本文為英文版的機器翻譯版本,如內容有任何歧義或不一致之處,概以英文版為準。
使用 API Gateway Lambda 授權方
使用 Lambda 授權方 (先前稱為自訂授權方 ) 來控制對您 的存取API。當用戶端提出請求時API,APIGateway 會呼叫您的 Lambda 授權方。Lambda 授權方會將呼叫者身分作為輸入,並傳回IAM政策作為輸出。
使用 Lambda 授權方實作自訂授權方案。您的配置可以使用請求參數來判斷來電者的身分,或使用承載符字符身分驗證策略,例如 OAuth或 SAML。在API閘道RESTAPI主控台中使用 AWS CLI或 建立 Lambda 授權方 AWS SDK。
Lambda 授權方授權工作流程
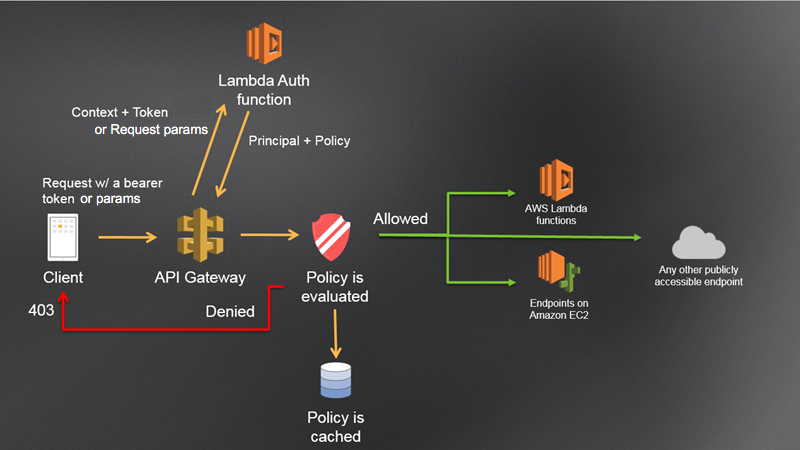
下圖顯示 Lambda 授權方的授權工作流程。
API Gateway Lambda 授權工作流程
-
用戶端在API閘道 上呼叫 方法API,傳遞承載符字符或請求參數。
-
API Gateway 會檢查方法請求是否使用 Lambda 授權方設定。如果是,APIGateway 會呼叫 Lambda 函數。
-
Lambda 函數會驗證呼叫者。該函數可以透過下列方式進行身分驗證:
-
Lambda 函數會傳回IAM政策和主體識別符。如果 Lambda 函數未傳回該資訊,則呼叫會失敗。
-
API Gateway 會評估IAM政策。
-
如果存取遭拒,APIGateway 會傳回適當的HTTP狀態碼,例如 403 ACCESS_DENIED。
-
如果允許存取,APIGateway 會叫用 方法。
如果您啟用授權快取,APIGateway 會快取政策,以便不再叫用 Lambda 授權方函數。
您可以自訂 403 ACCESS_DENIED或401 UNAUTHORIZED閘道回應。如需進一步了解,請參閱 閘道RESTAPIs中的API閘道回應。
選擇 Lambda 授權方的類型
Lambda 授權方有兩種類型:
- 請求參數型 Lambda 授權方 (
REQUEST 授權方)
-
REQUEST 授權方以標頭、查詢字串參數、 stageVariables和 $context變數的組合接收呼叫者身分。您可以使用REQUEST授權方,根據來自多個身分來源的資訊建立精細政策,例如 $context.path和$context.httpMethod內容變數。
如果您開啟REQUEST授權方的授權快取,APIGateway 會驗證請求中是否存在所有指定的身分來源。如果指定的識別來源遺失、無效或空白,APIGateway 會傳回401 UnauthorizedHTTP回應,而不會呼叫 Lambda 授權方函數。定義多個身分來源時,它們都會用來衍生授權方的快取金鑰,並保留順序。您可以使用多個身分來源來定義精細快取金鑰。
如果您變更任何快取金鑰部分,並重新部署您的 API,授權方會捨棄快取的政策文件並產生新的政策文件。
如果您關閉REQUEST授權方的授權快取,APIGateway 會直接將請求傳遞給 Lambda 函數。
- 以權杖為基礎的 Lambda 授權方 (
TOKEN 授權方)
-
TOKEN 授權方會以承載權杖接收呼叫者身分,例如 JSON Web 權杖 (JWT) 或OAuth權杖。
如果您開啟TOKEN授權方的授權快取,權杖來源中指定的標頭名稱會成為快取金鑰。
此外,您可以使用權杖驗證來輸入 RegEx 陳述式。API Gateway 會針對此表達式執行輸入權杖的初始驗證,並在驗證成功後叫用 Lambda 授權方函數。這有助於減少對 的呼叫API。
IdentityValidationExpression 屬性僅支援TOKEN授權方。如需詳細資訊,請參閱x-amazon-apigateway-authorizer 物件。
我們建議您使用REQUEST授權方來控制對 的存取API。與使用REQUEST授權方時單一身分來源相比,您可以在使用TOKEN授權方時API根據多個身分來源控制對 的存取。此外,您可以使用REQUEST授權方的多個身分來源來分隔快取金鑰。
REQUEST 授權方 Lambda 函數範例
下列範例程式碼會建立 Lambda 授權方函數,當用戶端提供的HeaderAuth1標頭、QueryString1查詢參數和階段變數分別StageVar1符合 headerValue1、 queryValue1和 的指定值時stageValue1,允許請求。
- Node.js
// A simple request-based authorizer example to demonstrate how to use request
// parameters to allow or deny a request. In this example, a request is
// authorized if the client-supplied HeaderAuth1 header, QueryString1
// query parameter, and stage variable of StageVar1 all match
// specified values of 'headerValue1', 'queryValue1', and 'stageValue1',
// respectively.
export const handler = function(event, context, callback) {
console.log('Received event:', JSON.stringify(event, null, 2));
// Retrieve request parameters from the Lambda function input:
var headers = event.headers;
var queryStringParameters = event.queryStringParameters;
var pathParameters = event.pathParameters;
var stageVariables = event.stageVariables;
// Parse the input for the parameter values
var tmp = event.methodArn.split(':');
var apiGatewayArnTmp = tmp[5].split('/');
var awsAccountId = tmp[4];
var region = tmp[3];
var restApiId = apiGatewayArnTmp[0];
var stage = apiGatewayArnTmp[1];
var method = apiGatewayArnTmp[2];
var resource = '/'; // root resource
if (apiGatewayArnTmp[3]) {
resource += apiGatewayArnTmp[3];
}
// Perform authorization to return the Allow policy for correct parameters and
// the 'Unauthorized' error, otherwise.
if (headers.HeaderAuth1 === "headerValue1"
&& queryStringParameters.QueryString1 === "queryValue1"
&& stageVariables.StageVar1 === "stageValue1") {
callback(null, generateAllow('me', event.methodArn));
} else {
callback("Unauthorized");
}
}
// Help function to generate an IAM policy
var generatePolicy = function(principalId, effect, resource) {
// Required output:
var authResponse = {};
authResponse.principalId = principalId;
if (effect && resource) {
var policyDocument = {};
policyDocument.Version = '2012-10-17'; // default version
policyDocument.Statement = [];
var statementOne = {};
statementOne.Action = 'execute-api:Invoke'; // default action
statementOne.Effect = effect;
statementOne.Resource = resource;
policyDocument.Statement[0] = statementOne;
authResponse.policyDocument = policyDocument;
}
// Optional output with custom properties of the String, Number or Boolean type.
authResponse.context = {
"stringKey": "stringval",
"numberKey": 123,
"booleanKey": true
};
return authResponse;
}
var generateAllow = function(principalId, resource) {
return generatePolicy(principalId, 'Allow', resource);
}
var generateDeny = function(principalId, resource) {
return generatePolicy(principalId, 'Deny', resource);
}
- Python
# A simple request-based authorizer example to demonstrate how to use request
# parameters to allow or deny a request. In this example, a request is
# authorized if the client-supplied headerauth1 header, QueryString1
# query parameter, and stage variable of StageVar1 all match
# specified values of 'headerValue1', 'queryValue1', and 'stageValue1',
# respectively.
import json
def lambda_handler(event, context):
print(event)
# Retrieve request parameters from the Lambda function input:
headers = event['headers']
queryStringParameters = event['queryStringParameters']
pathParameters = event['pathParameters']
stageVariables = event['stageVariables']
# Parse the input for the parameter values
tmp = event['methodArn'].split(':')
apiGatewayArnTmp = tmp[5].split('/')
awsAccountId = tmp[4]
region = tmp[3]
restApiId = apiGatewayArnTmp[0]
stage = apiGatewayArnTmp[1]
method = apiGatewayArnTmp[2]
resource = '/'
if (apiGatewayArnTmp[3]):
resource += apiGatewayArnTmp[3]
# Perform authorization to return the Allow policy for correct parameters
# and the 'Unauthorized' error, otherwise.
if (headers['HeaderAuth1'] == "headerValue1" and queryStringParameters['QueryString1'] == "queryValue1" and stageVariables['StageVar1'] == "stageValue1"):
response = generateAllow('me', event['methodArn'])
print('authorized')
return response
else:
print('unauthorized')
raise Exception('Unauthorized') # Return a 401 Unauthorized response
# Help function to generate IAM policy
def generatePolicy(principalId, effect, resource):
authResponse = {}
authResponse['principalId'] = principalId
if (effect and resource):
policyDocument = {}
policyDocument['Version'] = '2012-10-17'
policyDocument['Statement'] = []
statementOne = {}
statementOne['Action'] = 'execute-api:Invoke'
statementOne['Effect'] = effect
statementOne['Resource'] = resource
policyDocument['Statement'] = [statementOne]
authResponse['policyDocument'] = policyDocument
authResponse['context'] = {
"stringKey": "stringval",
"numberKey": 123,
"booleanKey": True
}
return authResponse
def generateAllow(principalId, resource):
return generatePolicy(principalId, 'Allow', resource)
def generateDeny(principalId, resource):
return generatePolicy(principalId, 'Deny', resource)
在此範例中,Lambda 授權方函數會檢查輸入參數,並運作如下:
-
如果所有必要的參數值都符合預期值,授權方函數會傳回如下所示的200 OKHTTP回應和IAM政策,且方法請求成功:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": "execute-api:Invoke",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "arn:aws:execute-api:us-east-1:123456789012:ivdtdhp7b5/ESTestInvoke-stage/GET/"
}
]
}
-
否則,授權方函數會傳回401 UnauthorizedHTTP回應,而方法請求會失敗。
除了傳回IAM政策之外,Lambda 授權方函數也必須傳回呼叫者的主要識別符。或者,它可以傳回context物件,其中包含可傳遞至整合後端的其他資訊。如需詳細資訊,請參閱從 API Gateway Lambda 授權方輸出。
在生產程式碼中,您可能需要在授予授權之前驗證使用者。您可以依照供應商文件中的指示,呼叫身分驗證提供者,在 Lambda 函數中新增身分驗證邏輯。
TOKEN 授權方 Lambda 函數範例
下列範例程式碼會建立 TOKEN Lambda 授權方函數,允許呼叫者在用戶端提供的權杖值為 時叫用方法allow。如果權杖值為 ,則不允許呼叫者叫用請求deny。如果權杖值為 unauthorized或空字串,則授權方函數會傳回401 UNAUTHORIZED回應。
- Node.js
// A simple token-based authorizer example to demonstrate how to use an authorization token
// to allow or deny a request. In this example, the caller named 'user' is allowed to invoke
// a request if the client-supplied token value is 'allow'. The caller is not allowed to invoke
// the request if the token value is 'deny'. If the token value is 'unauthorized' or an empty
// string, the authorizer function returns an HTTP 401 status code. For any other token value,
// the authorizer returns an HTTP 500 status code.
// Note that token values are case-sensitive.
export const handler = function(event, context, callback) {
var token = event.authorizationToken;
switch (token) {
case 'allow':
callback(null, generatePolicy('user', 'Allow', event.methodArn));
break;
case 'deny':
callback(null, generatePolicy('user', 'Deny', event.methodArn));
break;
case 'unauthorized':
callback("Unauthorized"); // Return a 401 Unauthorized response
break;
default:
callback("Error: Invalid token"); // Return a 500 Invalid token response
}
};
// Help function to generate an IAM policy
var generatePolicy = function(principalId, effect, resource) {
var authResponse = {};
authResponse.principalId = principalId;
if (effect && resource) {
var policyDocument = {};
policyDocument.Version = '2012-10-17';
policyDocument.Statement = [];
var statementOne = {};
statementOne.Action = 'execute-api:Invoke';
statementOne.Effect = effect;
statementOne.Resource = resource;
policyDocument.Statement[0] = statementOne;
authResponse.policyDocument = policyDocument;
}
// Optional output with custom properties of the String, Number or Boolean type.
authResponse.context = {
"stringKey": "stringval",
"numberKey": 123,
"booleanKey": true
};
return authResponse;
}
- Python
# A simple token-based authorizer example to demonstrate how to use an authorization token
# to allow or deny a request. In this example, the caller named 'user' is allowed to invoke
# a request if the client-supplied token value is 'allow'. The caller is not allowed to invoke
# the request if the token value is 'deny'. If the token value is 'unauthorized' or an empty
# string, the authorizer function returns an HTTP 401 status code. For any other token value,
# the authorizer returns an HTTP 500 status code.
# Note that token values are case-sensitive.
import json
def lambda_handler(event, context):
token = event['authorizationToken']
if token == 'allow':
print('authorized')
response = generatePolicy('user', 'Allow', event['methodArn'])
elif token == 'deny':
print('unauthorized')
response = generatePolicy('user', 'Deny', event['methodArn'])
elif token == 'unauthorized':
print('unauthorized')
raise Exception('Unauthorized') # Return a 401 Unauthorized response
return 'unauthorized'
try:
return json.loads(response)
except BaseException:
print('unauthorized')
return 'unauthorized' # Return a 500 error
def generatePolicy(principalId, effect, resource):
authResponse = {}
authResponse['principalId'] = principalId
if (effect and resource):
policyDocument = {}
policyDocument['Version'] = '2012-10-17'
policyDocument['Statement'] = []
statementOne = {}
statementOne['Action'] = 'execute-api:Invoke'
statementOne['Effect'] = effect
statementOne['Resource'] = resource
policyDocument['Statement'] = [statementOne]
authResponse['policyDocument'] = policyDocument
authResponse['context'] = {
"stringKey": "stringval",
"numberKey": 123,
"booleanKey": True
}
authResponse_JSON = json.dumps(authResponse)
return authResponse_JSON
在此範例中,當 API收到方法請求時,APIGateway 會將來源權杖傳遞至 event.authorizationToken 屬性中的此 Lambda 授權方函數。Lambda 授權方函數會讀取字符,並運作如下:
-
如果權杖值為 allow,則授權方函數會傳回如下所示的200 OKHTTP回應和IAM政策,且方法請求成功:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": "execute-api:Invoke",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Resource": "arn:aws:execute-api:us-east-1:123456789012:ivdtdhp7b5/ESTestInvoke-stage/GET/"
}
]
}
-
如果權杖值為 deny,則授權方函數會傳回如下所示的200 OKHTTP回應和DenyIAM政策,且方法請求會失敗:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Action": "execute-api:Invoke",
"Effect": "Deny",
"Resource": "arn:aws:execute-api:us-east-1:123456789012:ivdtdhp7b5/ESTestInvoke-stage/GET/"
}
]
}
在測試環境之外,APIGateway 會傳回403 ForbiddenHTTP回應,且方法請求失敗。
-
如果權杖值為 unauthorized或空字串,授權方函數會傳回401 UnauthorizedHTTP回應,且方法呼叫會失敗。
-
如果符記為其他值,用戶端會收到 500 Invalid token 回應,而且方法呼叫會失敗。
除了傳回IAM政策之外,Lambda 授權方函數也必須傳回呼叫者的主要識別符。或者,它可以傳回context物件,其中包含可傳遞至整合後端的其他資訊。如需詳細資訊,請參閱從 API Gateway Lambda 授權方輸出。
在生產程式碼中,您可能需要在授予授權之前驗證使用者。您可以依照供應商文件中的指示,呼叫身分驗證提供者,在 Lambda 函數中新增身分驗證邏輯。
Lambda 授權方函數的其他範例
下列清單顯示 Lambda 授權方函數的其他範例。您可以在與您建立 的相同 帳戶或不同 帳戶中建立 Lambda 函數API。
對於上一個範例 Lambda 函數,您可以使用內建 AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole,因為這些函數不會呼叫其他服務 AWS 。如果您的 Lambda 函數呼叫其他 AWS 服務,您將需要將IAM執行角色指派給 Lambda 函數。若要建立角色,請依照 AWS Lambda 執行角色中的指示。