XGBoost
When using gradient
boosting
Below is a brief illustration on how gradient tree boosting works.
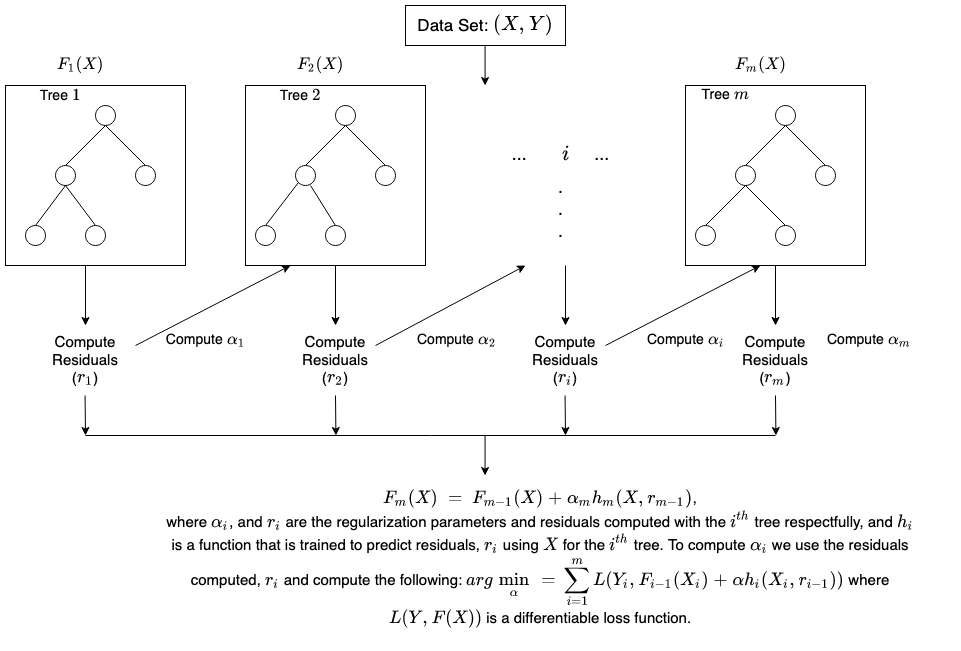
For more detail on XGBoost, see:
We use essential cookies and similar tools that are necessary to provide our site and services. We use performance cookies to collect anonymous statistics, so we can understand how customers use our site and make improvements. Essential cookies cannot be deactivated, but you can choose “Customize” or “Decline” to decline performance cookies.
If you agree, AWS and approved third parties will also use cookies to provide useful site features, remember your preferences, and display relevant content, including relevant advertising. To accept or decline all non-essential cookies, choose “Accept” or “Decline.” To make more detailed choices, choose “Customize.”
Essential cookies are necessary to provide our site and services and cannot be deactivated. They are usually set in response to your actions on the site, such as setting your privacy preferences, signing in, or filling in forms.
Performance cookies provide anonymous statistics about how customers navigate our site so we can improve site experience and performance. Approved third parties may perform analytics on our behalf, but they cannot use the data for their own purposes.
Functional cookies help us provide useful site features, remember your preferences, and display relevant content. Approved third parties may set these cookies to provide certain site features. If you do not allow these cookies, then some or all of these services may not function properly.
Advertising cookies may be set through our site by us or our advertising partners and help us deliver relevant marketing content. If you do not allow these cookies, you will experience less relevant advertising.
Blocking some types of cookies may impact your experience of our sites. You may review and change your choices at any time by selecting Cookie preferences in the footer of this site. We and selected third-parties use cookies or similar technologies as specified in the AWS Cookie Notice.
We will only store essential cookies at this time, because we were unable to save your cookie preferences.
If you want to change your cookie preferences, try again later using the link in the AWS console footer, or contact support if the problem persists.
XGBoost
When using gradient
boosting
Below is a brief illustration on how gradient tree boosting works.

For more detail on XGBoost, see:
Thanks for letting us know we're doing a good job!
If you've got a moment, please tell us what we did right so we can do more of it.
Thanks for letting us know this page needs work. We're sorry we let you down.
If you've got a moment, please tell us how we can make the documentation better.
