Hostname Rename option. You assign a temporary hostname to the target SAP HANA DB to facilitate hostname uniqueness for SAP HSR. After the migration completes the takeover milestone on the target SAP HANA environment, you can revert the target system hostname back to the hostname of the source system.
Prerequisites and limitations
Prerequisites
An active AWS account.
A virtual private cloud (VPC) with a virtual private network (VPN) endpoint or a router.
AWS Client VPN or AWS Direct Connect configured to transfer files from the source to the target.
SAP HANA databases in both the source and the target environment. The target SAP HANA DB patch level should be equal to or higher than the source SAP HANA DB patch level, within the same SAP HANA Platform edition. For example, replication cannot be set up between HANA 1.0 and HANA 2.0 systems. For more information, see question 15 in SAP Note: 1999880 – FAQ: SAP HANA System Replication.
SAP application servers in the target environment.
Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) volumes in the target environment.
Limitations
The following list of SAP documents covers known issues that are related to this workaround, including constraints regarding SAP HANA dynamic tiering and scale-out migrations:
2956397 – Renaming of SAP HANA Database System failed
2222694 – When trying to rename the HANA system, the following error appears "Source files are not owned by the original sidadm user (uid = xxxx)"
2607227 – hdblcm: register_rename_system: Renaming SAP HANA instance failed
2630562 – HANA Hostname Rename failed and HANA does not start up
2935639 – sr_register is not using the hostname that is specified under system_replication_hostname_resolution in the global.ini section
2710211 – Error: source system and target system have overlapping logical hostnames
2693441 – Failed to rename an SAP HANA System due to error
2519672 – HANA Primary and Secondary has different system PKI SSFS data and key or unable to check
2457129 – SAP HANA System Host Rename is not Permitted when Dynamic Tiering is Part of Landscape
2473002 – Using HANA System Replication to migrate scale out system (There are no restrictions provided by SAP in using this hostname rename approach for scale-out SAP HANA systems. However, the procedure must be repeated on each individual host. Other scale-out migration limitations also apply to this approach.)
Product versions
This solution applies to SAP HANA DB platform edition 1.0 and 2.0.
Architecture
Source setup
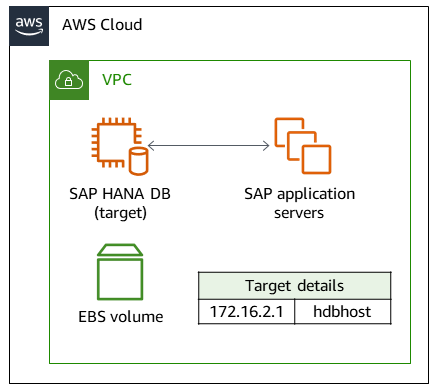
An SAP HANA database is installed on the source environment. All the SAP application server connections and DB interfaces use the same hostname for client connections. The following diagram shows the example source hostname hdbhost and its corresponding IP address.

Target setup
The AWS Cloud target environment uses the same hostname to run an SAP HANA database. The target environment on AWS includes the following:
SAP HANA database
SAP application servers
EBS volumes
Intermediate configuration
In the following diagram, the hostname on the AWS target environment is temporarily renamed as temp-host so that the hostnames on the source and target are unique. After the migration completes the takeover milestone on the target environment, the target system virtual hostname is renamed using the original name, hdbhost.
The intermediate configuration includes one of the following options:
AWS Client VPN with a Client VPN endpoint
AWS Direct Connect connecting to a router

SAP application servers on the AWS target environment can be installed either before replication setup or after the takeover. However, installing the application servers before replication setup can help with reduction of downtime during installation, configuration of high availability, and backups.
Tools
AWS services
AWS Client VPN is a managed client-based VPN service that enables you to securely access AWS resources and resources in your on-premises network.
AWS Direct Connect links your internal network to an AWS Direct Connect location over a standard Ethernet fiber-optic cable. With this connection, you can create virtual interfaces directly to public AWS services, bypassing internet service providers in your network path.
Amazon Elastic Block Store (Amazon EBS) provides block level storage volumes for use with Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances. EBS volumes behave like raw, unformatted block devices. You can mount these volumes as devices on your instances.
Other tools
SAP application servers
– SAP application servers provide programmers with a way to express business logic. The SAP application server performs the data processing based on the business logic. The actual data is stored in a database, which is a separate component. SAP HANA cockpit
and SAP HANA Studio – Both SAP HANA cockpit and SAP HANA Studio provide an administrative interface to the SAP HANA database. In SAP HANA Studio, the SAP HANA Administration console is the system view that provides relevant content for SAP HANA database administration. SAP HANA System Replication
– SAP HANA System Replication (SAP HSR) is the standard procedure provided by SAP for replicating SAP HANA databases. The required executables for SAP HSR are part of the SAP HANA server kernel itself.
Epics
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Install and configure the SAP HANA databases. | In the source and target environments, ensure that the SAP HANA DB is installed and configured according to SAP HANA on best practices. For more information, see SAP HANA on AWS. | SAP Basis administration |
Map the IP address. | In the target environment, ensure that the temporary hostname is assigned to an internal IP address.
| AWS administration |
Resolve target hostnames. | On the secondary SAP HANA DB, confirm that both hostnames ( | Linux administration |
Back up the source and target SAP HANA databases. | Use SAP HANA Studio or the SAP HANA cockpit to perform backups on the SAP HANA databases. | SAP Basis administration |
Exchange system PKI certificates. | (Applies only to SAP HANA 2.0 and later) Exchange certificates in the system public key infrastructure (PKI) secure store in the file system (SSFS) store between the primary and secondary databases. For more information, see SAP Note 2369981 – Required configuration steps for authentication with SAP HANA System Replication. | SAP Basis administration |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Stop target client connections. | In the target environment, shut down the SAP application servers and other client connections. | SAP Basis administration |
Rename the target SAP HANA DB to the temporary hostname. |
The SAP HANA DB stop and start will be controlled by | SAP Basis administration |
Assign replication networks. | In the | SAP Basis administration |
Enable replication on primary. | To enable replication on the source SAP HANA DB, run the following command.
| SAP Basis administration |
Register the target SAP HANA DB as a secondary system. | To register the target SAP HANA DB as a secondary system to source for SAP HSR, choose async replication.
Alternatively, you can choose the | SAP Basis administration |
Validate synchronization. | On the source SAP HANA DB, verify that all the logs are applied on the target system (because it is async replication). To verify the replication, on the source, run the following commands.
| SAP Basis administration |
Shut down the source SAP application and SAP HANA DB. | During the migration cutover, perform a shutdown of the source system (the SAP application and SAP HANA database. | SAP Basis administration |
Perform a takeover at the target. | To perform a takeover at the target on AWS, run the command | SAP Basis administration |
On the target SAP HANA DB, turn off replication. | To clear the replication metadata, stop replication on the target system by running the command NoteThis is in accordance with SAP Note 2693441 – Failed to rename an SAP HANA System due to error. | SAP Basis administration |
Back up the target SAP HANA DB. | After the takeover is successful, we recommend performing a full SAP HANA DB backup. | SAP Basis administration |
| Task | Description | Skills required |
|---|---|---|
Revert the target SAP HANA DB hostname to the original. |
You can validate other options as needed. However, be sure that you don’t mix up the host rename with a SID change (SAP Note 2598814 – hdblcm: SID rename fails). | SAP Basis administration |
Adjust hdbuserstore. | Adapt the To validate this step, run the command | SAP Basis administration |
Start up client connections. | In the target environment, start up the SAP application servers and other client connections. | SAP Basis administration |
Related resources
SAP references
SAP documentation references are frequently updated by SAP. To stay up to date, see SAP Note 2407186 – How-To Guides & Whitepapers For SAP HANA High Availability.
Additional SAP notes
2550327 – How-To Rename an SAP HANA System
1999880 – FAQ: SAP HANA System Replication
2078425 – Troubleshooting note for SAP HANA platform lifecycle management tool hdblcm
2592227 – FQDN suffix change in HANA systems
2048681 – Performing SAP HANA platform lifecycle management administration tasks on multiple-host systems without SSH or root credentials
SAP documents
AWS references
Additional information
The changes performed by hdblcm as part of the hostname rename activity are consolidated in the following verbose log.
