Creating a resource data sync for Inventory
This topic describes how to set up and configure resource data sync for AWS Systems Manager Inventory. For information about resource data sync for Systems Manager Explorer, see Setting up Systems Manager Explorer to display data from multiple accounts and Regions.
About resource data sync
You can use Systems Manager resource data sync to send inventory data collected from all of your managed nodes to a single Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) bucket. Resource data sync then automatically updates the centralized data when new inventory data is collected. With all inventory data stored in a target Amazon S3 bucket, you can use services like Amazon Athena and Amazon Quick Suite to query and analyze the aggregated data.
For example, say that you've configured inventory to collect data about the operating system (OS) and applications running on a fleet of 150 managed nodes. Some of these nodes are located in an on-premises data center, and others are running in Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) across multiple AWS Regions. If you have not configured resource data sync, you either need to manually gather the collected inventory data for each managed node, or you have to create scripts to gather this information. You would then need to port the data into an application so that you can run queries and analyze it.
With resource data sync, you perform a one-time operation that synchronizes all inventory data from all of your managed nodes. After the sync is successfully created, Systems Manager creates a baseline of all inventory data and saves it in the target Amazon S3 bucket. When new inventory data is collected, Systems Manager automatically updates the data in the Amazon S3 bucket. You can then quickly and cost-effectively port the data to Amazon Athena and Amazon Quick Suite.
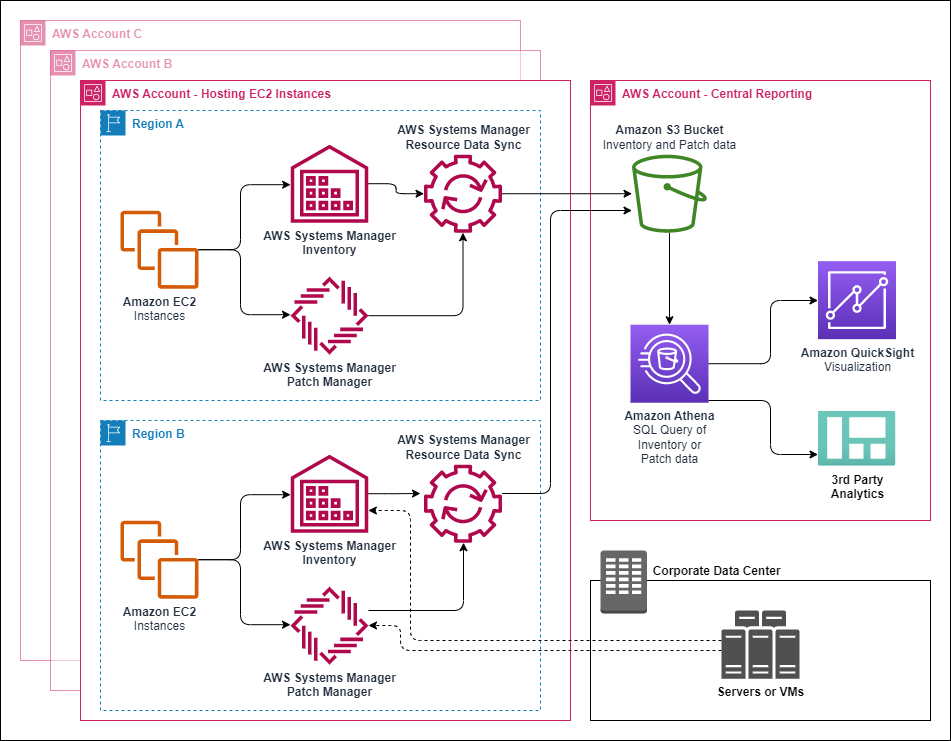
Diagram 1 shows how resource data sync aggregates inventory data from Amazon EC2 and other machine types in a hybrid and multicloud environment to a target Amazon S3 bucket. This diagram also shows how resource data sync works with multiple AWS accounts and AWS Regions.
Diagram 1: Resource data sync with multiple AWS accounts and AWS Regions
If you delete a managed node, resource data sync preserves the inventory file
for the deleted node. For running nodes, however, resource data sync
automatically overwrites old inventory files when new files are created and
written to the Amazon S3 bucket. If you want to track inventory changes over time,
you can use the AWS Config service to track the
SSM:ManagedInstanceInventory resource type. For more
information, see Getting Started
with AWS Config.
Use the procedures in this section to create a resource data sync for Inventory by
using the Amazon S3 and AWS Systems Manager consoles. You can also use AWS CloudFormation to create or
delete a resource data sync. To use AWS CloudFormation, add the AWS::SSM::ResourceDataSync resource to your AWS CloudFormation
template. For information, see one of the following documentation resources:
-
AWS CloudFormation resource for resource data sync in AWS Systems Manager
(blog) -
Working with AWS CloudFormation Templates in the AWS CloudFormation User Guide
Note
You can use AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) to encrypt inventory data in the Amazon S3 bucket. For an example of how to create an encrypted sync by using the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) and how to work with the centralized data in Amazon Athena and Amazon Quick Suite, see Walkthrough: Using resource data sync to aggregate inventory data.
Before you begin
Before you create a resource data sync, use the following procedure to create a central Amazon S3 bucket to store aggregated inventory data. The procedure describes how to assign a bucket policy that allows Systems Manager to write inventory data to the bucket from multiple accounts. If you already have an Amazon S3 bucket that you want to use to aggregate inventory data for resource data sync, then you must configure the bucket to use the policy in the following procedure.
Note
Systems Manager Inventory can't add data to a specified Amazon S3 bucket if that bucket is configured to use Object Lock. Verify that the Amazon S3 bucket you create or choose for resource data sync isn't configured to use Amazon S3 Object Lock. For more information, see How Amazon S3 Object Lock works in the Amazon Simple Storage Service User Guide.
To create and configure an Amazon S3 bucket for resource data sync
Open the Amazon S3 console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/s3/
. -
Create a bucket to store your aggregated Inventory data. For more information, see Create a Bucket in the Amazon Simple Storage Service User Guide. Make a note of the bucket name and the AWS Region where you created it.
-
Choose the Permissions tab, and then choose Bucket Policy.
-
Copy and paste the following bucket policy into the policy editor. Replace
amzn-s3-demo-bucketwith the name of the S3 bucket you created. Replaceaccount_ID_numberwith a valid AWS account ID number. -
Save your changes.
Create a resource data sync for Inventory
Use the following procedure to create a resource data sync for Systems Manager Inventory by using the Systems Manager console. For information about how to create a resource data sync by using the AWS CLI, see Using the AWS CLI to configure inventory data collection.
To create a resource data sync
Open the AWS Systems Manager console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/systems-manager/
. In the navigation pane, choose Fleet Manager.
-
In the Account management menu, choose Resource data sync.
-
Choose Create resource data sync.
-
In the Sync name field, enter a name for the sync configuration.
-
In the Bucket name field, enter the name of the Amazon S3 bucket you created using the To create and configure an Amazon S3 bucket for resource data sync procedure.
-
(Optional) In the Bucket prefix field, enter the name of an Amazon S3 bucket prefix (subdirectory).
-
In the Bucket region field, choose This region if the Amazon S3 bucket you created is located in the current AWS Region. If the bucket is located in a different AWS Region, choose Another region, and enter the name of the Region.
Note
If the sync and the target Amazon S3 bucket are located in different regions, you might be subject to data transfer pricing. For more information, see Amazon S3 Pricing
. -
(Optional) In the KMS Key ARN field, type or paste a KMS Key ARN to encrypt inventory data in Amazon S3.
-
Choose Create.
To synchronize inventory data from multiple AWS Regions, you must create a resource data sync in each Region. Repeat this procedure in each AWS Region where you want to collect inventory data and send it to the central Amazon S3 bucket. When you create the sync in each Region, specify the central Amazon S3 bucket in the Bucket name field. Then use the Bucket region option to choose the Region where you created the central Amazon S3 bucket, as shown in the following screen shot. The next time the association runs to collect inventory data, Systems Manager stores the data in the central Amazon S3 bucket.

Creating an inventory resource data sync for accounts defined in AWS Organizations
You can synchronize inventory data from AWS accounts defined in AWS Organizations to a central Amazon S3 bucket. After you complete the following procedures, inventory data is synchronized to individual Amazon S3 key prefixes in the central bucket. Each key prefix represents a different AWS account ID.
Before you begin
Before you begin, verify that you set up and configured AWS accounts in AWS Organizations. For more information, see in the AWS Organizations User Guide.
Also, be aware that you must create the organization-based resource data sync for each AWS Region and AWS account defined in AWS Organizations.
Creating a central Amazon S3 bucket
Use the following procedure to create a central Amazon S3 bucket to store aggregated inventory data. The procedure describes how to assign a bucket policy that allows Systems Manager to write inventory data to the bucket from your AWS Organizations account ID. If you already have an Amazon S3 bucket that you want to use to aggregate inventory data for resource data sync, then you must configure the bucket to use the policy in the following procedure.
To create and configure an Amazon S3 bucket for resource data sync for multiple accounts defined in AWS Organizations
Open the Amazon S3 console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/s3/
. -
Create a bucket to store your aggregated inventory data. For more information, see Create a Bucket in the Amazon Simple Storage Service User Guide. Make a note of the bucket name and the AWS Region where you created it.
-
Choose the Permissions tab, and then choose Bucket Policy.
-
Copy and paste the following bucket policy into the policy editor. Replace
amzn-s3-demo-bucketandorganization-idwith the name of the Amazon S3 bucket you created and a valid AWS Organizations account ID.Optionally, replace
bucket-prefixwith the name of an Amazon S3 prefix (subdirectory). If you didn't create a prefix, removebucket-prefix/ from the ARN in the following policy.
Create an inventory resource data sync for accounts defined in AWS Organizations
The following procedure describes how to use the AWS CLI to create a resource data sync for accounts that are defined in AWS Organizations. You must use the AWS CLI to perform this task. You must also perform this procedure for each AWS Region and AWS account defined in AWS Organizations.
To create a resource data sync for an account defined in AWS Organizations (AWS CLI)
Install and configure the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI), if you haven't already.
For information, see Installing or updating the latest version of the AWS CLI.
-
Run the following command to verify that you don't have any other AWS Organizations-based resource data syncs. You can have multiple standard syncs, including multiple standard syncs and an Organizations-based sync. But, you can only have one Organizations-based resource data sync.
aws ssm list-resource-data-syncIf the command returns other Organizations-based resource data sync, you must delete them or choose not to create a new one.
-
Run the following command to create a resource data sync for an account defined in AWS Organizations. For amzn-s3-demo-bucket, specify the name of the Amazon S3 bucket you created earlier in this topic. If you created a prefix (subdirectory) for your bucket, then specify this information for
prefix-name.aws ssm create-resource-data-sync --sync-namename--s3-destination "BucketName=amzn-s3-demo-bucket,Prefix=prefix-name,SyncFormat=JsonSerDe,Region=AWS Region, for example us-east-2,DestinationDataSharing={DestinationDataSharingType=Organization}" -
Repeat Steps 2 and 3 for every AWS Region and AWS account where you want to synchronize data to the central Amazon S3 bucket.
Managing resource data syncs
Each AWS account can have 5 resource data syncs per AWS Region. You can use the AWS Systems Manager Fleet Manager console to manage your resource data syncs.
To view resource data syncs
Open the AWS Systems Manager console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/systems-manager/
. In the navigation pane, choose Fleet Manager.
-
In the Account management dropdown, choose Resource data syncs.
-
Select a resource data sync from the table, and then choose View details to view information about your resource data sync.
To delete a resource data sync
Open the AWS Systems Manager console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/systems-manager/
. In the navigation pane, choose Fleet Manager.
-
In the Account management dropdown, choose Resource data syncs.
-
Select a resource data sync from the table, and then choose Delete.