此頁面僅適用於使用 Vault 和 REST API 2012 年原始版本的 S3 Glacier 服務的現有客戶。
如果您要尋找封存儲存解決方案,建議您在 Amazon S3、S3 Glacier S3 Instant Retrieval、S3 Glacier Flexible Retrieval 和 S3 Glacier Deep Archive 中使用 S3 Glacier 儲存類別。若要進一步了解這些儲存選項,請參閱 Amazon S3
本文為英文版的機器翻譯版本,如內容有任何歧義或不一致之處,概以英文版為準。
運算檢查總和
當上傳封存時,您必須同時包含 x-amz-sha256-tree-hash 和 x-amz-content-sha256 標頭。x-amz-sha256-tree-hash 標題是您的請求內文中承載的檢查總和。此主題說明如何計算 x-amz-sha256-tree-hash 標頭。x-amz-content-sha256 標頭是整個承載的雜湊,並且是授權所需。如需詳細資訊,請參閱 串流的簽名計算範例 API。
請求的承載內容可以是:
-
整個封存:在單一請求中使用上傳封存 API 上傳封存時,您在請求內文傳送整個封存。在這種情況下,您必須包含整個封存的檢查總和。
-
封存部分:使用分段上傳 API 以部分形式上傳封存時,您僅在請求內文傳送部分封存。在這種情況下,會包含封存部分的檢查總和。而且在上傳所有的部分後,您會完成分段上傳請求,其必須包含整個封存的檢查總和。
承載的檢查總和是 SHA-256 樹雜湊。其稱為樹雜湊的原因是,在運算檢查總和的過程中,您會計算 SHA-256 樹雜湊值。根的雜湊值是整個封存的檢查總和。
注意
本節說明運算 SHA-256 樹雜湊的方式。不過,您可以使用任何會產生相同結果的程序。
您運算 SHA-256 樹雜湊,如下所示:
-
對於每個 1 MB 區塊的承載資料,運算 SHA-256 雜湊。最後區塊的資料可能小於 1 MB。例如,如果上傳 3.2 MB 的封存,您為前三個 1 MB 的資料區塊的每一個運算 SHA-256 雜湊值,然後運算剩餘 0.2 MB 資料的 SHA-256 雜湊。這些雜湊值形成樹狀結構的分葉節點。
-
建置下一個層級的樹狀結構。
-
串連兩個連續的子節點雜湊值,並且運算已串連雜湊值的 SHA-256 雜湊。這個串連及 SHA-256 雜湊的產生會產生兩個子節點的父節點。
-
如果只剩一個子節點,就會將該雜湊值提升到樹狀結構的下一個層級。
-
-
重複步驟 2,直到產生的樹狀結構有根。樹狀結構的根提供整個封存的雜湊,而適當子樹狀結構則提供分段上傳部分的雜湊。
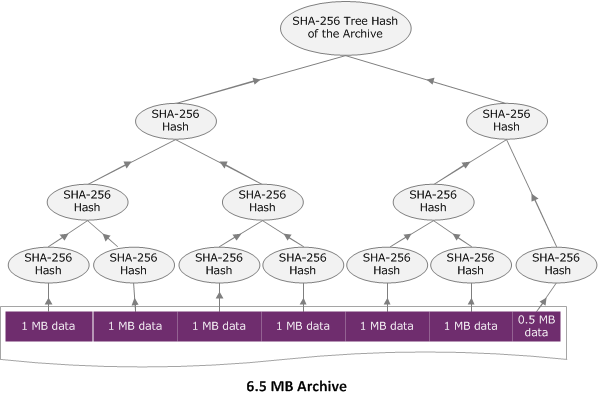
樹雜湊範例 1:在單一請求上傳封存
在單一請求中使用上傳封存 API 上傳封存時 (請參閱 上傳封存 (POST 封存)) 請求承載包含整個封存。因此,您必須在 x-amz-sha256-tree-hash 請求標頭中包含整個封存的樹雜湊。假設您想要上傳 6.5 MB 的封存。下圖說明建立封存的 SHA-256 雜湊的程序。您讀取封存並運算每 1 MB 區塊的 SHA-256 雜湊。您也運算剩餘 0.5 MB 資料的雜湊,然後依所述的樹狀結構建置程序。
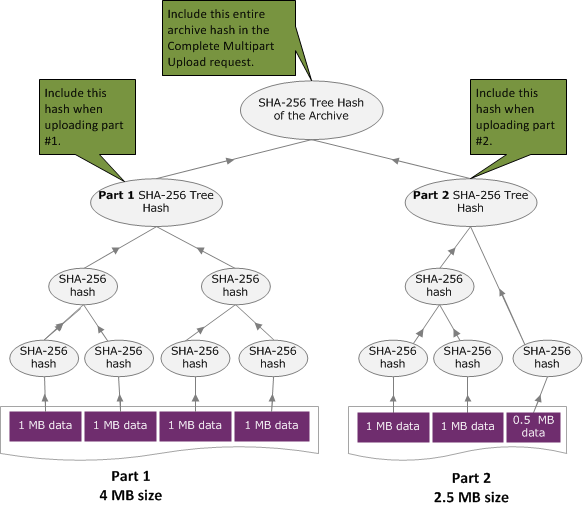
樹雜湊範例 2:使用分段上傳來上傳封存
在使用分段上傳來上傳封存時,其運算樹雜湊的程序和在單一請求上傳封存的程序是相同的。唯一的差別是,在分段上傳只上傳每個請求的一部分封存 (使用 分段上傳 (PUT uploadID) API),因此,您只提供 x-amz-sha256-tree-hash 請求標頭部分的檢查總和。不過,在上傳所有部分後,您必須隨著 完成分段上傳 (POST uploadID) 請求標頭中整個封存的樹雜湊,傳送「完成分段上傳」(請參閱 x-amz-sha256-tree-hash) 請求。
運算檔案的樹雜湊
這裡所顯示的演算法僅示範之目定而選定。您可以視您實作情況的需要最佳化程式碼。如果您使用 Amazon 開發套件,針對 Amazon S3 Glacier (S3 Glacier) 進行程式設計,系統便會為您完成樹雜湊計算,您只需提供檔案參考即可。
範例 1: Java 範例
以下範例說明如何計算使用 Java 的檔案的 SHA256 樹雜湊。您可以執行這個範例,做法是提供檔案位置做為引數,或可直接從您的程式碼使用 TreeHashExample.computeSHA256TreeHash 方法。
import java.io.File; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.security.MessageDigest; import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException; public class TreeHashExample { static final int ONE_MB = 1024 * 1024; /** * Compute the Hex representation of the SHA-256 tree hash for the specified * File * * @param args * args[0]: a file to compute a SHA-256 tree hash for */ public static void main(String[] args) { if (args.length < 1) { System.err.println("Missing required filename argument"); System.exit(-1); } File inputFile = new File(args[0]); try { byte[] treeHash = computeSHA256TreeHash(inputFile); System.out.printf("SHA-256 Tree Hash = %s\n", toHex(treeHash)); } catch (IOException ioe) { System.err.format("Exception when reading from file %s: %s", inputFile, ioe.getMessage()); System.exit(-1); } catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException nsae) { System.err.format("Cannot locate MessageDigest algorithm for SHA-256: %s", nsae.getMessage()); System.exit(-1); } } /** * Computes the SHA-256 tree hash for the given file * * @param inputFile * a File to compute the SHA-256 tree hash for * @return a byte[] containing the SHA-256 tree hash * @throws IOException * Thrown if there's an issue reading the input file * @throws NoSuchAlgorithmException */ public static byte[] computeSHA256TreeHash(File inputFile) throws IOException, NoSuchAlgorithmException { byte[][] chunkSHA256Hashes = getChunkSHA256Hashes(inputFile); return computeSHA256TreeHash(chunkSHA256Hashes); } /** * Computes a SHA256 checksum for each 1 MB chunk of the input file. This * includes the checksum for the last chunk even if it is smaller than 1 MB. * * @param file * A file to compute checksums on * @return a byte[][] containing the checksums of each 1 MB chunk * @throws IOException * Thrown if there's an IOException when reading the file * @throws NoSuchAlgorithmException * Thrown if SHA-256 MessageDigest can't be found */ public static byte[][] getChunkSHA256Hashes(File file) throws IOException, NoSuchAlgorithmException { MessageDigest md = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256"); long numChunks = file.length() / ONE_MB; if (file.length() % ONE_MB > 0) { numChunks++; } if (numChunks == 0) { return new byte[][] { md.digest() }; } byte[][] chunkSHA256Hashes = new byte[(int) numChunks][]; FileInputStream fileStream = null; try { fileStream = new FileInputStream(file); byte[] buff = new byte[ONE_MB]; int bytesRead; int idx = 0; int offset = 0; while ((bytesRead = fileStream.read(buff, offset, ONE_MB)) > 0) { md.reset(); md.update(buff, 0, bytesRead); chunkSHA256Hashes[idx++] = md.digest(); offset += bytesRead; } return chunkSHA256Hashes; } finally { if (fileStream != null) { try { fileStream.close(); } catch (IOException ioe) { System.err.printf("Exception while closing %s.\n %s", file.getName(), ioe.getMessage()); } } } } /** * Computes the SHA-256 tree hash for the passed array of 1 MB chunk * checksums. * * This method uses a pair of arrays to iteratively compute the tree hash * level by level. Each iteration takes two adjacent elements from the * previous level source array, computes the SHA-256 hash on their * concatenated value and places the result in the next level's destination * array. At the end of an iteration, the destination array becomes the * source array for the next level. * * @param chunkSHA256Hashes * An array of SHA-256 checksums * @return A byte[] containing the SHA-256 tree hash for the input chunks * @throws NoSuchAlgorithmException * Thrown if SHA-256 MessageDigest can't be found */ public static byte[] computeSHA256TreeHash(byte[][] chunkSHA256Hashes) throws NoSuchAlgorithmException { MessageDigest md = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256"); byte[][] prevLvlHashes = chunkSHA256Hashes; while (prevLvlHashes.length > 1) { int len = prevLvlHashes.length / 2; if (prevLvlHashes.length % 2 != 0) { len++; } byte[][] currLvlHashes = new byte[len][]; int j = 0; for (int i = 0; i < prevLvlHashes.length; i = i + 2, j++) { // If there are at least two elements remaining if (prevLvlHashes.length - i > 1) { // Calculate a digest of the concatenated nodes md.reset(); md.update(prevLvlHashes[i]); md.update(prevLvlHashes[i + 1]); currLvlHashes[j] = md.digest(); } else { // Take care of remaining odd chunk currLvlHashes[j] = prevLvlHashes[i]; } } prevLvlHashes = currLvlHashes; } return prevLvlHashes[0]; } /** * Returns the hexadecimal representation of the input byte array * * @param data * a byte[] to convert to Hex characters * @return A String containing Hex characters */ public static String toHex(byte[] data) { StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(data.length * 2); for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) { String hex = Integer.toHexString(data[i] & 0xFF); if (hex.length() == 1) { // Append leading zero. sb.append("0"); } sb.append(hex); } return sb.toString().toLowerCase(); } }
範例 2: C# .NET 範例
以下範例說明如何計算使檔案的 SHA256 樹雜湊。您可以執行此範例,做法是提供檔案位置做為引數。
using System; using System.IO; using System.Security.Cryptography; namespace ExampleTreeHash { class Program { static int ONE_MB = 1024 * 1024; /** * Compute the Hex representation of the SHA-256 tree hash for the * specified file * * @param args * args[0]: a file to compute a SHA-256 tree hash for */ public static void Main(string[] args) { if (args.Length < 1) { Console.WriteLine("Missing required filename argument"); Environment.Exit(-1); } FileStream inputFile = File.Open(args[0], FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read); try { byte[] treeHash = ComputeSHA256TreeHash(inputFile); Console.WriteLine("SHA-256 Tree Hash = {0}", BitConverter.ToString(treeHash).Replace("-", "").ToLower()); Console.ReadLine(); Environment.Exit(-1); } catch (IOException ioe) { Console.WriteLine("Exception when reading from file {0}: {1}", inputFile, ioe.Message); Console.ReadLine(); Environment.Exit(-1); } catch (Exception e) { Console.WriteLine("Cannot locate MessageDigest algorithm for SHA-256: {0}", e.Message); Console.WriteLine(e.GetType()); Console.ReadLine(); Environment.Exit(-1); } Console.ReadLine(); } /** * Computes the SHA-256 tree hash for the given file * * @param inputFile * A file to compute the SHA-256 tree hash for * @return a byte[] containing the SHA-256 tree hash */ public static byte[] ComputeSHA256TreeHash(FileStream inputFile) { byte[][] chunkSHA256Hashes = GetChunkSHA256Hashes(inputFile); return ComputeSHA256TreeHash(chunkSHA256Hashes); } /** * Computes a SHA256 checksum for each 1 MB chunk of the input file. This * includes the checksum for the last chunk even if it is smaller than 1 MB. * * @param file * A file to compute checksums on * @return a byte[][] containing the checksums of each 1MB chunk */ public static byte[][] GetChunkSHA256Hashes(FileStream file) { long numChunks = file.Length / ONE_MB; if (file.Length % ONE_MB > 0) { numChunks++; } if (numChunks == 0) { return new byte[][] { CalculateSHA256Hash(null, 0) }; } byte[][] chunkSHA256Hashes = new byte[(int)numChunks][]; try { byte[] buff = new byte[ONE_MB]; int bytesRead; int idx = 0; while ((bytesRead = file.Read(buff, 0, ONE_MB)) > 0) { chunkSHA256Hashes[idx++] = CalculateSHA256Hash(buff, bytesRead); } return chunkSHA256Hashes; } finally { if (file != null) { try { file.Close(); } catch (IOException ioe) { throw ioe; } } } } /** * Computes the SHA-256 tree hash for the passed array of 1MB chunk * checksums. * * This method uses a pair of arrays to iteratively compute the tree hash * level by level. Each iteration takes two adjacent elements from the * previous level source array, computes the SHA-256 hash on their * concatenated value and places the result in the next level's destination * array. At the end of an iteration, the destination array becomes the * source array for the next level. * * @param chunkSHA256Hashes * An array of SHA-256 checksums * @return A byte[] containing the SHA-256 tree hash for the input chunks */ public static byte[] ComputeSHA256TreeHash(byte[][] chunkSHA256Hashes) { byte[][] prevLvlHashes = chunkSHA256Hashes; while (prevLvlHashes.GetLength(0) > 1) { int len = prevLvlHashes.GetLength(0) / 2; if (prevLvlHashes.GetLength(0) % 2 != 0) { len++; } byte[][] currLvlHashes = new byte[len][]; int j = 0; for (int i = 0; i < prevLvlHashes.GetLength(0); i = i + 2, j++) { // If there are at least two elements remaining if (prevLvlHashes.GetLength(0) - i > 1) { // Calculate a digest of the concatenated nodes byte[] firstPart = prevLvlHashes[i]; byte[] secondPart = prevLvlHashes[i + 1]; byte[] concatenation = new byte[firstPart.Length + secondPart.Length]; System.Buffer.BlockCopy(firstPart, 0, concatenation, 0, firstPart.Length); System.Buffer.BlockCopy(secondPart, 0, concatenation, firstPart.Length, secondPart.Length); currLvlHashes[j] = CalculateSHA256Hash(concatenation, concatenation.Length); } else { // Take care of remaining odd chunk currLvlHashes[j] = prevLvlHashes[i]; } } prevLvlHashes = currLvlHashes; } return prevLvlHashes[0]; } public static byte[] CalculateSHA256Hash(byte[] inputBytes, int count) { SHA256 sha256 = System.Security.Cryptography.SHA256.Create(); byte[] hash = sha256.ComputeHash(inputBytes, 0, count); return hash; } } }