Migrating PostgreSQL Databases to Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL or Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL
This walkthrough gets you started with homogeneous database migration from PostgreSQL to Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) for PostgreSQL or Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL-Compatible Edition. This guide provides a quick overview of the data migration process and provides suggestions on how to select the best option to use.
Customers looking to migrate self-managed PostgreSQL databases to Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL or Aurora PostgreSQL, can use one of the three main approaches.
-
Use a native or third-party database migration method such as pg_dump and pg_restore for full load only migrations.
-
Use a managed service such as AWS Database Migration Service (AWS DMS) for full load and ongoing replication.
-
Use a native tool for full load and a managed AWS DMS service for ongoing replication. We call this strategy the hybrid approach.
This document describes the hybrid approach. The following diagram shows the components of the hybrid approach.
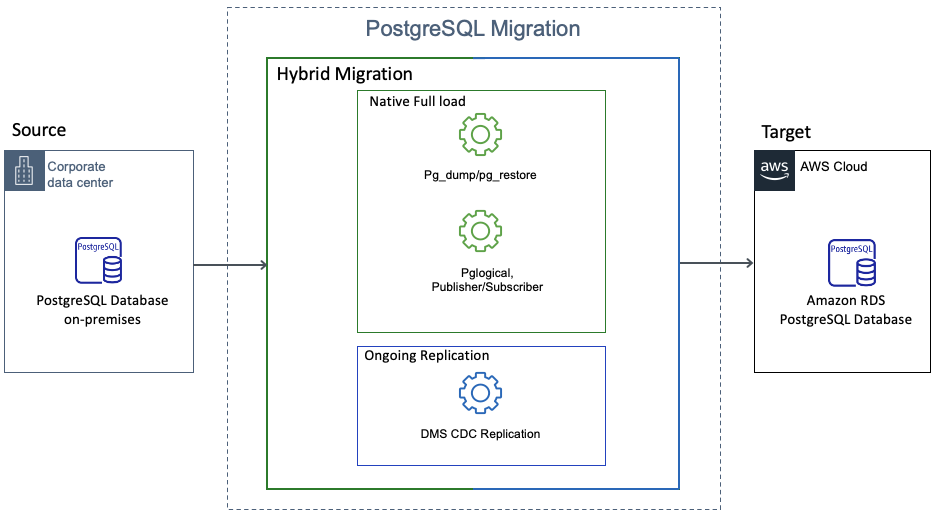
The hybrid approach provides the following advantages.
-
Automation of the creation of secondary database objects such as views, indexes, and constraints.
-
AWS DMS data validation to ensure that your target data matches with the source, row by row and column by column.
-
Other capabilities provided by AWS DMS, for example CloudWatch monitoring and table statistics. It may be simpler to use AWS DMS to track migration progress, transactional workload, receive and transmit throughput, source and target latency, and so on.
This document describes the native options for the full load. It also includes a comparison so that you can evaluate the options for your migration requirements. In conclusion, you can find a brief description of how to use AWS DMS for ongoing replication.
Topics
Summary
This document describes the hybrid approach for migrating between PostgreSQL databases. We analyzed three options for full load and demonstrated the relative performance of each for a test database.
If you need to create secondary database objects, then pg_dump and pg_restore is the most appropriate option. However, this option incurs a performance tradeoff compared to other options.
pglogical has a slight performance advantage over publisher and subscriber. However, you need to install the pglogical extension on your source database server.
You can use these guidelines to choose the option that best matches your migration goal.
For more information about the performance of these tools, see Performance Comparison.