Connecting to an Amazon Aurora DB cluster
You can connect to an Aurora DB cluster using the same tools that you use to connect to a MySQL or PostgreSQL database. You specify a connection string with any script, utility, or application that connects to a MySQL or PostgreSQL DB instance. You use the same public key for Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) connections.
In the connection string, you typically use the host and port information from special endpoints associated with the DB cluster. With these endpoints, you can use the same connection parameters regardless of how many DB instances are in the cluster. You also use the host and port information from a specific DB instance in your Aurora DB cluster for specialized tasks, such as troubleshooting.
Note
For Aurora Serverless DB clusters, you connect to the database endpoint rather than to the DB instance. You can find the database endpoint for an Aurora Serverless DB cluster on the Connectivity & security tab of the AWS Management Console. For more information, see Using Amazon Aurora Serverless v1.
Regardless of the Aurora DB engine and specific tools you use to work with the DB cluster or instance, the endpoint must be accessible. An Aurora DB cluster can be created only in a virtual private cloud (VPC) based on the Amazon VPC service. That means that you access the endpoint from either inside the VPC or outside the VPC using one of the following approaches.
Access the Aurora DB cluster inside the VPC – Enable access to the Aurora DB cluster through the VPC. You do so by editing the Inbound rules on the Security group for the VPC to allow access to your specific Aurora DB cluster. To learn more, including how to configure your VPC for different Aurora DB cluster scenarios, see Amazon Virtual Private Cloud VPCs and Amazon Aurora.
-
Access the Aurora DB cluster outside the VPC – To access an Aurora DB cluster from outside the VPC, use the public endpoint address of the DB cluster.
For more information, see Troubleshooting Aurora connection failures.
Contents
- Connecting to Aurora DB clusters with the AWS drivers
- Connecting to an Amazon Aurora MySQL DB cluster
- Connection utilities for Aurora MySQL
- Connecting to Aurora MySQL with the MySQL utility
- Connecting to Aurora MySQL with the Amazon Web Services (AWS) JDBC Driver
- Connecting to Aurora MySQL with the Amazon Web Services (AWS) Python Driver
- Connecting to Aurora MySQL with the Amazon Web Services (AWS) ODBC Driver for MySQL
- Connecting to Aurora MySQL with the Amazon Web Services (AWS) Advanced NodeJS Wrapper
- Connecting to Aurora MySQL using SSL
- Connecting to an Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster
- Troubleshooting Aurora connection failures
Connecting to Aurora DB clusters with the AWS drivers
The AWS suite of drivers has been designed to provide support for faster switchover and failover times, and authentication with AWS Secrets Manager, AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), and Federated Identity. The AWS drivers rely on monitoring DB cluster status and being aware of the cluster topology to determine the new writer. This approach reduces switchover and failover times to single-digit seconds, compared to tens of seconds for open-source drivers.
The following table lists the features supported for each of the drivers. As new service features are introduced, the goal of the AWS suite of drivers is to have built-in support for these service features.
| Feature | AWS JDBC Driver |
AWS Python Driver |
AWS ODBC Driver for MySQL |
AWS Advanced NodeJS Wrapper |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Failover support | Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
| Enhanced failover monitoring | Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
| Read/write splitting | Yes |
Yes |
No | Yes |
| Aurora connection tracker | Yes |
Yes |
No | Yes |
| Driver metadata connection | Yes |
N/A | N/A | N/A |
| Telemetry | Yes |
Yes |
No | Yes |
| Secrets Manager | Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
| IAM authentication | Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
| Federated Identity (AD FS) | Yes |
Yes |
No | Yes |
| Federated Identity (Okta) | Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
| Aurora PostgreSQL Limitless Database | Yes |
No | No | Yes |
For more information on the AWS drivers, see the corresponding language driver for your Aurora MySQL or Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster.
Connecting to an Amazon Aurora MySQL DB cluster
To authenticate to your Aurora MySQL DB cluster, you can use either MySQL user name and
password authentication or AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) database authentication. For more information on using
MySQL user name and password authentication, see
Access control and account management
When you have a connection to your Amazon Aurora DB cluster with MySQL 8.0 compatibility,
you can run SQL commands that are compatible with MySQL version 8.0. The minimum compatible
version is MySQL 8.0.23. For more
information about MySQL 8.0 SQL syntax, see the MySQL 8.0 reference
manual
When you have a connection to your Amazon Aurora DB cluster with MySQL 5.7 compatibility,
you can run SQL commands that are compatible with MySQL version 5.7. For more
information about MySQL 5.7 SQL syntax, see the MySQL 5.7 reference
manual
Note
For a helpful and detailed guide on connecting to an Amazon Aurora MySQL DB cluster,
you can see the Aurora connection management
In the details view for your DB cluster, you can find the cluster endpoint, which you
can use in your MySQL connection string. The endpoint is made up of the domain name and
port for your DB cluster. For example, if an endpoint value is
mycluster.cluster-123456789012.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com:3306, then
you specify the following values in a MySQL connection string:
-
For host or host name, specify
mycluster.cluster-123456789012.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com -
For port, specify
3306or the port value you used when you created the DB cluster
The cluster endpoint connects you to the primary instance for the DB cluster. You can perform both read and write operations using the cluster endpoint. Your DB cluster can also have up to 15 Aurora Replicas that support read-only access to the data in your DB cluster. The primary instance and each Aurora Replica has a unique endpoint that is independent of the cluster endpoint and allows you to connect to a specific DB instance in the cluster directly. The cluster endpoint always points to the primary instance. If the primary instance fails and is replaced, then the cluster endpoint points to the new primary instance.
To view the cluster endpoint (writer endpoint), choose Databases on the Amazon RDS console and choose the name of the DB cluster to show the DB cluster details.
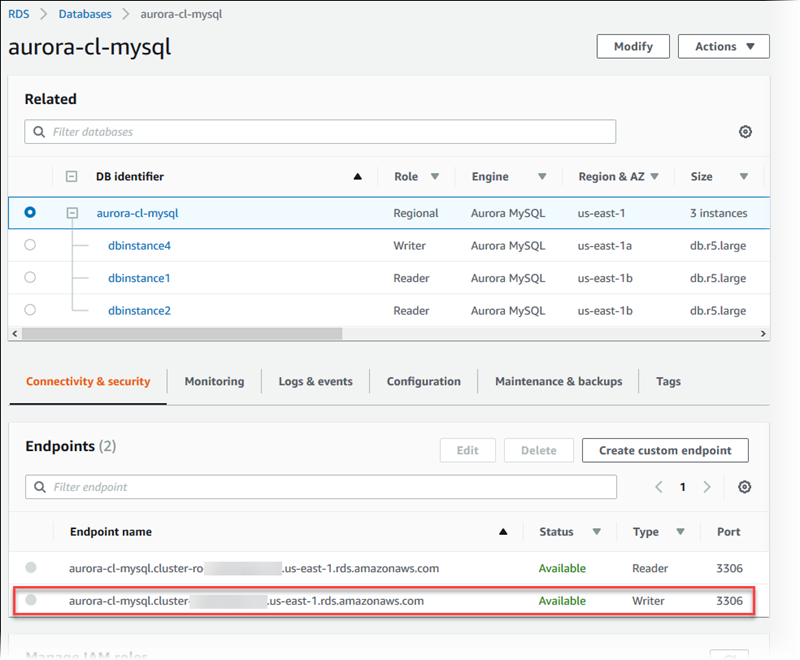
Topics
- Connection utilities for Aurora MySQL
- Connecting to Aurora MySQL with the MySQL utility
- Connecting to Aurora MySQL with the Amazon Web Services (AWS) JDBC Driver
- Connecting to Aurora MySQL with the Amazon Web Services (AWS) Python Driver
- Connecting to Aurora MySQL with the Amazon Web Services (AWS) ODBC Driver for MySQL
- Connecting to Aurora MySQL with the Amazon Web Services (AWS) Advanced NodeJS Wrapper
- Connecting to Aurora MySQL using SSL
Connection utilities for Aurora MySQL
Some connection utilities you can use are the following:
-
Command line – You can connect to an Amazon Aurora DB cluster by using tools like the MySQL command line utility. For more information on using the MySQL utility, see mysql — the MySQL command-line client
in the MySQL documentation. -
GUI – You can use the MySQL Workbench utility to connect by using a UI interface. For more information, see the Download MySQL workbench
page. -
AWS drivers:
-
Connecting to Aurora MySQL with the Amazon Web Services (AWS) JDBC Driver
-
Connecting to Aurora MySQL with the Amazon Web Services (AWS) Python Driver
-
Connecting to Aurora MySQL with the Amazon Web Services (AWS) ODBC Driver for MySQL
-
Connecting to Aurora MySQL with the Amazon Web Services (AWS) Advanced NodeJS Wrapper
-
Connecting to Aurora MySQL with the MySQL utility
Use the following procedure. It assumes that you configured your DB cluster in a private subnet in your VPC. You connect using an Amazon EC2 instance that you configured according to the tutorials in Tutorial: Create a web server and an Amazon Aurora DB cluster.
Note
This procedure doesn't require installing the web server in the tutorial, but it does require installing MariaDB 10.5.
To connect to a DB cluster using the MySQL utility
-
Log in to the EC2 instance that you're using to connect to your DB cluster.
You should see output similar to the following.
Last login: Thu Jun 23 13:32:52 2022 fromxxx.xxx.xxx.xxx__| __|_ ) _| ( / Amazon Linux 2 AMI ___|\___|___| https://aws.amazon.com/amazon-linux-2/ [ec2-user@ip-10-0-xxx.xxx~]$ -
Type the following command at the command prompt to connect to the primary DB instance of your DB cluster.
For the
-hparameter, substitute the endpoint DNS name for your primary instance. For the-uparameter, substitute the user ID of a database user account.mysql -hprimary-instance-endpoint.AWS_account.AWS_Region.rds.amazonaws.com -P 3306 -udatabase_user-pFor example:
mysql -h my-aurora-cluster-instance.c1xy5example.123456789012.eu-central-1.rds.amazonaws.com -P 3306 -u admin -p -
Enter the password for the database user.
You should see output similar to the following.
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MySQL connection id is 1770 Server version: 8.0.23 Source distribution Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. MySQL [(none)]> -
Enter your SQL commands.
Connecting to Aurora MySQL with the Amazon Web Services (AWS) JDBC Driver
The Amazon Web Services (AWS) JDBC Driver is designed as an advanced JDBC wrapper. This wrapper is complementary to and extends the functionality of an existing JDBC driver to help applications take advantage of the features of clustered databases such as Aurora MySQL. The driver is drop-in compatible with the community MySQL Connector/J driver and the community MariaDB Connector/J driver.
To install the AWS JDBC Driver, append the AWS JDBC Driver .jar file (located in the
application CLASSPATH), and keep references to the respective community
driver. Update the respective connection URL prefix as follows:
-
jdbc:mysql://tojdbc:aws-wrapper:mysql:// -
jdbc:mariadb://tojdbc:aws-wrapper:mariadb://
For more information about the AWS JDBC Driver and complete instructions for using it, see the
Amazon Web Services (AWS) JDBC Driver GitHub repository
Note
Version 3.0.3 of the MariaDB Connector/J utility drops support for Aurora DB clusters, so we highly recommend moving to the AWS JDBC Driver.
Connecting to Aurora MySQL with the Amazon Web Services (AWS) Python Driver
The Amazon Web Services (AWS) Python Driver is designed as an advanced Python wrapper. This wrapper is complementary to and extends the functionality of
the open-source Psycopg driver. The AWS Python Driver supports Python versions 3.8 and higher. You can install the
aws-advanced-python-wrapper package using the pip command, along with the psycopg open-source packages.
For more information about the AWS Python Driver and complete instructions for using it, see the
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Python Driver GitHub repository
Connecting to Aurora MySQL with the Amazon Web Services (AWS) ODBC Driver for MySQL
The AWS ODBC Driver for MySQL is a client driver designed for the high availability of Aurora MySQL. The driver can exist alongside the MySQL Connector/ODBC driver and is compatible with the same workflows.
For more information about the AWS ODBC Driver for MySQL and complete instructions for
installing and using it, see the Amazon Web Services (AWS) ODBC Driver for MySQL
Connecting to Aurora MySQL with the Amazon Web Services (AWS) Advanced NodeJS Wrapper
The AWS Advanced NodeJS Wrapper is complementary to and extends the functionality of an existing NodeJS driver. It helps applications take advantage of the features of clustered databases such as Aurora MySQL.
For more information about the AWS Advanced NodeJS Wrapper and complete instructions for using it, see the
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Advanced NodeJS Wrapper GitHub repository
Connecting to Aurora MySQL using SSL
You can use SSL encryption on connections to an Aurora MySQL DB instance. For information, see TLS connections to Aurora MySQL DB clusters.
To connect using SSL, use the MySQL utility as described in the following procedure. If you are using IAM database authentication, you must use an SSL connection. For information, see IAM database authentication.
Note
To connect to the cluster endpoint using SSL, your client connection utility must support Subject Alternative Names (SAN). If your client connection utility doesn't support SAN, you can connect directly to the instances in your Aurora DB cluster. For more information on Aurora endpoints, see Amazon Aurora endpoint connections.
To connect to a DB cluster with SSL using the MySQL utility
-
Download the public key for the Amazon RDS signing certificate.
For information about downloading certificates, see Using SSL/TLS to encrypt a connection to a DB cluster.
-
Type the following command at a command prompt to connect to the primary instance of a DB cluster with SSL using the MySQL utility. For the
-hparameter, substitute the endpoint DNS name for your primary instance. For the-uparameter, substitute the user ID of a database user account. For the--ssl-caparameter, substitute the SSL certificate file name as appropriate. Type the master user password when prompted.mysql -h mycluster-primary.123456789012.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com -uadmin_user-p --ssl-ca=[full path]global-bundle.pem --ssl-verify-server-cert
You should see output similar to the following.
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 350
Server version: 8.0.26-log MySQL Community Server (GPL)
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the buffer.
mysql> For general instructions on constructing RDS for MySQL connection strings and finding the public key for SSL connections, see Connecting to a DB instance running the MySQL database engine.
Connecting to an Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster
You can connect to a DB instance in your Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster using the same tools that you use to connect to a PostgreSQL database. As part of this, you use the same public key for Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) connections. You can use the endpoint and port information from the primary instance or Aurora Replicas in your Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster in the connection string of any script, utility, or application that connects to a PostgreSQL DB instance. In the connection string, specify the DNS address from the primary instance or Aurora Replica endpoint as the host parameter. Specify the port number from the endpoint as the port parameter.
When you have a connection to a DB instance in your Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster, you can run any SQL command that is compatible with PostgreSQL.
In the details view for your Aurora PostgreSQL DB cluster you can find the cluster
endpoint name, status, type, and port number. You use the endpoint and port number in your
PostgreSQL connection string. For example, if an endpoint
value is mycluster.cluster-123456789012.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com,
then you specify the following values in a PostgreSQL connection string:
-
For host or host name, specify
mycluster.cluster-123456789012.us-east-1.rds.amazonaws.com -
For port, specify
5432or the port value you used when you created the DB cluster
The cluster endpoint connects you to the primary instance for the DB cluster. You can perform both read and write operations using the cluster endpoint. Your DB cluster can also have up to 15 Aurora Replicas that support read-only access to the data in your DB cluster. Each DB instance in the Aurora cluster (that is, the primary instance and each Aurora Replica) has a unique endpoint that is independent of the cluster endpoint. This unique endpoint allows you to connect to a specific DB instance in the cluster directly. The cluster endpoint always points to the primary instance. If the primary instance fails and is replaced, the cluster endpoint points to the new primary instance.
To view the cluster endpoint (writer endpoint), choose Databases on the Amazon RDS console and choose the name of the DB cluster to show the DB cluster details.

Connection utilities for Aurora PostgreSQL
Some connection utilities you can use are the following:
-
Command line – You can connect to Aurora PostgreSQL DB clusters by using tools like psql, the PostgreSQL interactive terminal. For more information on using the PostgreSQL interactive terminal, see psql
in the PostgreSQL documentation. -
GUI – You can use the pgAdmin utility to connect to Aurora PostgreSQL DB clusters by using a UI interface. For more information, see the Download
page from the pgAdmin website. -
AWS drivers:
Connecting to Aurora PostgreSQL with the Amazon Web Services (AWS) JDBC Driver
The Amazon Web Services (AWS) JDBC Driver is designed as an advanced JDBC wrapper. This wrapper is complementary to and extends the functionality of an existing JDBC driver to help applications take advantage of the features of clustered databases such as Aurora PostgreSQL. The driver is drop-in compatible with the community pgJDBC driver.
To install the AWS JDBC Driver, append the AWS JDBC Driver .jar file (located in the
application CLASSPATH), and keep references to the pgJDBC community
driver. Update the connection URL prefix from jdbc:postgresql:// to
jdbc:aws-wrapper:postgresql://.
For more information about the AWS JDBC Driver and complete instructions for using it, see the
Amazon Web Services (AWS) JDBC Driver GitHub repository
Connecting to Aurora PostgreSQL with the Amazon Web Services (AWS) Python Driver
The Amazon Web Services (AWS) Python Driver is designed as an advanced Python wrapper. This wrapper is complementary to and extends the functionality of
the open-source Psycopg driver. The AWS Python Driver supports Python versions 3.8 and higher. You can install the
aws-advanced-python-wrapper package using the pip command, along with the psycopg open-source packages.
For more information about the AWS Python Driver and complete instructions for using
it, see the Amazon Web Services (AWS) Python Driver GitHub repository
Connecting to Aurora PostgreSQL with the Amazon Web Services (AWS) Advanced NodeJS Wrapper
The AWS Advanced NodeJS Wrapper is complementary to and extends the functionality of an existing NodeJS driver. It helps applications take advantage of the features of clustered databases such as Aurora PostgreSQL.
For more information about the AWS Advanced NodeJS Wrapper and complete instructions for using it, see the
Amazon Web Services (AWS) Advanced NodeJS Wrapper GitHub repository
Troubleshooting Aurora connection failures
Common causes of connection failures to a new Aurora DB cluster include the following:
-
Security group in the VPC doesn't allow access – Your VPC needs to allow connections from your device or from an Amazon EC2 instance by proper configuration of the security group in the VPC. To resolve, modify your VPC's Security group Inbound rules to allow connections. For an example, see Tutorial: Create a VPC for use with a DB cluster (IPv4 only).
-
Port blocked by firewall rules – Check the value of the port configured for your Aurora DB cluster. If a firewall rule blocks that port, you can re-create the instance using a different port.
-
Incomplete or incorrect IAM configuration – If you created your Aurora DB instance to use IAM–based authentication, make sure that it's properly configured. For more information, see IAM database authentication.
For more information about troubleshooting Aurora DB connection issues, see Can't connect to Amazon RDS DB instance.