Le traduzioni sono generate tramite traduzione automatica. In caso di conflitto tra il contenuto di una traduzione e la versione originale in Inglese, quest'ultima prevarrà.
Per rendere le tabelle del tuo account accessibili dai servizi di AWS analisi, integra i bucket da tavolo Amazon S3 con Amazon Lakehouse. SageMaker Questa integrazione consente ai servizi di AWS analisi di scoprire e accedere automaticamente ai dati delle tabelle. Puoi utilizzare questa integrazione per lavorare con le tue tabelle nei seguenti servizi:
Nota
Questa integrazione utilizza i AWS Lake Formation servizi AWS Glue and e potrebbe comportare costi di AWS Glue richiesta e archiviazione. Per ulteriori informazioni, consulta AWS Glue Prezzi
Vengono applicati costi aggiuntivi per l'esecuzione di query sulle tabelle S3. Per ulteriori informazioni, consulta le informazioni sui prezzi per il motore di query che stai utilizzando.
Funzionamento dell'integrazione
Quando crei un table bucket nella console, Amazon S3 avvia le seguenti azioni per integrare i table bucket nella regione che hai selezionato con i servizi di analisi: AWS
-
Crea un nuovo ruolo di servizio AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) che consente a Lake Formation di accedere a tutti i tuoi table bucket.
-
Utilizzando il ruolo di servizio, Lake Formation registra i bucket di tabelle nella Regione corrente. Ciò consente a Lake Formation di gestire l'accesso, le autorizzazioni e la governance per tutti i bucket di tabelle attuali e futuri in tale Regione.
-
Aggiunge il
s3tablescatalogcatalogo AWS Glue Data Catalog nella regione corrente. L'aggiunta dels3tablescatalogcatalogo consente di popolare tutti i bucket di tabelle, i namespace e le tabelle nel Data Catalog.
Nota
Queste azioni sono automatizzate tramite la console Amazon S3. Se esegui questa integrazione a livello di codice, devi eseguire manualmente tutte queste azioni.
Puoi integrare i tuoi table bucket una volta per regione. AWS Una volta completata l'integrazione, tutti i bucket di tabella, i namespace e le tabelle attuali e futuri vengono aggiunti alla AWS Glue Data Catalog regione.
La seguente illustrazione mostra come il s3tablescatalog catalogo popola automaticamente i bucket di tabelle, i namespace e le tabelle nella regione corrente come oggetti corrispondenti nel Data Catalog. I bucket di tabella vengono compilati come sottocataloghi. I namespace all'interno di un bucket di tabelle vengono popolati come database all'interno dei rispettivi sottocataloghi. Le tabelle vengono popolate come tabelle nei rispettivi database.
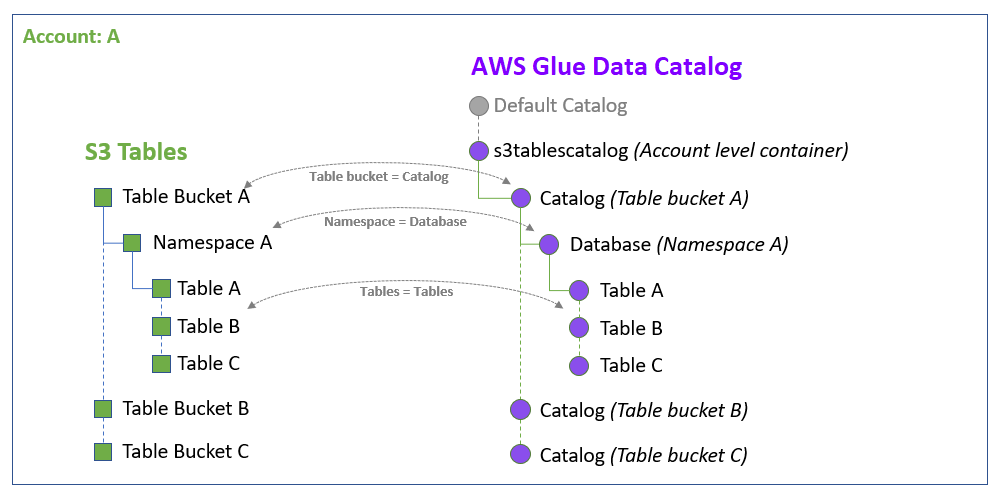
Come funzionano le autorizzazioni
Ti consigliamo di integrare i bucket di tabelle con i servizi di AWS analisi in modo da poter utilizzare i dati delle tabelle su tutti i servizi che li utilizzano AWS Glue Data Catalog come archivio di metadati. L'integrazione consente un controllo granulare degli accessi tramite. AWS Lake Formation Questo approccio alla sicurezza significa che, oltre alle autorizzazioni AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM), devi concedere le autorizzazioni principali di IAM Lake Formation sulle tue tabelle prima di poterle utilizzare.
Esistono due tipi principali di autorizzazioni in: AWS Lake Formation
-
Le autorizzazioni di accesso ai metadati controllano la possibilità di creare, leggere, aggiornare ed eliminare database e tabelle di metadati nel Catalogo dati.
-
Le autorizzazioni di accesso ai dati sottostanti controllano la capacità di leggere e scrivere dati nelle posizioni Amazon S3 sottostanti a cui fanno riferimento le risorse del Data Catalog.
Lake Formation utilizza una combinazione del proprio modello di autorizzazioni e del modello di autorizzazioni IAM per controllare l'accesso alle risorse del Data Catalog e ai dati sottostanti:
-
Affinché una richiesta di accesso alle risorse del Data Catalog o ai dati sottostanti abbia esito positivo, la richiesta deve superare i controlli di autorizzazione sia di IAM che di Lake Formation.
-
Le autorizzazioni IAM controllano l'accesso a Lake Formation AWS Glue APIs e alle risorse, mentre le autorizzazioni di Lake Formation controllano l'accesso alle risorse del Data Catalog, alle sedi Amazon S3 e ai dati sottostanti.
Le autorizzazioni di Lake Formation si applicano solo nella regione in cui sono state concesse e un mandante deve essere autorizzato da un amministratore del data lake o da un altro preside con le autorizzazioni necessarie per ottenere le autorizzazioni di Lake Formation.
Per ulteriori informazioni, consulta la pagina relativa alla panoramica delle autorizzazioni di Lake Formation nella Guida per gli sviluppatori di AWS Lake Formation .
Assicurati di seguire i passaggi indicati Prerequisiti per l'integrazione e Integrazione di tabelle bucket con i servizi di analisi AWS di disporre delle autorizzazioni appropriate per accedere alle risorse e alle tabelle AWS Glue Data Catalog e per lavorare con i servizi di analisi. AWS
Importante
Se non sei l'utente che ha eseguito l'integrazione dei table buckets con i servizi di AWS analisi per il tuo account, ti devono essere concesse le necessarie autorizzazioni Lake Formation sulla tabella. Per ulteriori informazioni, consulta Concessione dell'autorizzazione su una tabella o un database.
Prerequisiti per l'integrazione
I seguenti prerequisiti sono necessari per integrare i table bucket con i servizi di analisi: AWS
Allega il AWSLakeFormationDataAdmin AWS policy gestita al tuo responsabile AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) per rendere quell'utente un amministratore del data lake. Per ulteriori informazioni su come creare un amministratore di data lake, consulta Create a data lake administrator nella AWS Lake Formation Developer Guide.
-
Aggiungere autorizzazioni per l'operazione
glue:PassConnectional principale IAM. -
Aggiungi le autorizzazioni per le
lakeformation:RegisterResourceWithPrivilegedAccessoperazionilakeformation:RegisterResourcee al tuo principale IAM. Effettua l'aggiornamento all'ultima versione di AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI).
Integrazione di tabelle bucket con i servizi di analisi AWS
Questa integrazione deve essere eseguita una volta per regione. AWS
Importante
L'integrazione dei servizi di AWS analisi ora utilizza l'WithPrivilegedAccessopzione nell'operazione dell'API registerResource Lake Formation per registrare i bucket di tabelle S3. L'integrazione ora crea anche il s3tablescatalog catalogo AWS Glue Data Catalog utilizzando l'AllowFullTableExternalDataAccessopzione nell'operazione CreateCatalog AWS Glue API.
Se configuri l'integrazione con la versione di anteprima, puoi continuare a utilizzare l'integrazione attuale. Tuttavia, il processo di integrazione aggiornato offre miglioramenti delle prestazioni, quindi consigliamo di effettuare la migrazione. Per migrare all'integrazione aggiornata, consulta. Migrazione al processo di integrazione aggiornato
Apri la console Amazon S3 all'indirizzo. https://console.aws.amazon.com/s3/
Nel pannello di navigazione a sinistra, scegli Bucket di tabelle.
Seleziona Crea bucket di tabelle.
Viene visualizzata la pagina Create bucket di tabelle.
Inserisci il nome di un bucket Table e assicurati che la casella di controllo Abilita integrazione sia selezionata.
Seleziona Crea bucket di tabelle. Amazon S3 tenterà di integrare automaticamente i bucket di tabelle in tale Regione.
La prima volta che integri i table bucket in qualsiasi regione, Amazon S3 crea un nuovo ruolo di servizio IAM per tuo conto. Questo ruolo consente a Lake Formation di accedere a tutti i bucket di tabelle dell'account dell'utente e di federare l'accesso alle tabelle in AWS Glue Data Catalog.
Per integrare i secchi da tavolo utilizzando il AWS CLI
I passaggi seguenti mostrano come utilizzare i bucket AWS CLI da tavolo per integrare. Per utilizzare questi passaggi, sostituiscili user input placeholders
Creare un bucket di tabelle.
aws s3tables create-table-bucket \ --regionus-east-1\ --nameamzn-s3-demo-table-bucket-
Creare un ruolo di servizio IAM che consente a Lake Formation di accedere alle risorse della propria tabella.
-
Create un file chiamato
Role-Trust-Policy.jsonche contenga la seguente politica di attendibilità:{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Sid": "LakeFormationDataAccessPolicy", "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "Service": "lakeformation.amazonaws.com" }, "Action": [ "sts:AssumeRole", "sts:SetContext", "sts:SetSourceIdentity" ], "Condition": { "StringEquals": { "aws:SourceAccount": "111122223333" } } } ] }Crea il ruolo di servizio IAM utilizzando il seguente comando:
aws iam create-role \ --role-nameS3TablesRoleForLakeFormation\ --assume-role-policy-document file://Role-Trust-Policy.json -
Crea un file chiamato
LF-GluePolicy.jsonche contiene la seguente politica:{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Sid": "LakeFormationPermissionsForS3ListTableBucket", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "s3tables:ListTableBuckets" ], "Resource": [ "*" ] }, { "Sid": "LakeFormationDataAccessPermissionsForS3TableBucket", "Effect": "Allow", "Action": [ "s3tables:CreateTableBucket", "s3tables:GetTableBucket", "s3tables:CreateNamespace", "s3tables:GetNamespace", "s3tables:ListNamespaces", "s3tables:DeleteNamespace", "s3tables:DeleteTableBucket", "s3tables:CreateTable", "s3tables:DeleteTable", "s3tables:GetTable", "s3tables:ListTables", "s3tables:RenameTable", "s3tables:UpdateTableMetadataLocation", "s3tables:GetTableMetadataLocation", "s3tables:GetTableData", "s3tables:PutTableData" ], "Resource": [ "arn:aws:s3tables:us-east-1:111122223333:bucket/*" ] } ] }Associa la policy al ruolo utilizzando il seguente comando:
aws iam put-role-policy \ --role-nameS3TablesRoleForLakeFormation\ --policy-name LakeFormationDataAccessPermissionsForS3TableBucket \ --policy-document file://LF-GluePolicy.json
-
-
Create un file chiamato
input.jsonche contenga quanto segue:{ "ResourceArn": "arn:aws:s3tables:us-east-1:111122223333:bucket/*", "WithFederation": true, "RoleArn": "arn:aws:iam::111122223333:role/S3TablesRoleForLakeFormation" }Registra i bucket da tavola con Lake Formation utilizzando il seguente comando:
aws lakeformation register-resource \ --regionus-east-1\ --with-privileged-access \ --cli-input-json file://input.json -
Crea un file chiamato
catalog.jsonche contiene il seguente catalogo:{ "Name": "s3tablescatalog", "CatalogInput": { "FederatedCatalog": { "Identifier": "arn:aws:s3tables:us-east-1:111122223333:bucket/*", "ConnectionName": "aws:s3tables" }, "CreateDatabaseDefaultPermissions":[], "CreateTableDefaultPermissions":[] } }Create il
s3tablescatalogcatalogo utilizzando il seguente comando. La creazione di questo catalogo lo popola AWS Glue Data Catalog con gli oggetti corrispondenti ai bucket di tabella, ai namespace e alle tabelle.aws glue create-catalog \ --regionus-east-1\ --allow-full-table-external-data-access \ --cli-input-json file://catalog.json Verificate che il
s3tablescatalogcatalogo sia stato aggiunto utilizzando il comando AWS Glue seguente:aws glue get-catalog --catalog-id s3tablescatalog
Il processo di integrazione dei servizi di AWS analisi è stato aggiornato. Se hai configurato l'integrazione con la versione di anteprima, puoi continuare a utilizzare l'integrazione attuale. Tuttavia, il processo di integrazione aggiornato offre miglioramenti delle prestazioni, quindi consigliamo di effettuare la migrazione utilizzando i passaggi seguenti. Per ulteriori informazioni sul processo di migrazione o integrazione, consulta la sezione Creazione di un catalogo Amazon S3 Tables AWS Glue Data Catalog nella AWS Lake Formation Developer Guide.
-
Apri la AWS Lake Formation console all'indirizzo https://console.aws.amazon.com/lakeformation/
e accedi come amministratore del data lake. Per ulteriori informazioni su come creare un amministratore di data lake, consulta Create a data lake administrator nella AWS Lake Formation Developer Guide. -
Eliminate il
s3tablescatalogcatalogo effettuando le seguenti operazioni:-
Nel riquadro di navigazione a sinistra, scegli Cataloghi.
-
Seleziona il pulsante di opzione accanto al
s3tablescatalogcatalogo nell'elenco Cataloghi. Dal menu Actions (Operazioni), scegli Delete (Elimina).
-
-
Annulla la registrazione della posizione dei dati per il
s3tablescatalogcatalogo effettuando le seguenti operazioni:-
Nel riquadro di navigazione a sinistra, vai alla sezione Amministrazione e scegli le posizioni dei Data lake.
-
Seleziona il pulsante di opzione accanto alla posizione del
s3tablescatalogdata lake, ad esempios3://tables:.region:account-id:bucket/* -
Nel menu Azioni, scegli Rimuovi.
-
Nella finestra di dialogo di conferma che appare, scegli Rimuovi.
-
-
Ora che hai eliminato il
s3tablescatalogcatalogo e la posizione del data lake, puoi seguire i passaggi per integrare i tuoi table bucket con i servizi di AWS analisi utilizzando il processo di integrazione aggiornato.
Passaggi successivi
Creazione di un link di risorsa ai namespace della tabella (Amazon Data Firehose)
Per accedere alle tue tabelle, Amazon Data Firehose necessita di un link di risorsa indirizzato allo spazio dei nomi della tabella. Il collegamento di una risorsa è un oggetto del Catalogo dati che funge da alias o puntatore a un'altra risorsa del Catalogo dati, ad esempio un database o una tabella. Il collegamento è archiviato nel Catalogo dati dell'account o della Regione in cui è stato creato. Per ulteriori informazioni, consulta Come funzionano i collegamenti alle risorse nella Guida per gli AWS Lake Formation sviluppatori.
Dopo aver integrato i table bucket con i servizi di AWS analisi, puoi creare link a risorse per lavorare con le tue tabelle in Amazon Data Firehose. Per ulteriori informazioni sulla creazione di questi link, consulta. Streaming di dati alle tabelle con Amazon Data Firehose
Concessione delle autorizzazioni di Lake Formation sulle risorse del tavolo
Dopo l'integrazione dei table bucket con i servizi di AWS analisi, Lake Formation gestisce l'accesso alle risorse delle tabelle. Lake Formation utilizza il proprio modello di autorizzazioni (permessi Lake Formation) che consente un controllo granulare degli accessi per le risorse del Data Catalog. Lake Formation richiede che ogni principale IAM (utente o ruolo) sia autorizzato a eseguire azioni sulle risorse gestite da Lake Formation. Per ulteriori informazioni, consulta la pagina relativa alla panoramica delle autorizzazioni di Lake Formation nella Guida per gli sviluppatori di AWS Lake Formation . Per informazioni sulla condivisione dei dati tra account, consulta Condivisione dei dati tra account in Lake Formation nella AWS Lake Formation Developer Guide.
Prima che i responsabili IAM possano accedere alle tabelle nei servizi di AWS analisi, devi concedere loro le autorizzazioni Lake Formation su tali risorse.
Nota
Se sei l'utente che ha eseguito l'integrazione del table bucket, disponi già delle autorizzazioni Lake Formation per le tue tabelle. Se sei l'unico preside che accederà ai tuoi tavoli, puoi saltare questo passaggio. Devi solo concedere le autorizzazioni di Lake Formation sulle tue tabelle ad altri responsabili IAM. Ciò consente ad altri principali di accedere alla tabella durante l'esecuzione di query. Per ulteriori informazioni, consulta Concessione dell'autorizzazione su una tabella o un database.
È necessario concedere ad altri dirigenti IAM le autorizzazioni Lake Formation sulle risorse della tabella per utilizzarli nei seguenti servizi:
-
Amazon Redshift
-
Amazon Data Firehose
-
Amazon QuickSight
-
Amazon Athena
Nota
Per Amazon Data Firehose, che utilizza un link di risorsa per accedere alle tabelle, devi concedere separatamente le autorizzazioni sia al link alla risorsa che allo spazio dei nomi di destinazione (collegato). Per ulteriori informazioni, consulta Concessione dell'autorizzazione per un collegamento a una risorsa.
Concessione dell'autorizzazione su una tabella o un database
Puoi concedere le autorizzazioni principali di Lake Formation su una tabella o un database in un bucket di tabella, tramite la console Lake Formation o il. AWS CLI
Nota
Quando concedi le autorizzazioni di Lake Formation su una risorsa Data Catalog a un account esterno o direttamente a un responsabile IAM in un altro account, Lake Formation utilizza il servizio AWS Resource Access Manager (AWS RAM) per condividere la risorsa. Se l'account del beneficiario appartiene alla stessa organizzazione dell'account concedente, la risorsa condivisa è immediatamente disponibile per il beneficiario. Se l'account del beneficiario non appartiene alla stessa organizzazione, AWS RAM invia un invito all'account del beneficiario per accettare o rifiutare la concessione di risorse. Quindi, per rendere disponibile la risorsa condivisa, l'amministratore del data lake nell'account del beneficiario deve utilizzare la console o accettare l' AWS RAM invito. AWS CLI Per ulteriori informazioni sulla condivisione dei dati tra account, consulta Condivisione dei dati tra account in Lake Formation nella AWS Lake Formation Developer Guide.
-
Apri la AWS Lake Formation console all'indirizzo https://console.aws.amazon.com/lakeformation/
e accedi come amministratore del data lake. Per ulteriori informazioni su come creare un amministratore di data lake, consulta Create a data lake administrator nella AWS Lake Formation Developer Guide. Nel riquadro di navigazione, scegli Autorizzazioni dati, quindi scegli Concedi.
Nella pagina Concedi autorizzazioni, in Principali, esegui una delle seguenti operazioni:
Per Amazon Athena o Amazon Redshift, scegli utenti e ruoli IAM e seleziona il ruolo di amministratore IAM.
Per Amazon Data Firehose, scegli utenti e ruoli IAM e seleziona il ruolo di servizio che hai creato per lo streaming sulle tabelle.
Per Amazon QuickSight, scegli utenti e gruppi SAML e inserisci l'Amazon Resource Name (ARN) del tuo utente amministratore QuickSight Amazon.
In LF-Tags o risorse del catalogo, scegli Risorse Catalogo dati denominato.
Per Catalogs, scegli il sottocatalogo che hai creato quando hai integrato il tuo table bucket, ad esempio,.
account-id:s3tablescatalog/amzn-s3-demo-bucket-
Per Database, scegli lo spazio dei nomi del bucket di tabelle S3 che è stato creato.
-
(Facoltativo) Per le tabelle, scegli la tabella S3 che hai creato nel tuo table bucket.
Nota
Se stai creando una nuova tabella nell'editor di query Athena, non selezionare una tabella.
-
Esegui una di queste operazioni:
-
Se hai specificato una tabella nel passaggio precedente, per le autorizzazioni Table, scegli Super.
-
Se non hai specificato una tabella nel passaggio precedente, vai a Autorizzazioni del database. Per la condivisione dei dati tra account, non puoi scegliere Super per concedere all'altro principale tutte le autorizzazioni sul tuo database. Scegli invece autorizzazioni più dettagliate, come Descrivi.
-
-
Scegli Concessione.