Overview of the Performance Insights dashboard
The dashboard is the easiest way to interact with Performance Insights. The following example shows the dashboard for a PostgreSQL DB instance.

Time range filter
By default, the Performance Insights dashboard shows DB load for the last hour. You can adjust this range to be as short as 5 minutes or as long as 2 years. You can also select a custom relative range.
You can select an absolute range with a beginning and ending date and time. The following example shows the time range beginning at midnight on 9/25/24 and ending at 11:59 PM on 9/28/24.
By default, the time zone for the Performance Insights dashboard is Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). You can also choose the local time zone.
Counter metrics chart
With counter metrics, you can customize the Performance Insights dashboard to include up to 10 additional graphs. These graphs show a selection of dozens of operating system and database performance metrics. You can correlate this information with DB load to help identify and analyze performance problems.
The Counter metrics chart displays data for performance counters. The default metrics depend on the DB engine:
-
Aurora MySQL–
db.SQL.Innodb_rows_read.avg -
Aurora PostgreSQL –
db.Transactions.xact_commit.avg

To change the performance counters, choose Manage Metrics. You can select multiple OS metrics or Database metrics, as shown in the following screenshot. To see details for any metric, hover over the metric name.

For descriptions of the counter metrics that you can add for each DB engine, see Performance Insights counter metrics.
Database load chart
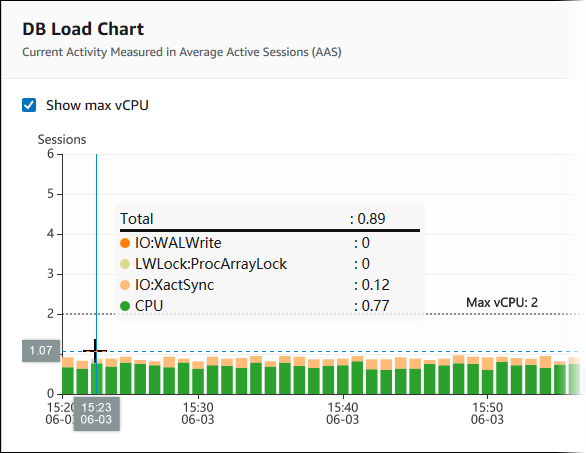
The Database load chart shows how the database activity compares to DB instance capacity as represented by the Max vCPU line. By default, the stacked line chart represents DB load as average active sessions per unit of time. The DB load is sliced (grouped) by wait states.

DB load sliced by dimensions
You can choose to display load as active sessions grouped by any supported dimensions. The following table shows which dimensions are supported for the different engines.
| Dimension | Aurora PostgreSQL | Aurora MySQL |
|---|---|---|
|
Host |
Yes |
Yes |
|
SQL |
Yes |
Yes |
|
User |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Waits |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Application |
Yes |
No |
|
Database |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Session type |
Yes |
No |
The following image shows the dimensions for a PostgreSQL DB instance.

DB load details for a dimension item
To see details about a DB load item within a dimension, hover over the item name. The following image shows details for a SQL statement.
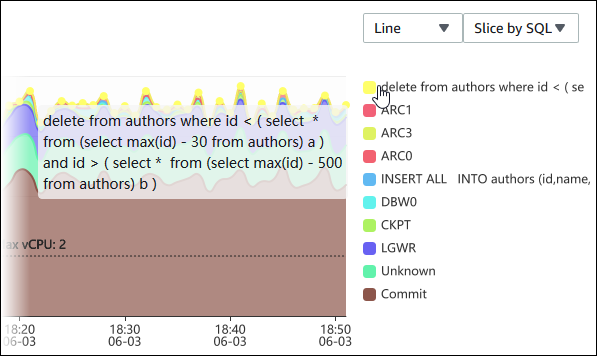
To see details for any item for the selected time period in the legend, hover over that item.
Top dimensions
table
The Top dimensions table slices DB load by different dimensions. A dimension is a category or "slice by" for different characteristics of DB load. If the dimension is SQL, Top SQL shows the SQL statements that contribute the most to DB load.

Choose any of the following dimension tabs.
| Tab | Description | Supported engines |
|---|---|---|
|
Top SQL |
The SQL statements that are currently running |
All |
|
Top waits |
The event for which the database backend is waiting |
All |
|
Top hosts |
The host name of the connected client |
All |
|
Top users |
The user logged in to the database |
All |
|
Top applications |
The name of the application that is connected to the database |
Aurora PostgreSQL only |
|
Top session types |
The type of the current session |
Aurora PostgreSQL only |
To learn how to analyze queries by using the Top SQL tab, see Overview of the Top SQL tab.