本文属于机器翻译版本。若本译文内容与英语原文存在差异,则一律以英文原文为准。
这个基于 Python 的教程使用适用于 Python 的软件开发工具包 (Boto3) 和 Amazon Studio Classic 笔记本。 SageMaker 要成功完成此演示,请确保您拥有使用 SageMaker 地理空间和 Studio Classic 所必需的 AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) 权限。 SageMaker 地理空间要求您拥有可以访问 Studio Classic 的用户、群组或角色。您还必须具有在信任策略中指定 SageMaker 地理空间服务主体的 SageMaker AI 执行角色。sagemaker-geospatial.amazonaws.com
要详细了解这些要求,请参阅SageMaker 地理空间 IAM 角色。
本教程向您展示如何使用 SageMaker 地理空间 API 来完成以下任务:
-
使用
list_raster_data_collections查找可用的栅格数据集合。 -
使用
search_raster_data_collection搜索指定的栅格数据集合。 -
使用
start_earth_observation_job创建地球观测作业 (EOJ)。
使用 list_raster_data_collections 查找可用的数据集合
SageMaker 地理空间支持多个栅格数据集合。要了解有关可用数据集合的更多信息,请参阅数据集合。
此演示使用从中收集的卫星数据 Sentinel-2 经过云优化的 GeoTIFF 卫星
要搜索感兴趣区域 (AOI),您需要与 Sentinel-2 卫星数据关联的 ARN。要在中查找可用的数据集合及其关联 ARNs 数据 AWS 区域,请使用 list_raster_data_collections API 操作。
由于响应可以分页,因此必须使用 get_paginator 操作来返回所有相关数据:
import boto3
import sagemaker
import sagemaker_geospatial_map
import json
## SageMaker Geospatial is currently only avaialable in US-WEST-2
session = boto3.Session(region_name='us-west-2')
execution_role = sagemaker.get_execution_role()
## Creates a SageMaker Geospatial client instance
geospatial_client = session.client(service_name="sagemaker-geospatial")
# Creates a resusable Paginator for the list_raster_data_collections API operation
paginator = geospatial_client.get_paginator("list_raster_data_collections")
# Create a PageIterator from the paginator class
page_iterator = paginator.paginate()
# Use the iterator to iterate throught the results of list_raster_data_collections
results = []
for page in page_iterator:
results.append(page['RasterDataCollectionSummaries'])
print(results)这是来自 list_raster_data_collections API 操作的 JSON 响应示例。它被截断为仅包括数据收集 (Sentinel-2) 这个代码示例中使用了。有关特定栅格数据集合的更多详细信息,请使用 get_raster_data_collection:
{
"Arn": "arn:aws:sagemaker-geospatial:us-west-2:378778860802:raster-data-collection/public/nmqj48dcu3g7ayw8",
"Description": "Sentinel-2a and Sentinel-2b imagery, processed to Level 2A (Surface Reflectance) and converted to Cloud-Optimized GeoTIFFs",
"DescriptionPageUrl": "https://registry.opendata.aws/sentinel-2-l2a-cogs",
"Name": "Sentinel 2 L2A COGs",
"SupportedFilters": [
{
"Maximum": 100,
"Minimum": 0,
"Name": "EoCloudCover",
"Type": "number"
},
{
"Maximum": 90,
"Minimum": 0,
"Name": "ViewOffNadir",
"Type": "number"
},
{
"Name": "Platform",
"Type": "string"
}
],
"Tags": {},
"Type": "PUBLIC"
}运行前面的代码示例后,您将获得 Sentinel-2 栅格数据集合 arn:aws:sagemaker-geospatial:us-west-2:378778860802:raster-data-collection/public/nmqj48dcu3g7ayw8 的 ARN。在下一节中,您可以使用 search_raster_data_collection API 查询 Sentinel-2 数据集合。
正在搜索 Sentinel-2 使用栅格数据采集 search_raster_data_collection
在上一节中,您曾经list_raster_data_collections获得了 ARN Sentinel-2 数据收集。现在,您可以使用该 ARN 在给定的感兴趣区域 (AOI)、时间范围、属性和可用的 UV 波段上搜索数据集合。
要调用 search_raster_data_collection API,您必须传入 Python RasterDataCollectionQuery参数的 dic 字典。此示例使用 AreaOfInterest、TimeRangeFilter、PropertyFilters 和 BandFilter。为方便起见,您可以使用变量 search_rdc_query 指定 Python 字典来保存搜索查询参数:
search_rdc_query = {
"AreaOfInterest": {
"AreaOfInterestGeometry": {
"PolygonGeometry": {
"Coordinates": [
[
# coordinates are input as longitute followed by latitude
[-114.529, 36.142],
[-114.373, 36.142],
[-114.373, 36.411],
[-114.529, 36.411],
[-114.529, 36.142],
]
]
}
}
},
"TimeRangeFilter": {
"StartTime": "2022-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"EndTime": "2022-07-10T23:59:59Z"
},
"PropertyFilters": {
"Properties": [
{
"Property": {
"EoCloudCover": {
"LowerBound": 0,
"UpperBound": 1
}
}
}
],
"LogicalOperator": "AND"
},
"BandFilter": [
"visual"
]
}在此示例中,您查询的 AreaOfInterest 包括犹他州的米德湖visual 波段即可。
创建查询参数后,您可以使用 search_raster_data_collection API 发出请求。
以下代码示例实现了 search_raster_data_collection API 请求。此 API 不支持使用 get_paginator API 进行分页。为了确保收集到完整的 API 响应,该代码示例使用 while 循环来检查 NextToken 是否存在。然后,该代码示例用于.extend()将卫星图像 URLs 和其他响应元数据附加到。items_list
要了解更多信息search_raster_data_collection,请参阅SearchRasterDataCollection《Amazon AI AP SageMaker I 参考》。
search_rdc_response = sm_geo_client.search_raster_data_collection(
Arn='arn:aws:sagemaker-geospatial:us-west-2:378778860802:raster-data-collection/public/nmqj48dcu3g7ayw8',
RasterDataCollectionQuery=search_rdc_query
)
## items_list is the response from the API request.
items_list = []
## Use the python .get() method to check that the 'NextToken' exists, if null returns None breaking the while loop
while search_rdc_response.get('NextToken'):
items_list.extend(search_rdc_response['Items'])
search_rdc_response = sm_geo_client.search_raster_data_collection(
Arn='arn:aws:sagemaker-geospatial:us-west-2:378778860802:raster-data-collection/public/nmqj48dcu3g7ayw8',
RasterDataCollectionQuery=search_rdc_query, NextToken=search_rdc_response['NextToken']
)
## Print the number of observation return based on the query
print (len(items_list))以下是来自您的查询的 JSON 响应。为清晰起见,该响应被截断。Assets 键值对中仅返回请求中指定的 "BandFilter": ["visual"]:
{
'Assets': {
'visual': {
'Href': 'https://sentinel-cogs.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/sentinel-s2-l2a-cogs/15/T/UH/2022/6/S2A_15TUH_20220623_0_L2A/TCI.tif'
}
},
'DateTime': datetime.datetime(2022, 6, 23, 17, 22, 5, 926000, tzinfo = tzlocal()),
'Geometry': {
'Coordinates': [
[
[-114.529, 36.142],
[-114.373, 36.142],
[-114.373, 36.411],
[-114.529, 36.411],
[-114.529, 36.142],
]
],
'Type': 'Polygon'
},
'Id': 'S2A_15TUH_20220623_0_L2A',
'Properties': {
'EoCloudCover': 0.046519,
'Platform': 'sentinel-2a'
}
}现在您已经有了查询结果,在下一节中,您可以使用 matplotlib 对结果进行可视化。这是为了验证查询结果是否来自正确的地理区域。
使用 matplotlib 可视化 search_raster_data_collection
在开始地球观测作业 (EOJ) 之前,您可以使用 matplotlib 可视化我们的查询结果。以下代码示例从上一个代码示例中创建的 items_list 变量中获取第一项 items_list[0]["Assets"]["visual"]["Href"],并使用 matplotlib 打印图像。
# Visualize an example image.
import os
from urllib import request
import tifffile
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
image_dir = "./images/lake_mead"
os.makedirs(image_dir, exist_ok=True)
image_dir = "./images/lake_mead"
os.makedirs(image_dir, exist_ok=True)
image_url = items_list[0]["Assets"]["visual"]["Href"]
img_id = image_url.split("/")[-2]
path_to_image = image_dir + "/" + img_id + "_TCI.tif"
response = request.urlretrieve(image_url, path_to_image)
print("Downloaded image: " + img_id)
tci = tifffile.imread(path_to_image)
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
plt.imshow(tci)
plt.show()检查结果是否位于正确的地理区域后,可以在下一步开始地球观测作业 (EOJ)。您可以使用 EOJ 通过一种称为土地分割的过程从卫星图像中识别水体。
启动对一系列卫星图像进行土地分割的地球观测作业 (EOJ)
SageMaker geospatial 提供了多个预训练模型,可用于处理来自栅格数据集合的地理空间数据。要了解有关可用的预训练模型和自定义操作的更多信息,请参阅操作类型。
要计算水面面积的变化,需要确定图像中哪些像素与水相对应。土地覆被分割是 start_earth_observation_job API 支持的一种语义分割模型。语义分割模型将标签与每张图像中的每个像素相关联。在结果中,每个像素都被分配了一个基于模型的类图的标签。以下是土地分割模型的类图:
{
0: "No_data",
1: "Saturated_or_defective",
2: "Dark_area_pixels",
3: "Cloud_shadows",
4: "Vegetation",
5: "Not_vegetated",
6: "Water",
7: "Unclassified",
8: "Cloud_medium_probability",
9: "Cloud_high_probability",
10: "Thin_cirrus",
11: "Snow_ice"
}要开始地球观测作业,请使用 start_earth_observation_job API。当您提交请求时,必须指定以下内容:
-
InputConfig(dict) – 用于指定要搜索的区域的坐标以及与搜索相关的其他元数据。 -
JobConfig(dict) – 用于指定您对数据执行的 EOJ 操作的类型。此示例使用LandCoverSegmentationConfig。 -
ExecutionRoleArn(字符串)-具有运行作业所需权限的 SageMaker AI 执行角色的 ARN。 -
Name(string) – 地球观测作业的名称。
这InputConfig是 Python 字典。使用下面的变量 eoj_input_config 来保存搜索查询参数。在发出 start_earth_observation_job API 请求时使用此变量。
# Perform land cover segmentation on images returned from the Sentinel-2 dataset.
eoj_input_config = {
"RasterDataCollectionQuery": {
"RasterDataCollectionArn": "arn:aws:sagemaker-geospatial:us-west-2:378778860802:raster-data-collection/public/nmqj48dcu3g7ayw8",
"AreaOfInterest": {
"AreaOfInterestGeometry": {
"PolygonGeometry": {
"Coordinates":[
[
[-114.529, 36.142],
[-114.373, 36.142],
[-114.373, 36.411],
[-114.529, 36.411],
[-114.529, 36.142],
]
]
}
}
},
"TimeRangeFilter": {
"StartTime": "2021-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"EndTime": "2022-07-10T23:59:59Z",
},
"PropertyFilters": {
"Properties": [{"Property": {"EoCloudCover": {"LowerBound": 0, "UpperBound": 1}}}],
"LogicalOperator": "AND",
},
}
}这JobConfig是 Python 字典,用于指定要对数据执行的 EOJ 操作:
eoj_config = {"LandCoverSegmentationConfig": {}}现在已指定了字典元素,您可以使用以下代码示例提交 start_earth_observation_job API 请求:
# Gets the execution role arn associated with current notebook instance
execution_role_arn = sagemaker.get_execution_role()
# Starts an earth observation job
response = sm_geo_client.start_earth_observation_job(
Name="lake-mead-landcover",
InputConfig=eoj_input_config,
JobConfig=eoj_config,
ExecutionRoleArn=execution_role_arn,
)
print(response)启动地球观测作业会返回 ARN 以及其他元数据。
要获取所有正在进行和当前的地球观测作业的列表,请使用 list_earth_observation_jobs API。要监控单一地球观测作业的状态,请使用 get_earth_observation_job API。要发出此请求,请使用在提交 EOJ 请求后创建的 ARN。要了解更多信息,请参阅GetEarthObservationJob《Amazon AI AP SageMaker I 参考》。
要查找与您 ARNs 关联的, EOJs 请使用 list_earth_observation_jobs API 操作。要了解更多信息,请参阅ListEarthObservationJobs《Amazon AI AP SageMaker I 参考》。
# List all jobs in the account
sg_client.list_earth_observation_jobs()["EarthObservationJobSummaries"]以下是 JSON 响应示例:
{
'Arn': 'arn:aws:sagemaker-geospatial:us-west-2:111122223333:earth-observation-job/futg3vuq935t',
'CreationTime': datetime.datetime(2023, 10, 19, 4, 33, 54, 21481, tzinfo = tzlocal()),
'DurationInSeconds': 3493,
'Name': 'lake-mead-landcover',
'OperationType': 'LAND_COVER_SEGMENTATION',
'Status': 'COMPLETED',
'Tags': {}
}, {
'Arn': 'arn:aws:sagemaker-geospatial:us-west-2:111122223333:earth-observation-job/wu8j9x42zw3d',
'CreationTime': datetime.datetime(2023, 10, 20, 0, 3, 27, 270920, tzinfo = tzlocal()),
'DurationInSeconds': 1,
'Name': 'mt-shasta-landcover',
'OperationType': 'LAND_COVER_SEGMENTATION',
'Status': 'INITIALIZING',
'Tags': {}
}在您的 EOJ 任务状态更改为后COMPLETED,继续下一节以计算 Lake 中的变化 Mead's 表面积。
计算湖泊的变化 Mead 表面积
要计算米德湖表面积的变化,请先使用 export_earth_observation_job 将 EOJ 的结果导出到 Amazon S3:
sagemaker_session = sagemaker.Session()
s3_bucket_name = sagemaker_session.default_bucket() # Replace with your own bucket if needed
s3_bucket = session.resource("s3").Bucket(s3_bucket_name)
prefix = "export-lake-mead-eoj" # Replace with the S3 prefix desired
export_bucket_and_key = f"s3://{s3_bucket_name}/{prefix}/"
eoj_output_config = {"S3Data": {"S3Uri": export_bucket_and_key}}
export_response = sm_geo_client.export_earth_observation_job(
Arn="arn:aws:sagemaker-geospatial:us-west-2:111122223333:earth-observation-job/7xgwzijebynp",
ExecutionRoleArn=execution_role_arn,
OutputConfig=eoj_output_config,
ExportSourceImages=False,
)要查看导出作业的状态,请使用 get_earth_observation_job:
export_job_details = sm_geo_client.get_earth_observation_job(Arn=export_response["Arn"])要计算米德湖水位的变化,请将土地覆盖掩码下载到本地 n SageMaker otebook 实例,然后从我们之前的查询中下载源图像。在土地分割模型的类图中,水体的类指数为 6。
要从中取出水面膜 Sentinel-2 图片,请按照以下步骤操作。首先,计算图像中标记为水(类指数为 6)的像素数。其次,将计数乘以每个像素所覆盖的面积。波段的空间分辨率可能有所不同。对于土地覆被分割模型,所有波段均向下采样至等于 60 米的空间分辨率。
import os
from glob import glob
import cv2
import numpy as np
import tifffile
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from urllib.parse import urlparse
from botocore import UNSIGNED
from botocore.config import Config
# Download land cover masks
mask_dir = "./masks/lake_mead"
os.makedirs(mask_dir, exist_ok=True)
image_paths = []
for s3_object in s3_bucket.objects.filter(Prefix=prefix).all():
path, filename = os.path.split(s3_object.key)
if "output" in path:
mask_name = mask_dir + "/" + filename
s3_bucket.download_file(s3_object.key, mask_name)
print("Downloaded mask: " + mask_name)
# Download source images for visualization
for tci_url in tci_urls:
url_parts = urlparse(tci_url)
img_id = url_parts.path.split("/")[-2]
tci_download_path = image_dir + "/" + img_id + "_TCI.tif"
cogs_bucket = session.resource(
"s3", config=Config(signature_version=UNSIGNED, region_name="us-west-2")
).Bucket(url_parts.hostname.split(".")[0])
cogs_bucket.download_file(url_parts.path[1:], tci_download_path)
print("Downloaded image: " + img_id)
print("Downloads complete.")
image_files = glob("images/lake_mead/*.tif")
mask_files = glob("masks/lake_mead/*.tif")
image_files.sort(key=lambda x: x.split("SQA_")[1])
mask_files.sort(key=lambda x: x.split("SQA_")[1])
overlay_dir = "./masks/lake_mead_overlay"
os.makedirs(overlay_dir, exist_ok=True)
lake_areas = []
mask_dates = []
for image_file, mask_file in zip(image_files, mask_files):
image_id = image_file.split("/")[-1].split("_TCI")[0]
mask_id = mask_file.split("/")[-1].split(".tif")[0]
mask_date = mask_id.split("_")[2]
mask_dates.append(mask_date)
assert image_id == mask_id
image = tifffile.imread(image_file)
image_ds = cv2.resize(image, (1830, 1830), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
mask = tifffile.imread(mask_file)
water_mask = np.isin(mask, [6]).astype(np.uint8) # water has a class index 6
lake_mask = water_mask[1000:, :1100]
lake_area = lake_mask.sum() * 60 * 60 / (1000 * 1000) # calculate the surface area
lake_areas.append(lake_area)
contour, _ = cv2.findContours(water_mask, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
combined = cv2.drawContours(image_ds, contour, -1, (255, 0, 0), 4)
lake_crop = combined[1000:, :1100]
cv2.putText(lake_crop, f"{mask_date}", (10,50), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1.5, (0, 0, 0), 3, cv2.LINE_AA)
cv2.putText(lake_crop, f"{lake_area} [sq km]", (10,100), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1.5, (0, 0, 0), 3, cv2.LINE_AA)
overlay_file = overlay_dir + '/' + mask_date + '.png'
cv2.imwrite(overlay_file, cv2.cvtColor(lake_crop, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR))
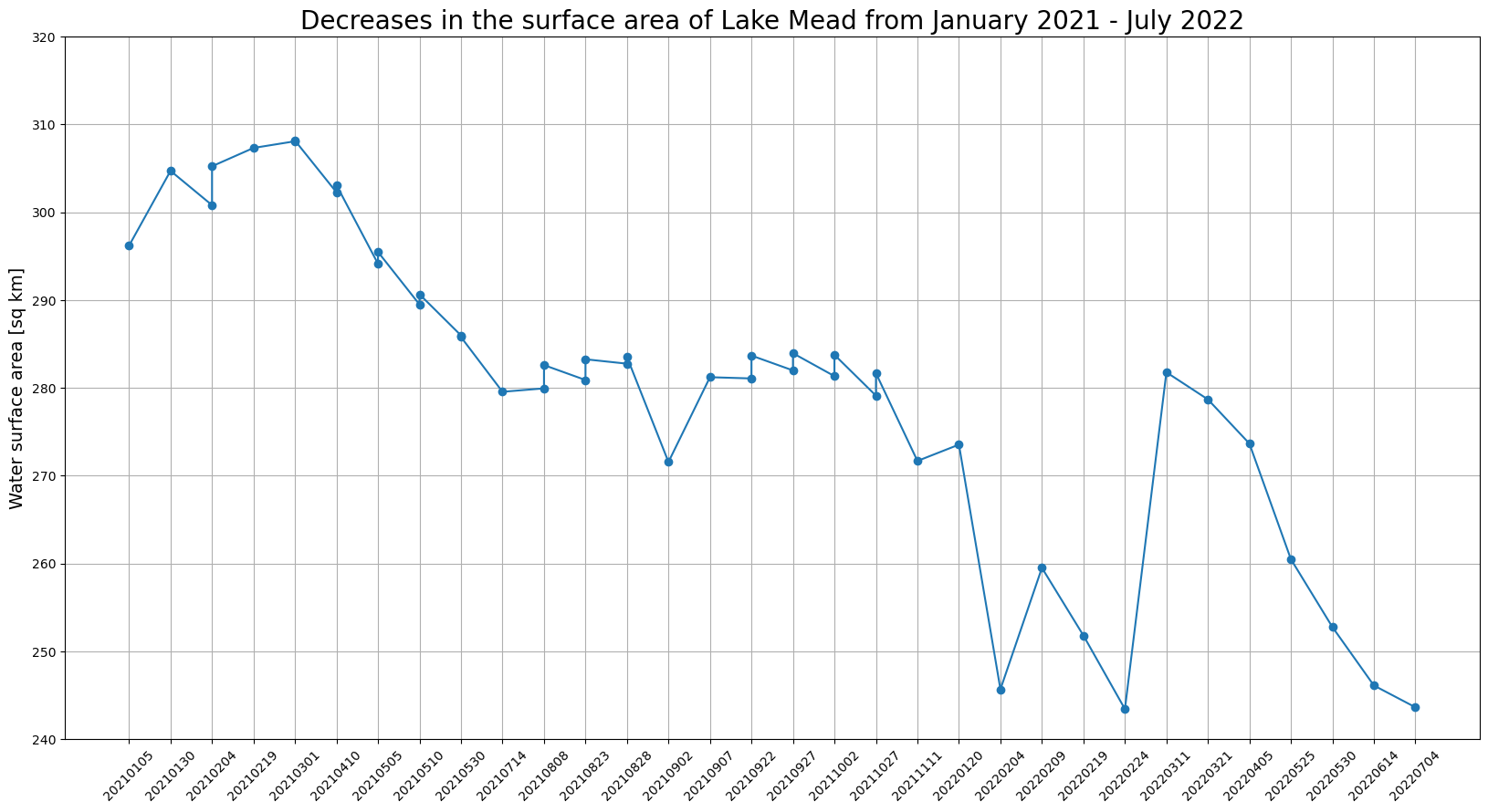
# Plot water surface area vs. time.
plt.figure(figsize=(20,10))
plt.title('Lake Mead surface area for the 2021.02 - 2022.07 period.', fontsize=20)
plt.xticks(rotation=45)
plt.ylabel('Water surface area [sq km]', fontsize=14)
plt.plot(mask_dates, lake_areas, marker='o')
plt.grid('on')
plt.ylim(240, 320)
for i, v in enumerate(lake_areas):
plt.text(i, v+2, "%d" %v, ha='center')
plt.show()使用 matplotlib,您可以通过图表直观显示结果。该图显示湖的表面积 Mead 从 2021 年 1 月到 2022 年 7 月有所下降。